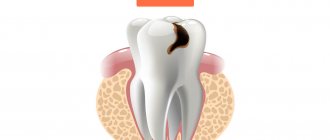
The essence of the disease
According to statistics, almost all of us have turned to dentists for help . This branch of medicine uses various types of pain relief.
Local anesthesia is performed for minor operations - tooth extraction, dental treatment, prosthetics. It is considered safe and is used without prior medical examination. The most common agents for local anesthesia are Ultracaine, Ledocaine, Articaine and Novocaine.
A feature of modern anesthetics is the presence of a huge list of preservatives and additional components (adrenaline, epinephrine) to enhance the analgesic effect.
The use of anesthesia is justified only when performing large-scale dental operations. Inhalation (Ftorotan) and non-inhalation (Ketamine, Thiopental sodium) methods of induction of anesthesia are used. These substances are extremely toxic to the human body.
Important! Any drug for pain relief in dentistry can lead to the development of allergic reactions, the clinical manifestations of which are very extensive.
Drugs used in local anesthesia and general anesthesia
Just ten years ago, the most common anesthetic drugs in dentistry were Lidocaine and Novocaine, and it was their administration that most often caused allergic reactions.
An allergy to lidocaine is explained by the multicomponent composition of this drug, and intolerance to novocaine in most cases occurs due to the presence of a preservative called methylparaben in this medicine.
In modern dental clinics, Lidocaine and Novocaine are practically not used.
Lidocaine can be used as a spray for superficial pain relief before the injection.
The most popular drugs for local anesthesia at present are:
- Ultracaine;
- Articaine;
- Ubistezin;
- Mepivacaine;
- Scandonest;
- Septonest.
The listed anesthetics are 5-6 times superior in pain relief to Novocaine and almost twice as effective as Lidocaine.
In addition to the main active ingredient, modern painkillers for dental procedures contain adrenaline or epinephrine.
These components constrict the blood vessels at the site of their injection and thus reduce the excretion of the anesthetic component, which in turn lengthens and increases the strength of local anesthesia.
Such drugs are immediately supplied in special capsules, these are original ampoules placed in the body of a metal syringe.
The syringe itself is equipped with a very thin needle and therefore the injection of the medicine into the gums remains practically unnoticed by the patient.
POPULAR WITH READERS: Allergy drops, review of effective remedies
General anesthesia in outpatient dentistry is prescribed to patients strictly according to indications. The anesthesiologist must talk with the patient before the procedure, find out his diseases and assess his state of health.
General anesthesia is divided into inhalation and non-inhalation:
- Inhalation anesthesia means the use of nitrous oxide with oxygen, fluorotane and a number of other substances through a mask. This method of pain relief is rarely used, since there is a danger that the dentist himself may inhale volatile narcotic substances. Using a mask also makes the doctor's work more difficult.
- Non-inhalation anesthesia refers to the administration of anesthetics through a vein. These may be drugs such as sodium Thiopental, Hexenal, Ketamine, Sombrevin, Propofol. These anesthetics act for a short time - from three to 30 minutes.
General anesthesia used by dentists does not adversely affect health, and therefore it can be used quite often.
But to ensure that there are no negative reactions, the doctor must first select the correct dosage depending on age and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Causes
Allergies do not have one specific cause that explains all pathological processes. There are a number of predisposing factors, the role of which is presumably important in the development of pathology:
- hereditary predisposition;
- history of allergic reactions;
- diseases accompanied by an immunodeficiency state (tumors, HIV);
- long-term chronic pathologies of internal organs leading to exhaustion.
The risk of developing allergy pathology increases significantly with:
- rapid administration of anesthetic;
- using the drug in an exhausted state;
- administration of large doses of medication.
The changes that occur in the body are called “Allergic reaction type I”. When the anesthetic first hits, special cells of the immune system are produced - class E immunoglobulins (IgE), which are antibodies.
