160
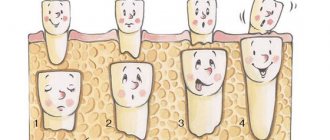
Human baby teeth are not designed to last long. Their task is to ensure the function of chewing, swallowing and speech during the period of main growth of the jaw apparatus.
After this, they must fall out, freeing up their place for permanent units that are able to perform their functions until the end of the owner’s life.
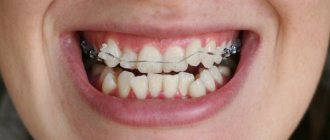
Dental veneering - what is it?
The technology for restoring anterior teeth was developed in the 30s by Dr. Charles Pincus for Hollywood stars.
Currently, there are 2 types of veneering:
- orthopedic;
- therapeutic.
The first involves the use of special plates, 0.5-1.2 mm thick, which are fixed on the outer surface of the teeth. To correct the smile area, you will need from 4 to 8 such products, and subsequent whitening of the remaining teeth is also possible in order to even out the color.
The second method uses a mixture similar to fillings. It is applied layer by layer to the surface of the teeth and then polished.
Milk teeth in dogs and cats
“At what age should baby teeth be removed from dogs and cats?.. Do they need to be removed?.. Can they be left?.. Will they fall out on their own?.. Are baby teeth removed from dogs and cats with or without anesthesia?.. What’s worse is anesthesia or remaining baby teeth teeth?.."
These questions are asked by every puppy or kitten owner.
Let's try to figure it out...
Changing baby teeth to permanent ones in a cat.
Replacement and removal of baby teeth in puppies and kittens
Milk, or temporary, teeth must be replaced with permanent teeth at the age of 4 to 6 months in puppies and kittens.
The change of teeth begins with the change of incisors, followed by the change of premolars and canines.
The age for removing baby teeth is not a specific number. Everything happens individually for each animal, and to say, for example, that the optimal age is 8 months is wrong. Each animal has a different age for extraction; some require removal of persistent teeth as early as 5 months of age.
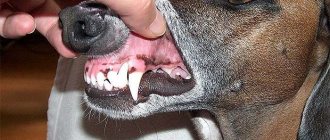
Persistent teeth in dogs and cats
Temporary teeth that do not fall out, which are already being replaced by permanent teeth, are called persistent and must be removed at the first visible changes in the bite.
It is impossible to leave persistent teeth, because the dentition of an adult dog is designed for 42 teeth, and for a cat it is 30, and if there are more teeth, periodontitis will begin.
Imagine the situation: you are flying on an airplane, there are 3 seats in a row, designed for 3 passengers, and suddenly 3 more larger passengers are seated next to them - the first 10 minutes are still nothing, but after 8 hours nothing good will happen in this situation. It's the same with teeth.
Persistent tooth on the upper jaw of a dog.
Anesthesia for tooth extraction in dogs and cats
The removal of any fixed teeth, no matter whether they are temporary or permanent, must be carried out using anesthesia and analgesia. Dental pain is a moderate pain and proper analgesia is required for every patient.
To the question, is it possible to anoint the gums with something anesthetic or give local anesthesia like in humans, I will answer right away - no, it is not possible.
Local analgesic gels will anesthetize the mucous membrane of the gums and tongue and increase salivation in the dog, which can lead to vomiting and aspiration of vomit into the trachea, and in cats their use is even more dangerous, since such gels can lead to laryngospasm and respiratory arrest.
Unfortunately, a local injection into the gum cannot be carried out without the use of sedatives that induce sleep. I have a hard time imagining a cat or dog whose gum someone tries to stick a needle into. But even if this happened, after such an injection no patient will ever be allowed near him again.
To questions about what can be done without sedation and without analgesia, just take it and pull it out, and it doesn’t matter with forceps or threads, I answer: “No!”
If the temporary tooth is mobile and “almost transparent to the light”, there is no need to remove it at all - let the animal chew on something in which to sink the teeth (for example, a not very hard “chew” or a large treat), and, believe me, the tooth will fall out on its own .
