What is pulpitis?
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the neurovascular bundle or pulp. In simple terms it is called a “nerve”. (in detail what is pulpitis, classification)
The disease code according to ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases) is K04: “Diseases of the pulp and periapical tissues.”
The pulp is a plexus of microvessels and nerve fibers. It penetrates into the tooth through the apex of the roots (apex or apical foramina), fills the inside of the crown and is responsible for its trophism - nutrition and blood supply.
The neurovascular bundle reacts acutely to any damage or infection. The patient feels unbearable pain: it occurs due to the fact that swelling, characteristic of any inflammation, cannot develop due to the small space of the pulp chamber.
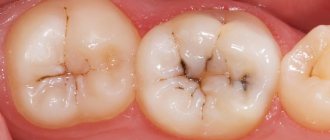
Most often, the nerve becomes inflamed due to the penetration of infection through dental tissues thinned by caries - enamel and dentin. Less commonly, pulpitis appears as a consequence of:
- errors in the treatment of caries - if the doctor did not remove all damaged tissue, poorly placed a gasket between the pulp chamber and the filling, or caused a burn to the neurovascular bundle;
- improper grinding for crowns - when preparing vital (living) teeth for dentures, pulp burns are possible;
- injuries - impacts, chips, dislocations;
- penetration of infection through root canals – retrograde route.
Hypertrophic pulpitis
With hypertrophic pulpitis, the tooth crown is destroyed and the pulp is exposed as a result. In the process of eating food, she experiences an impact that negatively affects her condition and, as a result of a reaction to external stimuli, the patient’s condition worsens. Thus, due to damage to the tooth, a person cannot fully use it when chewing food; bacteria accumulate in its area, caries forms and plaque occurs. The main reasons for this phenomenon are:
- process of crown destruction;
- removal of caries at a low quality level;
- getting a dental crown injury;
- accumulation of plaque on the tooth;
- penetration of infection.
When the polyp comes out, a painful reaction to any serious irritation begins, bleeding occurs, despite the fact that there are no mechanical damages, while eating, a person begins to experience discomfort, he has bad breath, when eating anything hard, cold or hot, aching pain appears.
Choosing a treatment method based on the form of the disease
Which method of treating pulpitis the doctor will choose depends on:
- type of pathology;
- stages of disease development;
- duration of inflammation.
Acute form
The acute form is the most favorable in terms of treatment. With timely treatment, in most cases it is possible to manage with conservative methods and preserve the pulp - in whole or in part.
Without a neurovascular bundle, nutrition, blood supply and tissue renewal in the tooth are stopped. After removal of the pulp, the unit is considered dead (devital), it becomes more fragile, and is more often susceptible to carious lesions and inflammatory processes. That’s why it’s so important to try to preserve your nerve.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of pulpitis includes amputation and pulp extirpation. The difference is that during extirpation the entire pulp is removed, while during amputation only the coronal part is removed (only possible for teeth with several roots).
Both of these methods can be either vital, with preservation of the healthy part of the pulp, or devital, without preserving individual sections of the pulp. It is used in cases where conservative treatment does not produce results.
Treatment of pulpitis using the surgical method
Classification of pulpitis treatment methods
All methods of treating pulp inflammation are divided into 2 groups:
- Conservative or biological. They are carried out using medications and physiotherapeutic procedures. Allows you to preserve the neurovascular bundle and restore its function.
- Operative or surgical. They involve removing the pulp - with the use of necrotizing pastes (devital method) or without them (vital method).
The pulp can be removed either completely or partially.
Amputation is a separate issue - partial removal of the pulp, namely its coronal part. Some researchers classify this method as conservative, because when excision of the apex of the nerve, the tooth’s ability to trophize is preserved, albeit not completely.
Moreover, only removal without the use of devitalizing pastes is considered biological, because the latter lead to necrotization and mummification of the remaining (root) section of the bundle.
Other doctors consider amputation to be a surgical method of treatment, regardless of the technique of its implementation - a vital or non-vital method.
Combined method
In some cases, it is impossible to cure pulpitis using one method - you have to resort to a combined method. It is used when:
- One or more canals are severely curved.