These molecules gradually accumulate in the body. Upon repeated contact of the anesthetic with the body, immunoglobulins bind to the antigen and cause the release of various inflammatory mediators from tissues rich in mast cells: histamine, serotonin, bradykinin, etc. They contribute to the involvement of all surrounding cells in allergopathology.
Allergy to painkillers used in dentistry
Medicines have become an integral part of the life of any person. One of the dangerous consequences of taking medications is an allergy, which occurs in approximately every third case. In some cases, an allergy to anesthesia in dentistry may develop, during the process of pain relief during tooth extraction, filling, or more complex procedures.
Prevalence and features of the course
An allergy to local painkillers in dentistry is a drug allergy. A similar phenomenon is observed in approximately 17% of cases of the total number of such diseases. This is quite a high figure.
The main irritant in such medications is most often lidocaine, as a result of which they began to not use it so often when performing dental procedures, but tried to replace it with more effective and harmless painkillers.
Most of the people who have a similar type of reaction to local anesthesia are children under 7 years of age, since their immune cells have not fully formed in the body (this determines the increased risk of developing allergies under the influence of conditional pathogens).
An allergy to anesthesia is most often detected within 5-15 minutes after the medicine is administered. Although sometimes (for example, if the first phase of the immune reaction is blurred or weakly expressed), the initial signs appear much later - 1-2 hours after the injection.
The basis for the pathogenetic development of allergic symptoms is the synthesis of inflammatory mediators, the main one of which is histamine. This substance is a catalyst for a rapid-type immunopathological response (signs that appear in the patient immediately upon contact with an irritant).
In addition to histamine, against the background of an allergic reaction to painkillers, the production of other inflammatory mediators - prostaglandins and cytokines - begins.
The main danger when administering painkillers to allergy sufferers is that there is a high possibility of the formation of life-threatening conditions: angioedema , anaphylactic shock (anaphylaxis), acute respiratory failure and asphyxia . Therefore, in honey. The institution where the dentist's office is located must have a resuscitator and equipment that may be required for emergency resuscitation.
Factors causing the problem
Allergies do not have one specific source that explains the course of all pathological processes. There are some factors that may contribute to the problem. Among them are:
- tendency at the genetic level;
- the presence of allergies in the anamnestic data;
- diseases in which an immunodeficiency state is noted (neoplastic tumors, HIV infection);
- prolonged course of chronic diseases in the internal organs, due to which exhaustion develops.
The possibility of developing an allergy to anesthesia increases if:
- the anesthetic is quickly administered;
- the medicine is used for a patient who is in a state of exhaustion;
- the drug is administered in large dosages.
The changes that occur in the body are called a type 1 allergic reaction. During the initial penetration of the painkiller, special immune cells are synthesized - immunoglobulins of group E (IgE), which are antibodies.
Allergic reaction after using anesthetic, skin itching
Over time, these molecules accumulate in the body. During the repeated introduction of anesthesia in the body, a connection arises between immunoglobulins and the antigen, which leads to the release of various inflammatory mediators in tissues enriched with fatty tissue: histamine, serotonin, bradykinin, etc. Under their influence, surrounding cells are involved in an allergic reaction.
Types of painkillers
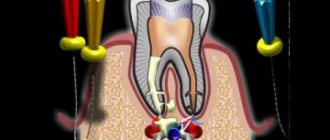
Anesthetics are of two types: local and general. Local anesthesia, in turn, happens:
- in the form of a spray, which has a pain-relieving effect when sprayed onto the gum tissue;
- infiltration;
- conductive;
- intraosseous.
General anesthesia is carried out by administering an injection solution.
Types of allergic reaction according to the distribution of symptoms
Allergies to anesthetics and other medications are of two types, which are characterized by different symptoms and varying severity.