But if temporary teeth are stationary, then removal should be carried out only with anesthesia.
But many owners, especially small animals, still experience fear.
“Anesthesia is so scary!!! A small dog, weighing less than 1 kg or a little more, it’s so harmful and scary for him, he could die from anesthesia!” - they are afraid.
I’ll answer with a question: “Why should a clinically healthy animal in the hands of an anesthesiologist die from anesthesia? Is it the job of an anesthesiologist to bring his patient to death?
Let's imagine the situation: the patient is a dog weighing 1.5 kg, which is held by 2-3 people. It takes so many people to hold the animal completely still, and at the same time you have to try not to break anything.
With every second, salivation and attempts to bite increase, in the eyes of the dog there is universal horror and fear... This situation can really lead to the death of the patient from a symptom complex called “shock”.
Or did you imagine it somehow differently? Unfortunately, this is exactly what the picture looks like.
What to do if the crown of a temporary tooth is broken?
If temporary teeth were removed and the crown was broken, leaving the root in the gum with the words “it will resolve on its own,” I answer – no, it will not resolve.
Why should the root of a tooth dissolve because you have broken the crown? It will remain in the gums as a foreign body and at a certain time can cause the process of periodontitis of adjacent teeth or osteomyelitis of the jaw bones.
And one more thing - in no case should you “bite off”, “saw off” or break the crowns of temporary fangs if they “bite” into the gums or to “improve” the change of teeth.
With any injury to the crown of a temporary canine, traumatic pulpitis occurs, and as a result, periodontitis develops with an abscess on the jaw, inside of which there is a rudiment of a permanent canine.
Trauma, pain, inflammation and the possible loss of not only a temporary, but also a permanent canine - this is the price to pay for an incompetent attempt at self-medication.
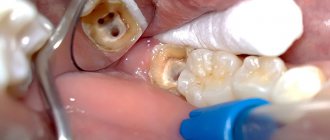
In case of traumatic pulpitis of a temporary canine, the tooth must be immediately extracted (removed).
A broken tooth crown on the upper jaw of a dog. The tooth is subject to immediate extraction (removal).
Signs of teeth changing in puppies and kittens
If your puppy has bad breath, look inside his mouth. Perhaps there is an active change of teeth, and your help is needed.
In some puppies and kittens, the change of teeth occurs with an increase in body temperature and a decrease in appetite, sometimes even with a refusal to feed. In such situations, it is better to consult a doctor for help.
In cats, during the change of teeth, a very strong odor from the oral cavity is not a strong pathology, and if you see double rows of teeth (both permanent and temporary), know that this occurs normally. But if you notice that your permanent teeth are starting to grow and interfere with each other, you need to consult a specialist.
In some breeds of cats prone to gingivitis (Maine Coons, British cats, Orientals, Sphynxes), it is necessary to conduct a daily examination of the oral cavity during the change of teeth and, at the first signs of gum inflammation, go to an appointment with a veterinary dentist to begin timely treatment.
Learn more about veterinary dental services
Conclusion
Teeth change occurs in absolutely all breeds of cats and dogs. There is no such thing as that only miniature dog breeds or, for example, only Maine Coons can have problems with changing teeth.
Believe me, it is often necessary to extract persistent canines from large and giant breeds of dogs.
Untimely or incorrect removal of baby teeth can lead to bite pathologies, and correcting the bite is another story and at a different price.
Be healthy you and your pets and don’t forget that healthy teeth mean a healthy body.
Best regards, Veronica Gil.
Source: https://gilvet.ru/stati/molochnye-zuby-u-sobak-i-koshek/
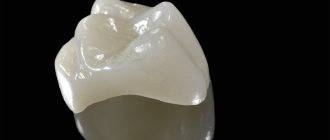
Why are veneers better than classic crowns?
These are fundamentally different designs. Crowns restore the functionality of the dentition and protect it from the recurrence of destructive processes.
