There are quite a lot of dental diseases. Over time, they begin to develop in almost everyone. On the one hand, maintaining the health of teeth and gums is a fairly simple task.
You just have to follow all the doctor’s recommendations. On the other hand, certain groups of diseases can develop regardless of the quality of oral hygiene and nutritional habits as the main factors of prevention.
The condition of the oral cavity largely depends on the person himself.
The main reasons for the development of dental pathologies
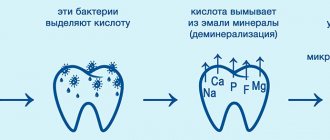
For a long time, there were many theories of tooth decay. To date, it has been proven theoretically and practically that pathogenic microorganisms play a special role in this process.
They actively develop in the oral cavity, supporting their vital activity with food debris. As a result, various types of acids of organic origin are formed.
Therefore, high-quality oral hygiene remains a fundamental measure in the prevention of dental and gum disease.
However, in addition to bacteria, there are other factors that contribute to the development of various dental diseases:
- Heredity . It can often be observed that enamel weakness is passed on from generation to generation. It consists in disrupting the structure of hydroxyapatite and its accumulation from an early age. In relation to periodontal disease, a negative hereditary factor is nothing more than a weakness of the vascular wall of the capillaries. Violation of trophic functions in the gums causes bleeding and inflammation.
- Violation of viscosity and pH of saliva . The condition of the oral fluid is what determines the health of teeth for many years. It is this that ensures natural and constant cleansing of the crown part from plaque and bacteria. The pH of saliva plays a special role. If there is a decrease in it, then beneficial substances are washed out from hard tissues.
- Bite abnormalities . Incorrectly located units in the dental arch are susceptible to abrasion, injury, and plaque accumulates on them in greater quantities. With a crowded bite, it is virtually impossible to clean the contact surfaces of the crown. In this area, caries and gum irritation quickly form.
- Tartar. This element is formed in the absence of normal oral hygiene, impaired saliva viscosity, excessive consumption of carbohydrate foods and flour products. The stone has a particular negative effect on the periodontium. Due to poor circulation in the gums, bleeding quickly appears, they swell, change color and settle.
- Consumption of sweets in large quantities. It is carbohydrate foods that are an excellent source for the existence of pathogenic bacteria. Consumption of sweets between meals has a strong negative effect on gums and teeth. Therefore, in order for children to have healthy teeth, they should not take sweets to kindergarten or school, especially at an early age.
- Profession-related hazards. Dental diseases most often affect confectioners, bakers, and people working in production where various acids and alkalis are used.
- Injuries. They contribute to the introduction of infection into soft tissues, resulting in inflammation. If you injure the enamel, this will reduce its resistance to an aggressive environment.
Tartar is a common cause of many dental diseases.
Crown destruction occurs more often on contact surfaces, the cervical region, blind fossae of incisors, and in the fissures of molars and premolars. Lumps and cutting edges are rarely involved in the pathological process.
Dental caries is a chronic infectious disease
The most common disease in dentistry is caries, which leads to slow but inevitable tooth decay and complete deterioration if measures are not taken in a timely manner. Caries has 2 forms: chronic and acute.
Chronic caries can occur in the following cases:
- poor quality and irregular hygiene, which is the main reason for the large accumulation of dangerous bacteria on tooth enamel;
- demineralization of enamel due to pathologies or deviations of hard tissues that have lost the ability to withstand negative factors;
- an incorrectly composed and unbalanced diet, in which carbohydrate-containing foods predominate, and there are no vegetables and foods rich in microelements beneficial for enamel.
This disease affects the tooth gradually; at the initial stage, pathological processes begin on the enamel, then move on to the dentin, and lastly the pulp becomes infected. To prevent the spread of caries, it is important to contact a specialist as soon as possible, who, using modern techniques, will help get rid of this disease and completely cure the patient’s teeth. Depending on the depth of the lesion, the dentist selects a suitable technique for treating the disease.
Chronic caries can only be cured with the help of specialists, so if you have the slightest suspicion of its development, contact a dental clinic as soon as possible.
Primary prevention measures
These are direct methods of preventing the development of diseases. This effect allows you to enhance the protection of the oral cavity up to 85-90%.
It includes hygienic, medical, educational and government preventive measures. It is customary to distinguish 2 methods that work best and only in combination.
Endogenous prevention
Such measures are aimed at strengthening the entire body. These include the following:
- Balancing nutrition. First of all, it is necessary that fats, proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements be present in the diet throughout life.
- Chew your food well. This point is especially relevant during the formation of the bite. This will help in the normal development of the maxillofacial area.
- Reducing stress loads. Here we are talking not only about factors affecting the psyche, but also physical fatigue, occupational hazards and environmental pollution.