Local (local) reaction
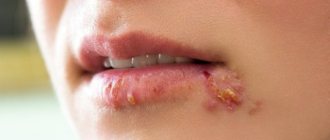
Local allergy is an immunopathological reaction (or a combination of reactions) that manifests itself only at the site of drug administration. Most often, this type of pathology disappears on its own with minor medication adjustments (taking an antihistamine) and cessation of contact with the irritant. Local allergy to painkillers in dentistry usually manifests itself in the form of:
- swelling and hyperemia of the lips, tongue and gum tissue;
- formation of microcracks and small aphthae in the mouth;
- increase and development of the inflammatory process in the papillae of the tongue;
- burning or decreased sensitivity (the patient complains of a feeling of numbness that does not disappear half an hour after anesthesia);
- rashes in the lips and mucous membranes of the mouth;
- pain when biting and applying pressure to the teeth.
If a minimum dosage is administered to a patient with a fairly stable immunological status, most often only a local allergic reaction occurs. If a person belongs to a risk group, especially when the body has already been sensitized to local anesthetics, more severe symptoms may develop.
Common reaction
This is a fairly serious form of allergic reaction to medications; it is associated with high production of immunoglobulin E, which belongs to the group of gamma globulins produced in plasma cells (B lymphocytes). In the body, a connection occurs between immunoglobulins and protein located on basophils and mast cells, which leads to the formation of an acute allergic reaction.
Symptoms of a common allergic reaction vary. This type of pathology is divided into several symptomatic groups. The development of these signs can be isolated or in the form of a combination of several groups, which determines the patient’s well-being and the severity of the allergy.
Dermatological symptoms
The skin becomes covered with bright red or pale pink rashes, blisters, small ulcers, and cracks may appear. There are areas on the skin with peeling, itching, burning, swelling and redness.
Dermatological manifestations of anesthesia in an adult in the form of urticaria
Signs of intoxication (urticaria)
This group of symptoms includes hyperthermia (the temperature may remain at subfebrile level, or rise to 39.5 degrees), headache, severe lethargy, drowsiness, and apathy. The patient complains of stinging or chills at times.
Gastrointestinal symptoms
Disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system are not typical for the immunological process against the background of an allergic reaction to anesthetics, although sometimes such signs precede a more serious form of allergy. This group of symptoms implies the occurrence of: stomach and intestinal pain, severe vomiting, diarrhea.
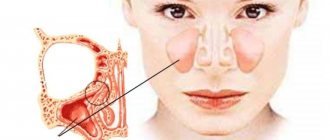
Signs of angioedema (Quincke's edema)
A very serious condition in which there is pathological swelling of the integument (including loose subcutaneous fat) with partial signs of nettle fever.
Provide immediate assistance to the patient if local swelling appears on the lips, nose, neck, throat, or mouth.
The development of the following signs is life-threatening: barking cough, hoarseness and hoarseness of the voice, an attack of suffocation, immediate formation of respiratory failure, severe swelling on the face or neck, pathological pallor of the skin.
Symptoms of anaphylaxis
Anaphylactic shock in dentistry is a very serious complication of an immediate allergic reaction; death in this condition is possible in 20% of cases.
The initial reaction in this case manifests itself in the form of sharp, sudden pain in the area where the painkiller was administered, severe swelling and hyperemia, burning and itching, quickly spreading over the skin.
The patient experiences a sharp decrease in blood pressure, the appearance of cyanosis in the lips and hands, and the formation of spasms in the bronchi and throat.
Important! After the administration of the anesthetic, death due to an allergic reaction to local anesthesia can occur after a few minutes or 1-2 hours. Emergency resuscitation should be started immediately when initial probable signs of Quincke's edema or anaphylaxis .
Diagnostic measures
In some cases, medications can provoke the development of pseudo-allergy. To determine exactly what is the reason for the formation of such a problem, the doctor prescribes the patient to undergo the following studies:
- blood test for specific antibodies (IgE) – makes it possible to detect an irritant to which the patient’s body has increased sensitivity;
- skin allergy tests for anesthetics (scarification and application) help to accurately determine the antigen;
- clinical blood test - makes it possible to identify a high number of eosinophils, which confirms the allergic origin of the symptoms;
- blood biochemistry - allows you to differentiate allergies from autoimmune diseases.