- It is impossible to completely go through and disinfect the canals mechanically.
- The instrument broke and remained in the root canal.
With the combined method, two types of pulpitis treatment are used simultaneously, most often vital and non-vital. Accessible sections of the canals are traversed, the pulp is extracted, and the rest are treated with necrotizing pastes.
Complications in the treatment of pulpitis, in most cases, arise due to medical errors.
Conservative or biological treatment of pulpitis
Treatment of pulpitis with a biological method involves preserving the nerve, relieving inflammation and restoring its functions. For this purpose, medications and physiotherapeutic procedures are used.
The biological method is rarely used: in 2.6-7.71% of cases (based on data from L.A. Dmitrieva and Yu.M. Maksimovsky “Therapeutic dentistry. National guidelines” - https://issuu.com/lattebar/docs/ _____________________.__.__________/406). This is due to frequent post-treatment complications and the need to comply with a number of conditions:
- the patient’s young age – the regenerative abilities of the neurovascular bundle are directly related to age, therefore, the biological method of treating pulpitis is predominantly used in children, adolescents and young people under 25 years of age;
- early treatment time: in 1-2 days, even better – in the first few hours;
- complete sterility of the oral cavity and the treated area - nearby foci of inflammation (caries, gingivitis, etc.) contribute to even greater infection of the pulp and its further damage.
In addition, not all forms of pulpitis can be treated biologically: treatment of acute focal, traumatic and catarrhal types, as well as diffuse chronic types, is possible.
Step-by-step algorithm for conservative treatment of pulpitis:
- Examination and differential diagnosis. This is carried out using a physical examination, history taking and electroodontodiagnosis (EDD). X-ray diagnostics is useless, because pulpitis does not appear in the photo.
- Tissue preparation and disinfection. Local anesthesia is administered, and the diseased tooth is isolated from the gums and oral mucosa with a latex handkerchief (rubber dam or rubber dam). Afterwards, the tooth is dried and the softened dentin is removed with an excavator. Hard affected tissues are ground down with spherical burs using turbine units with cooling. In this case, the pulp chamber is not opened. An exception is if it has already been damaged or intrapulpal pressure needs to be relieved. The resulting cavity is washed with warm antiseptic solutions.
- First stock of medicines. A paste containing antibiotics and corticosteroids is placed into the cavity. The tooth is covered with a temporary filling and the next visit is scheduled in 2-7 days. Sometimes this stage is skipped, considering the use of polyantibiotic agents to be irrational.
- The second tab of drugs. If there are no complaints of pain, zinc-eugenol cement (ZEC) or calcium hydroxide is placed into the cavity. The latter is combined with soda, eugenol, antiseptics, burnt magnesia, antibiotics, and potassium bromide. The tooth is again covered with a temporary filling and left for a week.
- Restoration of the coronal part. If the patient does not feel pain and the EDI indicators are normal, an insulating pad is applied and a permanent filling is installed.
At the second and third stages, simultaneously with the main treatment, the following is prescribed:
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs - Ibuprofen, Nimesil;
- desensitizing medications - “Desloratadine”;
- antibiotics – “Roxithromycin”;
- antimicrobial agents - Metronidazole.
At all stages of conservative treatment of pulpitis, it is important to carefully follow the rules of asepsis and antiseptics, otherwise the inflammation will intensify. They also monitor the tightness of the fillings: if a gap forms between them and the walls of the tooth, pathogenic microorganisms will get into it, which will aggravate the situation.
Removal of a nerve for tooth pulpitis
Removal or extraction of the neurovascular bundle (complete or partial) is the most common method of treating pulpitis. Most doctors prefer this method for 2 reasons:
- there are no strict restrictions and indications, as when using biological technology;
- lower risk of complications – because The pulp has been removed, there is nothing to hurt or become inflamed.
However, the absence of negative consequences is possible only with high-quality treatment. If the doctor made a mistake at any stage, inflammation will begin even in a dead tooth.