Veneers are designed primarily to improve the appearance of a smile . They are considered a more gentle and aesthetic restoration method. When installing a crown, complete grinding of the tooth enamel on all sides is required (1.5-2.0 mm). The process of fixing veneers involves removing a layer of enamel 0.2-0.6 mm thick. The procedure does not cause much discomfort for the patient and takes much less time.
Prevention measures
Prevention of oral teeth position consists mainly of the same measures that are used to prevent other dental anomalies:
- Fighting children's bad habits.
- Timely transition from artificial or breastfeeding to regular feeding.
- The correct diet, containing all the substances necessary for the child and including both soft and solid foods.
- Avoiding premature removal of milk jugs whenever possible. And if this could not be avoided, temporary replacement of the defect with a prosthesis.
Basic preventive measures also include regular visits to the dentist (at least twice a year) for timely detection of developing anomalies.
All the pros and cons of dental veneering
The advantages of the method include:
- speed of the procedure;
- high aesthetic properties;
- long service life of the plates;
- the ability to correct both one tooth and the entire row;
- color stability over a long period of time;
- minimal grinding of teeth;
- allows you to hide almost any defects.
Veneers prevent the development of caries and protect teeth from negative external factors.
Among the disadvantages are:
- In most cases, it is necessary to grind the surface of the teeth under the plate, which can lead to increased sensitivity and pain.
- The procedure is irreversible. It is impossible to remove the plates, but even if this is done, the damaged enamel underneath becomes unattractive. Therefore, having installed veneers once, they will have to be constantly changed in the future.
- Low strength. Cracks and chips may appear on microprostheses due to strong mechanical stress. The patient will have to be very careful, avoid solid foods and visit the dentist regularly.
- Products require increased care - oral hygiene rules must be observed more carefully than usual.
Reasons for formation
“Milk jugs” fall out due to the resorption of their roots, which occurs under the influence of permanent units growing under them. The embryos rest against the roots of temporary teeth and start the process of their resorption.
Naturally, if the embryo is absent or displaced to the side, resorption of the roots of the “milk jugs” does not occur, and they become persistent.
Consequently, the main reason for the formation of persistent teeth is the absence or displacement of the germs of permanent units. This can be caused by underdevelopment of the alveolar process, genetic predisposition, disorders in the embryonic period, diseases of women during pregnancy and other factors.
About the importance of the retention period of orthodontic treatment and the structures used.
Come here to learn more about the dangers of oral teeth.
At this address https://zubovv.ru/ortodontiya/prikus/perestroyki-kostnoy-tkani-pri-peremeshhenii.html we will discuss the principle of bone tissue restructuring when moving teeth.
When is it possible and worth betting?
Plates are used when it is necessary to eliminate or hide aesthetic defects in the enamel or shape of the front teeth:
- diastemas (wide interdental spaces);
- chipped areas, unevenness and curvature;
- old darkened fillings;
- focal or systemic hypocalcification;
- age-related changes;
- “gummy” smile;
- worn or uneven cutting edge;
- abnormal arrangement of individual units;
- cracks, erosion or damage to the enamel;
- tooth decay (no more than 60%);
- spots or yellowness;
- teeth that are too short or long.
Veneers are installed only if the patient has a correct bite and relatively straight teeth. If one of the problems is present, it may be necessary to first install an orthodontic system to eliminate the defect.
Diagnostic measures
The lingual position of the teeth and other signs accompanying this anomaly (interdental spaces in the lower jaw due to its excessive development, underdevelopment of the upper jaw) are easily diagnosed at the initial stage of diagnosis - during examination of the patient.
The position of the roots and the presence of impacted teeth are determined by an orthopantomogram and teleroentgenogram. If necessary, cephalometry is performed - measuring the linear and angular parameters of the jaws.
To select a treatment method, it is important to establish the type of bite, the amount of reverse overlap of the abnormally located frontal teeth with the lower ones, and the availability of space in the row for the units to be moved.
The choice of treatment protocol is influenced by the age and patient.