Pseudoallergy is a pathological process whose end stage (histamine release) and symptoms are similar to a typical allergic reaction (type 1), although there are differences in the underlying immune mechanisms. The patient does not experience secondary development of pseudoallergy.
Methods for treating allergies to anesthetics
For such pathology, standard therapy is carried out. Actions are determined by how severe any of the symptoms are. To cope with skin symptoms and swelling, intramuscular administration of Diphenhydramine or Suprastin is performed.
If anaphylaxis , the patient needs to be given an injection of adrenaline and call an ambulance. Typically, such actions are sufficient to eliminate allergic symptoms and prevent their further progression.
If treatment is started in a timely manner, the development of complications can be avoided. By carefully studying the patient's medical history and conducting appropriate research before administering the anesthetic, the risk of an allergic reaction is reduced.
In addition to antihistamines, patients with allergies to anesthesia are recommended to take sorbents. Under their influence, the irritant is removed from the body faster. In such a situation, it is recommended to use activated carbon or Polysorb.
Providing emergency assistance for severe allergies
First aid when serious symptoms appear is provided by a dentist. He injects the patient with adrenaline and calls the emergency room. The patient is transported to the hospital to provide medication and eliminate the consequences. In such a situation, treatment is carried out with both antihistamines and drugs to maintain the person’s overall health.
Relief of mild to moderate symptoms
Many patients are interested in how dental treatment will proceed if they have an allergic reaction to painkillers. To avoid the development of allergic symptoms, increased immunity is required. You can determine the possible allergen before starting dental treatment.
In cases where treatment without anesthetics is impossible, special therapy is carried out. It is based on the administration of a minimum amount of medication to the patient over a certain period of time. They identify where the allergen is hidden and gradually increase the dosage of the medicine. As a result of intolerance, the irritant is almost undetectable.
Treatment with folk remedies
It is difficult to cope with such a pathology using traditional methods. Thanks to this treatment, there is a weakening of symptoms and an improvement in the person’s well-being. Such means must be used very carefully. To prevent the possible development of allergies to medications, breathing exercises, massage, and hardening will help.
Herbal treatment for this disease is allowed only if there are no contraindications. There is a great danger that under their influence there will be an increase in allergic symptoms. To use folk remedies as therapy for such a disease, you need to consult with your doctor.
An allergic reaction to analgesia is a common but low-risk condition that can develop in anyone. Usually all symptoms disappear quickly and do not cause serious complications.
Source: https://allergy-med.ru/allergeny/lekarstvennye-preparaty/allergiya-na-zubnuyu-anesteziyu
Symptoms
In dental practice, local symptoms often develop, strictly limited to the area of drug administration. Common pathologies, such as anaphylactic shock or even urticaria, practically do not occur and are more exceptions to the rule.
A typical manifestation of allergies is allergic contact dermatitis. How it manifests itself:
- Swelling of the mucous membrane and underlying tissues. It can spread in all directions, causing a lot of discomfort.
- Itching, soreness or crawling sensations. Such symptoms occur in almost 80% of patients who seek medical help at a dental clinic. Only in some individuals the symptoms do not go away after 2-3 minutes.
- Difficulty breathing (asthmatic type) develops as a result of the spread of edema and partial obstruction of the airways. In most cases, the condition is not life-threatening.
Symptoms
The reaction to anesthesia varies in the speed of its manifestation - it can develop within 15 minutes, an hour after manipulation, or 12-24 hours. When the manifestation is observed instantly, doctors can quickly provide qualified assistance and reduce the risks of complications.
Allergy to general anesthesia in an adult or child has similar forms of manifestation:
- development of Quincke's edema ,
- active spread of edema in the larynx,
- respiratory depression,
- problems with the functioning of the heart, even to the point of cardiac arrest,
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure.