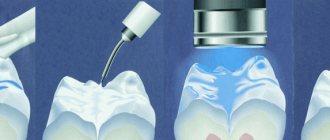
This is what the canals look like prepared for treatment
Vital method
Most often, the nerve is removed in a vital way: using special instruments - pulp extractors and scalpels. This approach allows you to get rid of pain and inflammation in one visit within a few minutes. In subsequent visits, only painless procedures will remain - root canal filling and restoration of the crown part of the tooth.
After removing the pulp, the canals must be sanitized using antiseptics, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drugs. If only the upper part of the neurovascular bundle has been excised, the use of polyantibiotic agents, COE, and calcium hydroxide is mandatory.
Devital method
With the devital method, the pulp is not removed immediately: first it is killed with necrotizing pastes.
Previously, toxic arsenic agents were used. Sometimes they are still used today. Such drugs require high precision when applied: if they get on healthy tissue, they will provoke necrosis and mummification.
Pastes with arsenic are placed in the cavity for 24 hours (for single-canal teeth) or for 48 hours (for two- and three-canal units). You cannot walk over: during this time the pulp dies and toxins penetrate beyond the apex.
With the devital method, the pulp is removed after killing with special preparations.
Resorcinol-formaldehyde pastes began to be used as an alternative to arsenic agents. Previously, they were considered less toxic and safer. However, practice has shown that such funds have many negative aspects:
- paint the crown of the tooth pinkish-gray;
- gradually destroy the root canals;
- often lead to inflammation.
Teeth depulped using resorcinol-formalin pastes often have to be re-treated. Moreover, this can rarely be done: the canals become impassable, difficult to open and sanitize. After a few years, the units inevitably break down and have to be removed.
Arsenic-free products are considered the best today. They are low-toxic, affect only the pulp, and do not have a negative effect on surrounding tissues and structures. In addition, they are suitable for patients with little discipline: you can walk with them for up to 2 weeks.
Pulp amputation
Pulp amputation is the removal of its apical part. It can be carried out in single-root and multi-root units. But more often the method is applied to the 1st and 2nd molars, as well as wisdom teeth - in them the boundary between the coronal and root sections is clearly defined.
Amputation is carried out using vital and devital methods. Their technology is similar in the initial stages:
- infiltration anesthesia is administered;
- isolate the tooth with a rubber dam;
- prepare the tooth cavity with dental burs - spherical or fissure: remove all non-viable tissue and provide access to the pulp chamber;
- open the pulp chamber and excise the coronal part of the nerve with a pulp extractor or bur;
- Pulp tissue is removed from the mouths of the root canals using a reverse-cone bur and ledges are formed.
Amputation is most often applied to the 1st and 2nd molars.
Further treatment tactics differ. Thus, during non-vital amputation, necrotizing pastes are placed into the cavity. They mummify the remaining pulp. That. the tooth becomes dead - although the nerve remains in it, it is killed and cannot nourish the unit.
The devital amputation method is rarely used - only in teeth where it is impossible to pass through severely curved root canals. This method often leads to infection and inflammation: dead pulp remains inside the unit - an excellent breeding ground for germs and bacteria.
But vital amputation allows you to preserve the viability of the neurovascular bundle and ensure trophism of the tooth. This method involves preserving the root part - it will power the unit.
The stages of vital amputation after excision of the coronal part are similar to the method of biological treatment of pulpitis. Carry out step by step:
- adding antibiotic-corticosteroid paste for 2 days - this step can be skipped;
- applying a paste of calcium hydroxide and zinc eugenol;
- installation of an artificial dentin gasket;
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
The patient is observed for 3-4 weeks. If pain or other symptoms do not appear during this time, the temporary filling is removed and a permanent one made of photopolymer materials is placed.
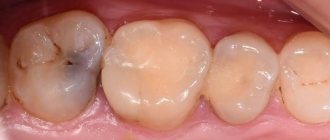
Restored tooth after pulpitis treatment
Vital amputation is rarely used, mainly in adolescents with recently erupted molars, whose root system is unformed. The success of this treatment method reaches only 40% (according to L.A. Dmitrieva and Yu.M. Maksimovsky “Therapeutic dentistry. National guidelines”).