Contraindications for wearing veneers
Plates are not recommended in cases where problems are identified:
- bruxism;
- malocclusion;
- severe damage to teeth;
- thinned enamel;
- a large number of fillings;
- pronounced destruction of the inner surface;
- increased abrasion (2nd degree and higher);
- tooth mobility;
- after dental treatment with resorcinol-formalin;
- bad habits (smoking, biting threads, biting nails);
- absence of the 6th and 7th chewing teeth;
- extreme lifestyle (contact martial arts, mountaineering, etc.);
- insufficient oral hygiene.
Veneering should be avoided if the teeth are very weakened, since coating with plates can further worsen their condition. If the disease is in an acute stage, the procedure must be postponed until recovery.
What materials are they made from?
Most often, ceramics (porcelain) , composite or zirconium . Each of the materials has pros and cons when assessing their appearance, reliability and cost.
- Porcelain veneers well convey the natural color and texture of natural teeth enamel, so it is almost impossible to distinguish them. This material prevents discoloration and the formation of dark spots on the surface.
- The composite allows you to achieve high aesthetic results in simple clinical cases, for example, with a chipped tooth. However, such a restoration does not provide the desired effect - the transparency of the enamel, which increases from the neck to the body of the tooth. The material is very fragile and quickly loses its original color (darkens and fades).
- Zirconium is used only in exceptional cases, since plates made from it require significant tooth preparation before installation. Due to the low adhesive properties of zirconium, microprostheses do not adhere well.
The material is selected in accordance with the original color of the enamel of natural teeth. If it is dense, any model will do, and if it is transparent, preference should be given to porcelain plates.
Alphanumeric system
It provides an indication of not only the number of the dental unit, but also its functional purpose. Thus, incisors are designated by the letter I, canines by the letter C, premolars by the letter P and molars by the letter M. As for the numbers, they indicate the serial number of a specific functional unit in the segment (whereas in other systems the functions of the dental unit are not taken into account, only its position is taken into account in a row).
We invite you to read Answers to questions | Peekaboo
For example, if according to the Viola system the wisdom tooth is numbered 8, then according to the alphanumeric system it is also designated as M3, that is, the third molar in the segment. Additionally, digital segment designations are also used, which is why the serial number becomes two-digit. The same 48th tooth mentioned more than once with such a scheme will be designated as M43.
For milk teeth, lowercase (small) Latin letters are used in the recording, and instead of numbers, sometimes letter values from A to K are also indicated, counting dental units clockwise from the upper right incisor.
Manufacturing process and techniques
Depending on the manufacturing method and purpose, veneers are divided into 2 types:
- Orthopedic . To create them, the patient will need to visit the orthopedic dentist 2 times, with an interval of 1-2 weeks. At the first visit, the dentist takes an impression of your teeth and sends it to a dental laboratory. There, a plaster model is cast, according to which the dental technician creates microprostheses. Finally, the finished structures are carefully polished.
- Therapeutic . They are formed from a composite (a modern analogue of the material for fillings), in the laboratory or directly in the patient’s oral cavity.
Some clinics use computer modeling, which allows a preliminary assessment of the appearance of future plates on the teeth.
The manufacturing method depends on the material used. Porcelain veneers are made from pressed or unpressed ceramics. In the first case, the material is subjected to injection molding under high pressure and temperature. This allows us to achieve the necessary strength and reliability of products.
The non-pressed method means the use of ceramic mass, which is applied layer by layer to the base and fired. Such models look more aesthetically pleasing, but are inferior in strength to the first ones.
When creating zirconium dioxide plates, porcelain is also used, but the base for it is a durable zirconium frame. It is made using CAD/CAM technology, through three-dimensional milling on a computer-controlled machine (without human intervention). Finished products are characterized by maximum strength and natural appearance, but they are less transparent.
A persistent (baby) tooth at 80 years old is not as incredible as it might seem
151
Dental anomalies are incredibly diverse. In dental practice, sometimes there are cases that seem completely impossible.
For example, the formation in the alveolar process of several hundred follicles at once that are actively growing.
A less exotic, but also rare anomaly is the categorical refusal of the “milkman” to fall out and make way for a permanent unit.