Local anesthesia can also provoke serious consequences, including anaphylactic shock . Such risks most often accompany anesthesia with Lidocaine, although Novocaine and Benzocaine also have reactions of this type. The most common manifestations are:
- redness, soreness and swelling of tissues in the area of contact with the drug,
- urticaria and the formation of blisters on the skin,
- the formation of small red dots on the skin, which are localized in the area of the bends of the elbow or knee joint,
- itching sensation,
- allergic rhinitis and increased lacrimation,
- epigastric pain,
- nausea with vomiting,
- diarrhea of varying intensity,
- pain in the head with risk of loss of consciousness,
- angioedema of angioedema nature.
It is also important to remember the fact that sometimes symptoms are not a consequence of the reaction to the drug itself, but are determined by the weakness of the body or non-compliance with the dosage. In particular, this is typical for intravenous general anesthesia, since its individual elements are toxic in nature and can adversely affect the functioning of the heart and respiratory system.
Diagnostics
Pseudo-allergy often develops to medications. What to do to make a diagnosis and isolate the exact allergen:
- Determination of specific antibodies (IgE) in the blood. A blood test allows you to identify the allergen to which the human body is sensitized.
- Performing skin prick and application tests (allows for reliable detection of antigen).
- A complete blood count reveals an elevated level of eosinophils, which indicates the allergic nature of the symptoms.
- Biochemical blood test (allows for differential diagnosis with autoimmune diseases).
Pseudoallergy is a pathological process, the final stage of which (histamine release) and symptoms are similar to a typical allergic reaction (type I), but the underlying immune mechanisms differ. Pseudoallergy does not occur again.
How to take allergy tests for anesthetics
A referral for allergy testing for anesthesia can be obtained from a doctor at a local clinic - an allergist or immunologist. Most likely, you will have to pay for the tests. Indications for such studies are as follows:
- Previously occurring reaction to local anesthesia during treatment or extraction of teeth,
- Existing drug allergies to any drugs,
- Skin rashes of unknown etiology,
- Constant nasal congestion, cough in the absence of other signs of infectious diseases,
- Watery eyes, itching inside the ears,
- Dizziness, nausea, digestive disorders without signs of hypotension, hypertension, food poisoning.
To get results on the quality of the body’s response to drugs, the doctor can choose one of the following methods:
- Injection of purified allergen under the skin
- Injecting the drug into a scratch on the skin made with a sterile needle,
- Introduction of the allergen by scratching the skin through a drop of the allergen (special markings are made on the skin, which the doctor is guided by when analyzing the test results),
- Injecting the allergen through a cut on the forearm is a rather painful method,
- Fastening to the skin with a fabric application impregnated with an allergen.
When should you not take allergy tests?
- Against the background of increased body temperature,
- Against the background of infectious diseases,
- In a state of pregnancy or the first weeks after childbirth/abortion,
- During exacerbations of chronic diseases.
The reaction of a weakened organism can be unpredictably strong, so this result cannot be considered reliable and the sample will have to be retaken.
Treatment
If an allergic reaction develops during dental care, there is no danger to health. Doctors always have an emergency kit prepared in case of any emergency.
When pathology develops, Adrenaline and Prednisolone are injected into the anesthetic injection site. If after a few minutes the general condition does not return to normal or worsens, then intravenous or intramuscular administration of Suprastin and Prednisolone is indicated.
In the future, if pathological symptoms persist (itching, swelling), then antihistamines should be used for 5-7 days. This group includes Suprastin, Loratadine, Zyrtec.
Tips and recommendations for further treatment:
- The most important thing is to find out the source of the allergy. If it is a preservative or any additional component, then pure solutions of painkillers should be used in the future. If the source of the allergy is the drug itself, then you need to check using skin tests for the presence of allergic reactions to other drugs.