- Prevention of common diseases. It will consist of all kinds of methods of hardening the body, taking medications to strengthen the immune system.
- Taking fluoride and calcium supplements. They should only be prescribed by a doctor. In excess, such drugs can cause side effects.
Primary prevention allows not only to ensure the preservation of teeth for many years, but also to improve overall health.
Exogenous prevention
It consists of a positive effect directly in the oral cavity.
These are well-known and simple measures such as:
- proper oral hygiene;
- visiting the dentist at least 2 times a year;
- local use of products containing calcium and fluoride;
- professional teeth cleaning;
- reducing the consumption of carbohydrates and flour products;
- fissure sealing, especially in childhood.
Table No. 1. Toothpastes to strengthen enamel:
| Brand name | Main cast | Action |
| Xylitol, calcium compounds, papain aloe vera extract. | Remineralizing, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, whitening, sensitive. |
| Hydroxyapatite, calcium with bioactive ability. | Anticarious, antiseptic, remineralizing. |
| Sodium fluoride, essential oils, urea, plant extracts. | Strengthening, antibacterial, deodorizing. |
| Zinc chloride, sodium fluoride, allantoin, vitamin complex. | It has a rejuvenating effect on the mucous membrane and strengthens the enamel. |
Secondary and tertiary prevention of dental diseases
If it was not possible to keep your teeth healthy, then it is necessary to treat them in a timely manner. Eliminating caries will help prevent the development of inflammatory diseases.
The result of untreated caries
Tertiary prevention is aimed at restoring the dentition. This is the installation of various orthopedic structures. They may be permanent or removable if all oral units are lost.
Prevention of dental and oral diseases
Diseases caused by viral, bacterial or fungal microflora can occur in the oral cavity. Prevention of diseases of teeth, gums and non-carious lesions of teeth can be general (proper care, visiting a doctor) and specific. Specific measures are aimed at eliminating or preventing a specific disease.
Prevention of dental and jaw injuries
Prevention of tooth bruises, injuries to teeth and jaws is to use special mouthguards during sports (boxing, wrestling). Mouthguards are a thin plastic plate that follows the characteristics of the dentition.
The design can be standard or individual (made at a dentist’s appointment). An individual mouthguard more effectively protects the soft tissues of the cheeks, gums and tongue from injury.
Prevention of tooth sensitivity
Prevention of hyperesthesia and wedge-shaped dental defects consists of using suitable personal hygiene products:
- Brushes of the required hardness. Using a hard brush in the presence of thin enamel provokes hyperesthesia. Using a brush of insufficient rigidity can result in poor plaque removal and the formation of caries.
- Pastes with the necessary content of microelements.
If the first symptoms of sensitivity occur, you should consult a doctor. If necessary, special procedures will be carried out: teeth cleaning and coating with special solutions.
At home, it is also necessary to use anti-sensitivity paste and gel. Name of gels for the prevention of hyperesthesia:
- Fluocal gel prevents the growth of pathogenic bacteria, increases the resistance of enamel to acids, and is used once a year for prevention.
- Gelato for the prevention of destruction and remineralization of initial caries.
- Belagel F enhances mineralization and restores tooth enamel.
Prevention of dental hypoplasia
Prevention of tooth enamel hypoplasia is carried out during pregnancy, when the formation of rudiments occurs. Systemic hypoplasia (underdevelopment of enamel) occurs when the expectant mother’s body receives insufficient vitamins and minerals. To prevent local hypoplasia, trauma to baby teeth should be avoided.
Prevention of dental fluorosis
Fluorosis is a systemic disease that occurs when excessive fluoride enters the body. The disease manifests itself in the formation of streaks, inclusions, yellow and brown spots on the enamel. Recommendations for preventing fluorosis:
- Do not drink water containing fluoride; use a special filter on your tap. The fluoride content in water should be 1.5 mg per liter.
- Reduce your consumption of seafood, tea (black and green), and lard.
- Buy toothpastes without fluoride.
- Visit your dentist regularly (twice a year).
Prevention of tooth neck exposure
Exposure of the neck of the tooth is a common symptom of soft tissue diseases of the gums. With periodontitis, periodontal disease, receding gums and root exposure occur. The pathology is accompanied by an aesthetic defect, sensitivity, mobility and threatens tooth loss. Prevention of exposure of the neck of the tooth consists of regular removal of dental plaque in a professional manner, careful home care, and treatment of gum pathologies.
Prevention of dental cysts
Prevention of radicular dental cysts involves high-quality treatment of root canal diseases. If the canals are not cleaned sufficiently, the infection can reach the tissues of the root apex and cause a cyst. Congenital cysts are rare, but it is almost impossible to prevent its occurrence.