Radiography (orthopantomography, targeted images, teleradiography)
Gives information:
- about the condition and length of the roots of problem units, relative to the roots of neighboring elements;
- o the presence of germs or retained permanent units;
- o periodontal condition (according to the width of the periodontal fissure);
- about infraposition;
- about the loss of bone tissue of the alveolar process.
Next, the occlusion is checked using carbon paper.
What color can you make your teeth in the end?
The color is chosen individually, in accordance with the wishes of the patient, which allows you to achieve the desired effect. Selection is carried out using a special Vita scale. This is a set of tooth-shaped plates covered in different shades - from A1 (lightest) to B1 (darkest).
Microprostheses in color B1 do not look ideal, but they are more natural than models in shade A1. This can be useful when you need to install a veneer on only 1-2 teeth.
It is impossible to bleach the structures, and if in the future you want to improve the appearance of the oral cavity, they will have to be replaced with lighter ones.
Features of the shape of the chewing tooth, tubercles
Here, for example, is a chewing tooth. It has five tubercles on top: 3 in front and 2 in back. This allows him to work with high efficiency. And if the chewing tooth is affected from above, and this, alas, happens too often due to these depressions between the tubercles, where food debris accumulates, which some careless people are in no hurry to remove, then it is often necessary to cut off this upper part along with the tubercles and replace it filling.
A good doctor will definitely take care of selecting the material for such a filling, taking into account the load that will fall on it, and especially about restoring the shape of the tubercles. After all, if you don’t do this and just create some kind of smooth surface, the efficiency of such a tooth will be close to zero.
Veneering without grinding teeth
This is not a completely correct concept, more like advertising. The fact is that when installing plates, turning has to be used in almost 95% of cases. This is required to adjust the shape and size of the tooth so that the veneer can be fixed to it. Curled, large and medium-sized teeth are subjected to intensive preparation.
Grinding can only be avoided if the teeth are small and there are sufficient spaces between them. Another option is to use lumineers, which can be as thin as 0.2mm. Such thin plates will not appear too convex or unnatural.
Orthopedic veneers are installed in stages:
- Preparation, cleaning of plaque and grinding down the surface of the tooth so that the veneer is firmly attached.
- Taking an impression of the jaw for the manufacture of structures.
- Selecting the appropriate shade for future products.
- Installation of temporary plastic microprostheses to protect the enamel.
- When the plates are ready, the dentist removes the temporary ones, grinds and dries the teeth.
- Attaches permanent products to the surface using a special adhesive or cementing composition.
- Checks the tightness, consistency of color and shape of structures, and also tests them for strength.
This method is known as “indirect” veneering .
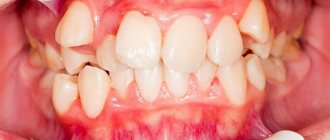
Anomalies of teeth
Disorders of dental development include anomalies in the position, number, shape and size of teeth.
Treatment of anomalies in the position of individual teeth
Treatment of palatal position of teeth . Retained milk or supernumerary teeth are removed. If there is not enough space for an abnormally located tooth due to a narrowing of the dentition, it is necessary to expand it to normal limits. In cases where neighboring teeth have shifted and there are gaps between them, it is advisable to move them to the mesial or distal side and free up space. If it is impossible to achieve the desired result in this way, then they resort to removing individual teeth. Teeth that have lost their value are removed. When all the teeth are intact, the premolar is removed and the canine is moved to the place of the first premolar. Then the first premolar and canine are moved distally. After freeing up space, the movement of the palatally located incisors into the dental arch can be carried out, depending on the indications, using various devices: an Angle arch, a plate with a screw or a protracting spring, a Katz crown, a Schwarz mouthguard, a Brückle apparatus.
Treatment of lingual position of teeth . Supernumerary and retained primary teeth are removed, and then the expansion of the dental arch begins. To do this, it is advisable to apply a plate with an expansion screw. In the process of expanding the dentition, the lingually located teeth are installed in the dental arch. In case of deep incisal overlap, the bite should be separated in order to free the anterior part of the lower dentition from the block that inhibits growth. After expanding the dental arch, the lingually located teeth are moved using a plate with a protracting spring. You can also use a plate with two screws, one on each side in the premolar area. At an older age, you can use the Angle apparatus.