Extirpation
Extirpation (also called pulpectomy or depulpation) is the most common method of treating pulpitis. It consists of complete removal of the nerve from the root canals, their subsequent sanitation and filling.
Extirpation is also carried out in two ways. They differ in only one thing: with the devital method, after opening the pulp chamber, a necrotizing paste is placed, which is removed after a few days along with the remains of the mummified nerve. And with vital therapeutic tactics, the neurovascular bundle is removed immediately, on the first visit.
Otherwise the methods are similar. They are carried out in 3-4 visits. On your first visit:
- numb the tooth and isolate it with a rubber dam;
- prepare a carious cavity: grind off dead tissue, remove overhanging edges, form a cavity;
- remove the nerve with a pulp extractor - on the first visit or a few days after using devitalizing pastes;
- measure the length of each channel using a special device (apex locator) or radiography using contrast files;
- root canals are passed through: they are opened and cleaned along their entire length with special needles (files, reamers) manually or using the SONIC AIR endodontic acoustic system, in the process they are slightly expanded and given a cone-shaped shape - this will make them easier to seal;
- the canals are sanitized: they are irrigated with antiseptic solutions (sodium hypochlorite, ethylenedimethyltetraacetic acid) and treated with medications based on calcium hydroxide;
- A temporary filling is installed for 2-7 days.
On the second visit:
- remove the temporary filling and isolate the crown with a rubber dam;
- the channels are sanitized again;
- root canals are filled: with cement pastes, gutta-percha (using a single pin method or latex condensation) or using vertical condensation of hot gutta-percha, the latter method is the best choice, because allows you to fill not only the main root branches, but also microtubules with molten plastic material;
- check the quality of filling using X-ray photographs - if the canals are not completely sealed or the material is removed beyond the apex, it is necessary to re-fill the tooth;
- a temporary filling is placed again for at least a day - a break is needed for the filling material to harden and settle into the canal.
On the third visit:
- remove the temporary filling, isolate the unit with a rubber dam;
- restore the coronal part: with a photopolymer filling, in case of destruction of more than 50%, strengthen the unit with a pin, and if only the root system remains of the tooth, it is covered with a prosthesis - a crown;
- check occlusal contacts and adjust the filling if necessary;
- grind and polish the restored tooth.
Extirpation involves complete removal of the nerve
The vital extirpation method is preferable to the devital one. However, if the canals are difficult to pass, there is a suspicion that false microtubules are present - it is better to apply a necrotizing paste on the first visit, and on the second visit, remove the nerve with instruments and rinse the cavity with solutions that will dissolve and remove the remaining pulp.
Combined method of treating pulpitis
The method consists of combining two techniques at once: vital and non-vital amputation. It is used when some canals are smooth and pass well, while others are curved and cannot be mechanically obturated.
In this case, the nerve is removed from the straight canals using a pulp extractor, and necrotizing agents are placed in the curved canals. After a few days, the pastes are washed out of the crooked canals along with the remaining pulp.
Devital extirpation
Stages of pulpitis treatment.
Devital extirpation is similar in method to amputation. The difference lies in the complete, rather than partial, killing of the pulp. Devital extirpation is not used for tissue necrosis or purulent pulpitis.
Removal is carried out in 3 visits:
- Removal of tissues affected by caries using a drill.
- Application of devitalizing pastes: arsenic or arsenic-free. Preparations with arsenic are applied from 24 (for single-canal teeth) to 48 (for multi-canal teeth) hours. Arsenic-free products – up to 14 days.
- Closing the cavity with a temporary filling.
- Removal of temporary filling material and extraction of dead nerve bundle.
- Mechanical cleaning of root canals and treatment with antiseptics.
- Restoration of the crown part of the tooth using photopolymer materials.
Some dentists still practice the method of devital extirpation using resorcinol-formalin paste. However, this drug is toxic, stains the enamel in a pinkish-gray tint and there is a high risk of complications with subsequent retreatment or removal of the tooth.
Laser treatment
Laser treatment of pulpitis is used as part of complex therapy using a biological method or vital amputation method.