Prevention of caries
Caries is the destruction of hard tissues of enamel and dentin with the formation of a defect. Pathology occurs in the presence of plaque, microorganisms and carbohydrates. Microbes from carbohydrates ferment acid, which destroys hard tissue. Prevention of tooth decay consists of:
- thorough removal of dental plaque;
- using mouthwash after meals;
- strengthening the enamel. You can use a gel to prevent dental caries, which strengthens the enamel.
Means for preventing dental diseases
All preventative measures for preserving teeth can be minimal without the use of special drugs. Some of them can be used from a very early age.
Such means include:
- Gel Rox Medical. It is quite suitable for babies. It contains calcium glycerophosphate and magnesium chloride. The amino fluoride film reliably covers the crown. This ensures long-term penetration of beneficial substances into hard tissues.
- Fluoride-containing pastes. They are used from 6 years of age. During this period, they will be more relevant, as the bite begins to change. Pastes with extracts of medicinal herbs, mineral complexes and antiseptics are suitable for periodontal disease.
- Use of special varnishes. Positive results are observed from the effects of such agents as Bifluorid 12 and Fluoridin No. 15. For older children, it is allowed to use Albadent with mumiyo. Starting from adolescence, Fluoride varnish, Duraphat, Composeal are suitable.
- Electrophoresis. For adults, it is carried out with fluoride preparations: Belagel or STAN-GARD. This procedure is necessary 2-3 times a year. To maintain healthy gums, solutions of vitamins, decoctions of medicinal herbs, and exposure to a helium-neon laser are suitable.
- Fissure sealing. It can be used in both primary and permanent dentition. Argenate and Saforite are suitable for sealing.
- Taking special medications orally. Calcium gluconate and glycerophosphate and sodium fluoride will help keep your teeth healthy. They are prescribed in solutions and tablets. The duration of treatment is calculated individually.
- Proper nutrition. You should select a menu with foods rich in fluoride and calcium.
Fissure sealing, before and after
This is not a complete list of tips and remedies. They can be expanded or, on the contrary, reduced, individually after examination of the oral cavity.
Top recommendations from a dentist
All the tips are quite simple and widely known, but they have certain subtleties.
Experts suggest following 10 rules for healthy teeth and gums:
- Be sure to visit the dentist. This should be done at least once every 5-6 months. This will help prevent the development of pathologies and possible complications from existing diseases.
- Avoid or limit your consumption of coffee, alcohol and sugary soda. These drinks contain large amounts of phosphorus. Of course, it is useful, but with excessive intake, calcium is washed out. This element is most important for teeth and gums. The best drinks are milk and simple clean drinking water.
- Use dental floss. It is known that caries and periodontal diseases quite often develop secretly in the interdental spaces. Only flosses are capable of completely removing food debris, plaque and polishing rough areas of enamel. Even one treatment per day will be enough to provide good prevention.
- Stop smoking. The secrets of healthy teeth also lie in their frequency. Tobacco smoke significantly changes the color of the enamel due to the huge amount of tar deposited in the oral cavity. Quitting smoking will further reduce the risk of developing cancer, freshen your breath and reduce the consumption of lollipops and various fresheners to mask bad breath.
- Enrich the body with vitamins and minerals. Nutrition for healthy teeth should be balanced. You need fats and proteins, fresh fruits and vegetables, as well as meat products. Vitamins and minerals will strengthen the oral cavity, and also increase the resistance of the entire body.
- Don't endure toothache. You should not postpone a visit to the dentist if the discomfort has become unbearable. As the pathology progresses, you can lose a tooth unit. The doctor will diagnose and eliminate the cause of the disease.
- Use dental rinses. Today, a product under the brand name Listerine has proven itself well. It has a positive effect on hard and soft tissues. Thanks to chlorine dioxide, plaque is eliminated, bacterial growth is reduced, and bad breath disappears.
- Prevention and treatment of common diseases. It is known that everything in the body is interconnected. The development of certain pathologies negatively affects the functioning of various organs and systems, including the oral cavity. So noticeable changes in teeth and gums are observed in diseases of the cardiovascular system, endocrine lesions and gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, various somatic pathologies cannot be left to chance. Timely treatment will help avoid serious health problems.
- Clean your tongue. As a rule, little attention is paid to the hygiene of this organ. However, it is known that it is on the tongue that a large number of pathogenic bacteria accumulate. They are not only dangerous due to inflammatory diseases, but also emit an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
- Careful daily oral hygiene. This is a very simple and easy way to prevent many dental diseases. The most common accessory is a brush and paste. But few people know that there are several cleaning methods that are specially designed and can be prescribed individually by the dentist. There is also a standard method. It is a set of recommendations for performing various movements and positioning the brush.