When lingual eruption of molars and premolars occurs, treatment is fraught with great difficulties. To correct their position, a release plate is applied, and then these teeth are inserted one by one into the dental arch. In such cases, we recommend using a plastic mouth guard on the lingual lower teeth with a pelot that is in contact with the vestibular surface of the upper molars and premolars. The pelot is modeled when the lower jaw is displaced by half a tooth in the direction where there is an anomaly.
The effect of this device is that the lower jaw, being retracted to the side, tends to return to its original familiar position when the muscles contract. In this case, the upper molars, in contact with the vestibular area, experience a load in the oral direction and gradually deviate towards the palatal side.
At the same time, the lower molars experience stress in the opposite direction and move towards the cheek. After the patient gets used to the device, it is necessary to layer quick-hardening plastic weekly on the inner surface of the pelota, moving the lower jaw towards the abnormally located molars by approximately 0.5-1 mm.
Treatment of vestibular position and inclination of teeth . Supernumerary teeth are removed, nasal breathing is normalized, and bad habits are eliminated. If there is not enough space in the dental arch, space is made available for the abnormally located tooth(s). After this, vestibular or inclined teeth are installed in the dental arch using plates with elastic labial arches, a sliding Angle arch or a high labial arch.
Simultaneously with hardware treatment, myogymnastics of the orbicularis oris muscle should be performed. This measure not only speeds up treatment, but also consolidates the achieved results, i.e., prevents the possibility of relapse.
Treatment of mesial position of teeth . Mesially erupted teeth are moved distally using devices: plates with a screw and a sectoral cut or with arm-shaped springs, an intermaxillary rubber rod, an intraoral arch apparatus in combination with an extraoral fastening, an apparatus of our design (Fig. 189).
Treatment of distal position of teeth . It consists of moving these teeth into the correct position using the same devices that are used for distal movement. After this, the abnormally located adjacent teeth are installed in the dental arch using an appropriate apparatus. In case of primary adentia or tooth extraction after orthodontic treatment, prosthetics are performed in accordance with age indications.
In cases where distal or mesial teething does not cause aesthetic or functional disturbances and does not affect the position of adjacent teeth, their movement is not indicated.
Diastema is the gap between the central incisors. It is quite common in children and, according to our data, accounts for 7.8% of all anomalies of the dental system. Most often it is observed at the beginning of the mixed dentition. With age, its frequency decreases and by the age of 16 this figure is almost 5 times less than in 7-year-old children. Diastema is mainly observed between the incisors of the upper jaw, but sometimes on the lower jaw (Fig. 190).
The size of the gap can vary from 2-3 mm to 6-7 mm and more. Its shape also varies depending on the location of the central incisors. One or both central incisors can be displaced distally without tilting the crowns and roots of these teeth in any direction. However, cases of inclination of the crowns of these teeth to the distal side (divergence) are more often observed. At the same time, their roots are inclined towards the midline. Much less common is the inclination of the crowns of the incisors to the mesial side (convergence) and the deviation of the roots of these teeth in the opposite distal direction.
In addition to the above-mentioned anomalies in the position of the central incisors in relation to the sagittal plane, their deviations in relation to the frontal and horizontal planes are also possible, i.e. these teeth can be displaced distally and at the same time oral or vestibular, be higher or lower than neighboring teeth. They can be without rotation along the axis or with rotation in any direction.
All forms of diastema are accompanied by aesthetic disturbances and distort speech to a greater or lesser extent.
Treatment of diastemia. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the cause, remove the supernumerary teeth located between the roots of the central incisors. Sometimes, with small diastemas (2-3 mm) after the removal of supernumerary teeth in children during the period of mixed dentition, in the process of eruption of the lateral incisors or canines, the central incisors are installed in the correct position without hardware treatment. If the cause of the diastema is a highly developed and low-attached frenulum of the upper lip, then it is plastically moved and the connective tissue of the incisive papilla and the anterior part of the median palatal suture are excised. Sometimes it is advisable to loosen it surgically and perform a compactosteotomy in the area of the incisors to be moved. These measures not only facilitate subsequent hardware treatment, but also help consolidate the achieved results and prevent the possibility of relapse.