- If you cannot find the right drug, then general anesthesia methods can be used as an alternative. Neuroleptanalgesia is now widespread. A person is “half asleep”, he hears, sees, feels everything, but his consciousness is immersed in his own world. You can also use hypnosis or not use anesthesia at all (for non-traumatic operations or low individual sensitivity).
- And the best way: you need to carefully monitor the health of your teeth so as not to meet with the doctor only for a routine examination.
Signs of an allergy to dental painkillers
The use of anesthesia for dental treatment is common these days. In the arsenal of specialists there are a number of drugs that make going to the dentist seem not such a scary undertaking. But do not forget that not every anesthetic is suitable for every patient. Sometimes anesthesia can even cause death in a person with an allergy.
Types of allergic reactions
Practicing dentists note the two most common types of allergies to painkillers in patients:
- Allergic dermatitis - in this case, swelling appears at the injection site;
- Anaphylactic shock is extremely rare with dental anesthesia, but is a serious reaction. If shock is not prevented in time, it can be fatal.
Important! A patient who has previously taken a particular pain medication and has not experienced complications is much less likely to have an allergic reaction than a person who has never tried the medication before.
Sometimes local anesthetics can cause disruption of the central nervous system. Before starting treatment, the dentist must study the patient’s medical record to determine the correct dosage of the drug.
In addition, some people have individual intolerance to preservatives in the injection. In this case, after the injection, weakness, sweating, accelerated heartbeat, and sometimes dizziness may appear.
However, all these symptoms are not a sign of an allergic reaction.
Before the anesthesia procedure, it is necessary to conduct a drug tolerance test.
Allergy symptoms
Allergy to local anesthesia is an undesirable reaction to pain medication. Unlike side effects, which can be predicted, allergies develop suddenly and unpredictably, making them more difficult to prevent.
Symptoms of an allergy to anesthetics may include the following body reactions:
- Urticaria (body rash with itching)
- Rhinitis, nasal congestion
- Tears in my eyes
- Itchy eyes
- Cough
- Nausea, vomiting
- Dizziness, weakness
- Decreased pressure
In particularly severe cases, the patient experiences
Anaphylactic shock can lead to swelling of the larynx and loss of consciousness
, which is characterized not only by the symptoms described above (often several at once), but also by more serious ones:
- Loss or impairment of consciousness
- Quincke's edema (suffocation)
Possible consequences of allergies
In most cases, the consequences of an allergy to dental painkillers are not too serious. Skin rash or itching usually goes away quickly and does not bother the patient. The situation with anaphylactic shock is more complicated, but in this case, every self-respecting clinic should have special equipment to provide emergency assistance.
Important! If the patient is suspected of being allergic to any anesthetic, you can simply replace it with another. As a rule, this is enough to solve the problem
Allergy sufferer at the dentist: rules of conduct
If a person with an allergy goes to see a dentist for the first time, he is obliged to inform the doctor about his peculiarities. Even if the patient is intolerant to one drug, it is better to test the others.
The dentist is obliged to test any patient for anesthesia, and even more so for those with allergies.
This is the only way to avoid unwanted consequences from the use of an anesthetic. The test is done using the following method: on the patient’s arm, the dentist subcutaneously injects a small dose of anesthesia, which he plans to use during treatment. If the skin at the injection site does not turn red within 15-20 minutes, anesthesia can be used to treat the tooth.
Options for solving the problem
If the patient’s body reacts negatively to the preservatives included in the injection, the dentist can simplify the composition of the solution, leaving only one active ingredient. At the same time, the specialist must increase the dosage of the drug so that it is enough until the end of the treatment. By the way, epinephrine can be replaced with prilocaine or melivacaine, which are much less likely to be allergens.