The technique involves exposing the pulp to laser beams, thereby achieving:
- disinfection;
- relieving inflammation from the affected area;
- activation of metabolic and regenerative processes;
- pain relief.
The use of a laser coupled with drug treatment for pulpitis greatly increases the chances of preserving the nerve. Pain and inflammation disappear after a day. If they do not return within 1-2 weeks, the tooth can be covered with a permanent filling.
However, the use of a laser increases the amount of treatment by an average of 7-9 thousand rubles.
Vital amputation
Vital extirpation consists of complete removal of the pulp using an operative (surgical) method.
Vital amputation is somewhat similar to non-vital amputation. The upper, coronal part of the pulp is removed in the same way. However, this is done surgically, and the nerve bundle in the apical part of the canal remains intact. Due to this, nutrition and protection of the tooth from pathogenic microorganisms continues.
Important! Vital amputation is performed only when treating multi-channel teeth. In single-root units there are no clear boundaries between the outer and inner parts of the pulp.
The method involves a number of procedures:
- Opening the cavity and cleaning caries-affected tissues.
- Removal of the coronal part of the pulp.
- Application of a rubber dam and antiseptic treatment of the tooth.
- Installation of the medicinal material, and on top of it - an insulating gasket.
- Closing the cavity with temporary filling materials.
Further treatment is similar to non-vital amputation. The patient is prescribed physical therapy and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Treatment of pulpitis under a microscope, review of clinics in Moscow
There are special dental (dental) microscopes. They enlarge the treated area by 30-40 times and allow for more thorough sanitization and obturation of the root canals. Therapy using these devices is considered the most progressive.
Special microscopes improve visibility by 30-40 times
Advantages of treating pulpitis under a dental microscope:
- all channels are visible: main, false, hidden and microtubules, which are not detected by ordinary x-rays;
- the risk of poor obstruction and associated complications is minimal;
- the doctor does not “hover” over the patient, but sits next to him, slightly behind – this is important for people who do not like violation of personal boundaries;
- It is possible to navigate curved and tangled root canals that are difficult or impossible to obturate using standard methods.
A dental microscope really increases the chances of successful treatment, but at the same time it increases the cost of treatment by 2-3 times. Therefore, if you have straight, even channels, it is better not to overpay. But if you have crooked roots or the need to re-treat previously obstructed teeth, you should look for a clinic with such equipment.
In Moscow, treatment of pulpitis under a microscope is carried out by the following dentists:
| Clinic name | Cost of service for a single-channel tooth |
| Belgravia Dental Studio | from 14,670 rub. |
| "Delta-Dent" | from 3,000 rub. without filling |
| "The president" | from 3,700 rub. without restoration of the coronal part |
| "Orthodont-Center" | from 15,400 rub. |
| "Healthy smile" | from 5,300 rub. up to 9,400 rub. |
| Dentistry of D. Boguslavsky | from 13,000 rub. |
| “Top Smile” | from 19,000 rub. |
| "Evita" | from 12,400 rub. |
| "Partner-Med" | from 7,500 rub. |
Algorithm for the treatment of pulpitis using a specific example -
If you have pulpitis, treatment of a single-rooted tooth with one canal is usually carried out in two visits (at the second visit a permanent filling is already placed). In multi-rooted teeth, which have a significantly larger number of canals (from 2 to 4), pulpitis treatment is carried out in 3 visits.
The rule is categorical - a permanent filling on a tooth is not placed in the same visit as the root canal filling, i.e. The filling material in the root canals must first harden (moisture evaporates). Only after this can a permanent filling be placed. But to save time, some dentists neglect this. Below we will look at the algorithm for treating pulpitis of a multi-canal tooth in three visits.
Treatment of pulpitis during breastfeeding and pregnancy
Any interventions during gestation and lactation are undesirable. However, pulpitis is an emergency whose treatment cannot be delayed. The disease is accompanied by infectious processes - toxins are carried by the blood throughout the body, penetrate the placenta and harm the child. The stress and pain experienced by the expectant mother also affects the baby's health.