After eliminating the cause of the diastema, the central incisors are moved to the midline using devices that use a rubber rod or the elastic properties of a wire. When choosing an appliance, you should take into account the location of the central incisors. If both central incisors are displaced evenly distally without tilting or turning in any direction, it is necessary to move them bodywise (Fig. 191, a, b).
In case of divergence, i.e. diatal deviation of the crowns of the central incisors and mesial inclination of their roots, treatment is carried out using devices: plates with arm-shaped Kalvelis springs, a plate with a vestibular arch and a U-shaped bend, Brückl, Schwartz devices (see Fig. 156 ).
The central incisors can also be brought together using the Korkhaus apparatus (Fig. 192) or a rubber traction device. To do this, the teeth to be moved must be covered with rings with hooks or rods soldered to them. To avoid rotation of the teeth along the longitudinal axis, the hooks must be soldered at the mesial edge of the rings or on two surfaces - vestibular and oral.
Rubber rings should not be placed on incisors without orthodontic appliances; since this can lead to serious complications. Rubber rings can slip off the teeth under the gum line and cause inflammation of the soft tissue of the gums and destruction of the bone in the socket.
Diastemas are often observed due to distal displacement and inclination to the same side of one central incisor. In these cases, only one tooth moves obliquely. To do this, a stronger fulcrum is created by blocking 2-3 teeth, and the incorrectly positioned incisor is gradually pulled towards this block. If the crowns of the incisors are significantly tilted, it is first better to straighten them, eliminating the tilt of the crowns to the distal side, and then bring them together using devices for body movement.
With convergence, i.e., mesial inclination of the crowns of the central incisors and divergence to the sides of their roots, an apparatus with a spacer along the cutting edge and a Begg arc, an apparatus with a versatile rubber traction, are used to eliminate the diastema (Fig. 193).
Orthodontic hardware removal of diastema should be carried out slowly using small forces. Otherwise, complications are possible: pathological changes in the pulp and periodontal tissues, resorption of the root tips. With accelerated movement of permanent teeth with incomplete root formation, a bayonet-shaped curvature of their apices is possible.
After eliminating the diastema, it is necessary to secure the central incisors in a new position before erupting the lateral incisors using the same devices that were used for treatment.
Tremors between teeth. More often they appear in the anterior part of the dental arch, less often - between the lateral teeth. The size of the spaces between the teeth can vary - from 0.5 to 1.5 mm or more.
The reasons for the appearance of three can be partial edentia, small teeth, increased jaw size, retention of individual teeth or their incorrect position.
Treatment for three. If the gaps have arisen due to edentulism or small teeth, but their shape is correct, then the front teeth are brought together by moving them mesiodistally. The resulting gap is replaced with a removable prosthesis, which at an older age (17-28 years) is replaced with a fixed one. If the teeth are irregular in shape and small in size, then they are covered with crowns. When gaps between the front teeth have arisen due to vestibular inclination (protrusion), a sliding Angle arch, a high labial Lurie arch, or plates with a vestibular retraction arch should be used.
Treatment of rotation of teeth around the longitudinal axis . Depends on the availability of space in the dentition, concomitant deformation, the position of adjacent teeth and antagonists, the depth of the incisal overlap and other reasons.
After freeing up the space, begin to rotate the tooth. Simultaneously or sequentially, it is tilted and moved in the desired direction. To rotate a tooth around its longitudinal axis, it is necessary to apply two forces to it, equal in magnitude, but directed in opposite directions. Rotation of teeth is carried out; an Angle arc, a removable plate with a vestibular arch and springs, or with a screw and a sectoral cut of a mouth guard with hooks. After completing the rotation of the tooth, it is necessary to secure it in the new position with a removable or non-removable retention device.