If the problem is still an allergy to “cains,” then you can solve the problem using one of the following methods:
- Apply general anesthesia
- Apply histamine blockade. This is a painful method, so it is used only in extreme cases
- Try using other "cains". Often a patient who cannot tolerate, say, lidocaine will tolerate marcaine or septocaine
- Treatment without anesthesia. Allowed only for simple dental operations (such as cleaning tartar) and with the agreement of the doctor and the patient
Important! If during dental treatment the patient develops symptoms of a side effect of the anesthesia, the doctor should stop the session and advise a different type of treatment or wait until the effect of the given anesthetic wears off and then use another. At the same time, the doctor is obliged to enter all the information into the patient’s record in order to avoid such situations in the future.
The safest anesthetics
The most popular pain reliever is lidocaine
Typically, the most popular dental anesthetics do not cause allergies in people. In addition, they are as effective as possible. Among these drugs is lidocaine in combination with a vasoconstrictor. This drug is actively used not only in dental practice, but also in other areas of medicine.
Another fairly harmless anesthetic is mepivacaine. In terms of its effectiveness, the drug is not inferior to lidocaine and almost never causes allergies. It is worth considering that mepivacaine constricts blood vessels.
The drug articaine also has a high level of safety. This is a non-toxic, long-acting anesthetic that is suitable not only for people with allergies, but also for patients who have liver or kidney problems.
Conclusion
Allergies to dental painkillers can manifest themselves in different ways and in most cases do not pose a threat to the health and life of the patient. However, in some cases the most dire consequences are possible.
If you suddenly develop an allergy, it is important to stop dental treatment using anesthesia and consult an allergist-immunologist.
This specialist will prescribe tests for you, as well as conduct a survey and examination, which will help determine the culprit allergen.
Source: https://ZubNeBoley.ru/lechenie/priznaki-allergii-na-zubnoe-obezbolivayushhee/
The effect of general anesthesia on the body
Since the task of general anesthesia is to make a person unconscious with the help of drugs, it significantly affects:
- Cognitive function, the dysfunction of which is expressed in weakening of memory, absent-mindedness, decreased level of learning and concentration on some specific objects or subjects surrounding a person;
- Nervous system – expressed by strong emotional excitability;
- Liver and kidneys - in this case, the effect is not only negative (patients with diseases of these organs are not allowed to undergo treatment under general anesthesia), but also positive - the described organs are filters of the body, therefore, with large fluid intake and dieting, they quickly remove harmful substances from the body;
- Vision – after surgery, blindness or partial loss of vision may occur.
To avoid the consequences of general anesthesia or reduce the risk of their occurrence, doctors advise:
- a week before surgery, follow a strict diet, including boiled food and lean dishes;
- one and a half months before surgery, give up alcohol and tobacco products;
- stop taking medications that relieve spasms;
- to be in a good mood;
- After treatment, follow a diet that promotes accelerated recovery and adaptation of the body.
How does general anesthesia affect the brain?
In adult patients, memory impairment occurs. The duration of the side effect is about a year. The manifestation is more common in people with heart disease.
Effect of general anesthesia on the heart
The effects of general anesthesia, the consequences of which are unpredictable for the body, occur through the action of anesthetics, which are used to induce the patient into an unconscious state. The variability of side effects depends on the type of medication, for example, “Ftorotan” has a negative effect on the functioning of the heart muscle, but it is short-lived - 30 minutes, then the body returns to normal.
General anesthesia is necessary for complex operations, but it often entails negative consequences for the body in the form of impaired functionality of various internal organs.
The most powerful drugs have a negative effect on blood pressure, expressed by its decrease. It is also possible to experience symptoms indicating a heart rhythm disorder.
How does general anesthesia affect a woman’s body?
General anesthesia has a negative effect on the female body during pregnancy, especially in the 3rd and 8th months of fetal development:
- in the first trimester, the manifestation of pathology in the baby is likely;
- in the third trimester, premature birth, miscarriage, and bleeding are possible.
In the absence of an interesting position, the menstrual cycle is disrupted.
The reasons for changes in the body may be:
- infection;
- gynecological surgery;
- change of food products;
- additional drug load on the body.