Pulpitis during pregnancy must be treated
Therefore, pulpitis must be cured, despite pregnancy and breastfeeding. However, several nuances are taken into account:
- The first and third trimester are the most unfavorable for interventions. Manipulations during these periods can provoke fetal rejection or premature birth and affect the formation of the child’s body. Therefore, if possible, therapy is postponed until the 2nd trimester: for example, in case of chronic pulpitis with mild symptoms.
- In the third trimester, the fetus puts strong pressure on the aorta and inferior vena cava. This leads to increased heart rate and low blood pressure. To reduce pressure, during dental treatment the pregnant woman should lie on her left side at an angle of 15°.
- The use of medications is limited. Thus, anesthesia with a minimal content of adrenaline is used - “Ubistezin”, “Ultracain-DS”. Of the devitalizing pastes, only arsenic-free ones are allowed, for example, “Devit-S”. Pain relief with NSAIDs is undesirable, but relatively harmless drugs can be used to relieve pain - Paracetamol, Ibuprofen. Antibiotics are excluded - for pulpitis they are usually not required.
- During lactation, restrictions are imposed only on medications. They enter the baby's body through breast milk and can harm him. If medications cannot be stopped, the child is transferred to artificial formulas for the period of treatment.
Complications after treatment of pulpitis
Negative consequences after treatment for pulp inflammation are common. Usually they are associated with medical errors, less often – with the patient’s failure to comply with the dentist’s recommendations.
The following errors are possible:
- Choosing the wrong treatment protocol. Applies to cases when therapy is carried out conservatively or via vital amputation. The doctor incorrectly determines the form of the disease or does not fully assess the risks.
- Poor sanitation and obturation of root canals. It occurs when the tubules are filled hastily, without X-ray control at each stage or in one visit. In most cases, the mistake is made in public clinics, where 20-30 minutes are allotted for each patient, and there are no necessary materials and equipment.
- Not completely removed pulp. Particles of the neurovascular bundle may remain during vital extirpation in false canals invisible on x-rays or during the non-vital method of treatment if the doctor made a mistake in choosing the dosage of the necrotizing paste.
- Extraction of filling material beyond the apex. Appears due to pushing instruments beyond the root apex, with excessive expansion of the apical foramen.
- Perforation of the root canal. Occurs due to the “moving” of the file or reamer to the side during excessively intense cleaning or the doctor working “blindly”, without a dental microscope and x-ray control. Perforations must be urgently closed with amalgam, glass ionomer cement, and calcium hydroxide.
- Incorrect placement of arsenic or resorcinol-formalin paste. There are 2 options: the doctor incorrectly determined the dosage and put more than required, or the patient did not come at the appointed time and “passed” with a toxic drug. It threatens the development of necrosis of the gingival papilla or periodontitis, which are difficult to treat.
- A piece of tool or material left in the canal. Most often these are needle fragments, channel fillers, and paper files for drying. Such mistakes happen even among experienced doctors if all the rules are followed. The dentist should immediately report the problem and begin to fix it.
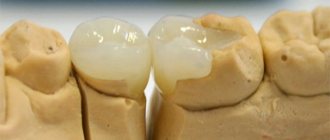
The photo shows a fragment of the instrument in the canal
All medical errors threaten neuralgia, pain, inflammation of various kinds: periodontitis, granulomas, cysts. Complications must be eliminated immediately: if this is not done, the tooth will have to be removed after a few months or years - depending on your luck.
The dentist must report any failures immediately. However, some therapists hide mistakes so they don't have to fix them for free. Therefore, demand that all stages of treatment be carried out under X-ray control, that you be shown the pictures and have them interpreted. Otherwise, you will have to undergo long and expensive treatment, and it is not guaranteed that it will be successful.
How to relieve pain, review of painkillers
You can numb the tooth yourself before visiting a doctor with two groups of drugs: analgesics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). The first have a weak effect, so they are used if there are no other options. But NSAIDs are the best choice. They not only relieve pain, but also reduce swelling and inflammation.