Treatment of dental transposition is an anomaly in which individual teeth change places. For example, the first premolar may be located in place of a premolar. The lower canines and lateral incisors change places much less frequently. If transposition of teeth does not cause functional and aesthetic disturbances, then treatment is not indicated.
Treatment of vertical anomalies in the position of the teeth with a high position of the upper and low lower teeth comes down to creating space in the dentition (if there is a deficiency) and stretching the teeth. When the dentition narrows, it is expanded, and adjacent teeth, which partially take the place of a given tooth and prevent it from erupting, are moved to the mesial or distal side. Then they begin to stretch the teeth using a rubber rod, an Engle apparatus with an elastic spring lever. To do this, a crown, cap or ring with hooks or loops soldered to it is secured to the tooth to be moved.
Treatment of dental alveolar elongation is carried out with therapeutic bite plates, mouthguards or fixed devices on which the bite is increased. These teeth experience increased load with each closure of the dentition, as a result of which the alveolar process is rebuilt and the teeth sink.
The remaining teeth are separated from the bite (do not experience occlusal load), this leads to dentoalveolar elongation, i.e., to the establishment of these teeth in the correct position.
Other methods of installation on teeth
If the tooth surface is not ideal, more thorough preliminary grinding of the enamel will be required. Usually a layer about 0.5-0.7 mm thick is removed. To ensure that the patient does not feel discomfort for 1-2 weeks while the permanent plates are being made, temporary therapeutic veneers are installed. The technology for installing them is quite simple:
- The treated tooth surface is coated with an adhesive substance to improve adhesion to the plate.
- The composite material is applied, distributed evenly, and then exposed to a stream of light, which promotes rapid hardening.
- The veneer will be completely formed after applying 2-3 such layers.
- Finally, it is ground to a perfectly smooth shape and polished to achieve maximum aesthetic results.
This method of restoration is called “direct” veneering . The procedure takes no more than an hour.
Purpose of chewing teeth
Next come the chewing teeth. Small chewing teeth – fourth, fifth. Large chewing teeth - sixth, seventh, eighth.
Chewing teeth are millstones that are designed to grind food before it enters the body to ensure normal digestion.
Each tooth has its own task and can only be removed as a last resort.
Even after these general facts, it becomes clear how wrong is the person who prefers to remove a tooth rather than cure it. And having lost it, he is in no hurry to make a prosthesis. Responsibilities and load are clearly distributed between the teeth. Each of your teeth has an individual anatomical shape, verified by nature over tens of thousands of years.
How long can plates stay on teeth?
The service life of veneers made from high-quality material can reach 10-15 years . To extend it, you need to follow the recommendations:
- Do not drink coloring drinks (coffee, wine), avoid foods with high acidity.
- Avoid excessive load on the products. Nuts, seeds, etc. can cause damage to the linings.
- Maintain oral hygiene. When brushing your teeth, use a non-abrasive toothpaste to avoid micro-scratches on the surface. Regular maintenance with an irrigator and careful treatment of the joints are recommended.
- Periodically visit your dentist for professional cleaning and polishing of the surface of the veneers.
People suffering from bruxism need to wear a mouth guard at night.
How long will a tooth last after pulpotomy?
It is important to understand that the resource of a pulpless tooth may vary from patient to patient. Even in one person, two different teeth after depulpation can “behave” differently.
If the procedure is carried out in compliance with the protocol, the canals are thoroughly cleaned, their sealing is achieved, and pathological tissue is completely removed, the tooth can last several decades. The service life of a tooth after pulpotomy increases significantly if a high-quality and reliable crown is installed on it.
Cost of veneering in dentistry
Prices vary depending on the materials used and the complexity of the work. The veneering procedure is estimated to cost from 2000 rubles. Average prices for plates (in rubles per unit):
- porcelain - from 15,000 ;
- ceramic - from 25,000 ;
- from zirconium dioxide - from 16,000 ;
- regular composite - from 1,500 ;
- modern nanocomposite - from 7,000 .
In some Moscow clinics, the total cost can reach 50,000 rubles per unit.