The best NSAIDs are shown in the table:
| Drug name | Effect | average price |
| "Ketonal" | Tablets based on propionic acid. One of the best medicines: in a matter of minutes it relieves even post-operative pain, plus eliminates swelling and lowers temperature. Prohibited for patients with asthma, stomach or intestinal ulcers, severe liver diseases, and adolescents under 15 years of age. Pregnant women can use it in the 1st and 2nd trimester. | 190 rub. |
| "Ketanov" | Analogue of "Ketonal" from the Indian campaign Ranbaxy. The drugs are similar in action, but Ketanov has a less pronounced effect and more side effects. It often causes allergies and negative reactions from the digestive tract. Prohibited for pregnant women. | 60 rub. |
| "Nurofen" | One of the best drugs based on ibuprofen. There are forms for adults and children. Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, allergies, and neurological disorders are possible. Prohibited for pregnant women in the last trimester. | 170 rub. |
| "Voltaren" | A strong pain reliever that quickly relieves pain and inflammation. However, it often leads to digestive system disorders, allergies, and dizziness. | 250 rub. |
| "Nise" | One of the safest NSAIDs: it rarely causes side effects, most of which go away on their own after discontinuation of the drug. Contraindicated during pregnancy planning, childbearing, breastfeeding and children under 12 years of age. | 350 rub. |
| "Paracetamol" | A safe pain reliever, it is allowed to be used even by pregnant and nursing mothers under medical supervision. However, the effect is the weakest among all drugs. | 40 rub. |
| "Nimesil" | Medicines in powder form for preparing drinks. It relieves inflammation and swelling well, and to a lesser extent – pain and fever. Contraindications and side effects are typical for all NSAIDs. Prohibited for pregnant women and children under 12 years of age. Not compatible with alcohol. | 300 rub. |
Effective rinses, review of medications
To relieve pain and inflammation during pulpitis, rinses are sometimes used - from pharmaceutical solutions or folk remedies. It is worth understanding that the disease cannot be cured using such methods: the pathology is caused by cariogenic bacteria that are resistant even to antibiotics and antimicrobials.
Eliminates swelling and disinfects the oral cavity
Therefore, rinses and other folk remedies are used only in 2 cases:
- to reduce pain and alleviate the condition before visiting a doctor, if there are no painkillers at hand;
- in the biological treatment of pulpitis as an addition to the main therapy.
The following solutions will help relieve pain and swelling:
- "Stomatofit A". Alcohol solution with extracts of medicinal herbs and anesthesin. Eliminates swelling and disinfects the oral cavity, which prevents bacteria from entering the carious cavity and further inflammation of the pulp. Costs 215 rubles. per 50 ml bottle.
- "Tantum Verde". Made on the basis of benzydamine hydrochloride - NSAID. Soothes pain and prevents bacterial growth. Average price – 320 rub.
- Soda-salt solution. The best anti-inflammatory home remedy, and the ingredients can be found in any kitchen. It disinfects and helps cope with inflammation and swelling. Dilute 1 tsp in a glass of warm water. soda and salt, rinse your mouth 3-4 times a day.
- Tincture of propolis and calamus. It has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and, to a small extent, analgesic effects. Take 1 tsp per glass of warm water. propolis tincture with vodka and 1 tbsp. l. calamus infusion. Mix and use for rinsing twice a day.
- Pomegranate peel. Has an astringent and anti-inflammatory effect. The peel of 2 fruits is finely chopped and boiled in a water bath for 1.5-2 hours. Afterwards, the broth is filtered, cooled to a comfortable temperature and used every 4 hours.
- Bay leaf. Relieves swelling and helps fight pathogenic microflora. 10 leaves are poured into a glass of boiling water, left for an hour, filtered and used once every 3 hours.
- Sage and chamomile. A decoction of these herbs helps eliminate hyperemia, disinfect the oral cavity and slightly reduce pain. 2 tbsp. l. raw materials are poured with a glass of boiling water, left for 20 minutes, filtered and diluted with boiled water to the required volume. Use 3-4 times a day.
- Onion peel. Helps cope with inflammation and reduce the number of pathogenic microorganisms. Peel 1-2 large or 4-5 small onions, wash, pour boiling water and simmer over low heat for 15 minutes. After cooling, strain and apply 3 times a day.
- Tea tree oil. Reduces pain and disinfects the cavity. Add 4-6 drops to a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth 3-4 times a day.
Frequently asked questions from readers:
Is home treatment effective?
No, pulpitis therapy at home is not feasible. It is necessary to relieve inflammation and hyperemia of the pulp, which is located inside the tooth. Not a single folk remedy is capable of penetrating the walls of the crown and somehow affecting the nerve.
Not to mention the fact that the affected tissue must be removed mechanically and restored with special materials.
Is it painful to treat pulpitis?
No, it doesn’t hurt: the treated area is numbed. If you still feel pain, ask the doctor for another injection: it happens that due to individual characteristics (excess weight, high sensitivity, low pain threshold) the patient needs a double or triple dose of anesthetic.
The only moment when unpleasant sensations are possible and even necessary: root canal filling. The procedure is carried out without anesthesia in order to monitor the patient’s reaction: as soon as he feels discomfort, it means that the doctor has reached the apex and there is no need to add filling material further.
Is it possible to treat pulpitis in one visit?
No therapeutic method is performed in one session. A minimum of 2 visits is required, on average you will have to come to the clinic 3-4 times.
In public dentistry, all procedures are often carried out in one visit: the nerve is removed, the canals are filled and the crown is restored. This is a gross violation of technology: such a tooth with a 99% probability will have poorly obturated and sanitized root canals.
Moreover, it is likely that untraversed tubules, foci of inflammation, remnants of the neurovascular bundle, and even instruments will remain inside the unit. Such a tooth will not last long and after a couple of years it will have to be removed.
Tooth hurts after treatment
Pulpectomy is a minimally invasive, but still surgical intervention. Therefore, post-filling pain is possible after removal. This is normal if the sensations are not strong, aching, dull, gradually subside and finally disappear after 1-2 days. To alleviate the condition, you can take NSAIDs, but usually the symptoms are mild and do not need to be stopped.
If you experience severe, acute pain, discomfort when chewing, and cannot touch or press on the tooth, contact the clinic immediately. This indicates complications: repeated inflammation, incompletely removed pulp, perforation of the canal, etc.
Vital extirpation
Vital extirpation is the most common method of treating pulpitis. With its help, any stage of pathology is treated. The method involves complete removal of the pulp using an operative (surgical) method.
Important! Treatment of pulpitis with vital extirpation is carried out over at least 3 visits. You cannot immediately fill the canals and restore the crown of the tooth after removing the pulp. It takes time for the root canals to heal and for the material to shrink.
Vital extirpation is carried out in several stages:
First visit:
- the tooth is numbed;
- the cavity is opened and cleaned;
- the pulp is extracted using a pulp extractor - a dental instrument with notches;
- the length of the canals is measured with an apex locator (a device for identifying the anatomical ends of tooth roots) or based on x-ray diagnostics;
- root canals are cleaned and expanded with reamers and files - small needles;
- antiseptic treatment and application of medications are carried out;
- a temporary filling is installed.
The patient is prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuprofen, Nise, Ketonal.
Second visit:
- the temporary filling is removed;
- drugs are removed from the canals, they are re-cleaned and treated with antiseptics - sodium hypochlorite or chlorhexidine;
- root canals are filled with gutta-percha or cement pastes;
- the cavity is closed with temporary filling materials.
Third visit:
- the filling is removed;
- the crown part of the tooth is restored using photo-curing materials;
- the filling is adjusted to the bite - excess layers are removed;
- grinding;
- polishing
At the first two stages of vital extirpation, X-ray monitoring of treatment is required. It is necessary to determine the length of the canals, their anatomical structure and whether the pulp has been completely removed.
Modern treatment methods are aimed at preserving the vitality of the tooth.
The most important part of the therapy is the passage and cleaning of the root canals. Before the procedure, the tooth cavity is necessarily isolated with a rubber dam. The dentist must accurately determine the length of the canals: incomplete filling or removal of materials beyond the apex - the maximum physiological narrowing - will lead to complications, and the tooth will have to be re-treated.
Important! The length of each channel is measured separately: the size of each of them can vary greatly.