Dental care for schoolchildren (8-17 years old)
Children this age can care for their teeth on their own, but parents or a hygienist can periodically check the quality of brushing using plaque tablets or liquid. It is good to use mouth rinses or special foams. Fluoride-containing pastes (1000-1500ppm) and Tuss Mousse gel applications can be used to strengthen tooth enamel (as prescribed by the dentist). At this age, it is necessary to pay attention to the condition of the gums: it is important to teach a teenager to use dental floss and an irrigator. Proper oral hygiene is especially important if you have braces. It is better to visit a hygienist to learn how to properly brush your teeth with braces. To help with self-hygiene, you can have your teeth professionally cleaned by a hygienist.
Attention , eating disorders, as well as poor hygiene when wearing orthodontic equipment worsen the condition of the oral cavity, increasing carious lesions!
At school age, it is advisable to see the dentist every six months, unless the doctor prescribes a different schedule of visits.
Standard oral cleaning
Brush movement with a healthy bite
How to keep your teeth healthy until old age and visit the dentist less often? Perhaps everyone dreams of this. Our healthy habits and the correctness of their implementation play a special role here.
The steps of a standard dental care method will be as follows:
- Wet the brush well with water and apply the paste in a volume ratio no larger than a pea. If its quantity is significantly greater, there is nothing wrong with that. However, a lot of foam is formed during processing.
- Bring the bristles to the gums of the upper jaw at an angle of 45 degrees. The movement is made vertically, from the periodontium, to the cutting edge or chewing surface of the crown.
- Cleaning should begin from distant areas and gradually move towards the center. For each unit you need to devote 3-4 movements.
- Cleaning should be both internal and external surfaces of the crown. The frontal areas, namely the canines and incisors, are processed by arranging the bristles in a vertical manner. This will be the best option for removing plaque using sweeping movements.
- The chewing surfaces of molars and premolars are processed in a reciprocating direction. The brush can be positioned horizontally.
- After cleaning the upper jaw, I proceed to the lower jaw. At the very end of the hygiene procedure, the tongue is treated with a special brush. In this case, the movements should go from the root to its tip.
- Don't forget about contact surfaces. To remove food debris and plaque from there, it is better to use floss. When using the thread, the reciprocating movement should be done very carefully to avoid periodontal injury.
- At the very end, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with one of the dental rinses. You need to spend about 30 seconds on this. The brush should be stored openly, for example in a special cup, with the top head pre-soaped.
Table No. 2. Dental rinses with complex effects:
| Product name | The main components in the composition | Therapeutic effect and recommendations |
| Chlorhexidine, sodium fluoride, aluminum lactate | Astringent, anti-caries, antiseptic effect. Use no more than 2 weeks. |
| Eugenol alcohol base, chlorhexidine, sodium fluoride. | Antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect. Not for use by children and drivers. |
| Extracts of sage, chamomile, lemon balm, xylitol, chlorhexidine. | Anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects. Not suitable for long-term use. |
| Eucalyptus extracts, thymol, thyme oil, methyl salicylate, sodium fluoride, chlorine dioxide. | Remineralizing, deodorizing and anti-inflammatory effects. Suitable for complex treatment of the oral cavity. |
| Sodium fluoride, potassium citrate, cytylpyridinium chloride. | Reduces sensitivity to food irritants, has antiseptic, deodorizing and anti-inflammatory effects. |
Prevention of dental diseases in children
Of course, oral health needs to be addressed from an early age. It is worth saying even more, the expectant mother should take care of this already in utero. This includes proper nutrition, giving up bad habits, and preventing infectious and other somatic diseases.
Device for oral hygiene in infants
At an early age in children, special attention should be paid to preventing the development of caries. It will also consist of endogenous and exogenous influences, as in adults.
The main activities in this case are:
- Taking vitamins. Good results are achieved by products containing trace elements of calcium compounds, such as VitaMishka or Multi-tabs Baby Calcium.
- Limit your intake of carbohydrates and polysaccharides. It is known that it is these products that negatively affect the still weak enamel in children’s bite. In addition, uncontrolled consumption of sweets can undermine the normal development and functioning of the baby’s pancreas.
- Vegetables and fruits are a must on the menu. They must be fresh on the child’s table. Containing useful substances in them will ensure the prevention of not only caries, but also gum disease. Hard varieties will provide a natural periodontal massage and strengthen the chewing muscles, which will positively affect the development of the entire maxillofacial area.
- Consultation with a pediatrician. At a young age, oral health should not only be taken care of by the dentist. The pediatrician will help you select all means of protection, taking into account the individual characteristics of the body and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
- Systematic oral hygiene. As soon as the first tooth appears, it already requires some care. From the age of 5, flosses and rinses can be used under parental supervision.
- Choosing the right brush. For children, the best option would be a device with an X-shaped arrangement of bristles. This form will ensure plaque removal even in the most difficult areas. The main thing is not to forget to change it once after 3 months of use.
- Despite their early age, a child, like an adult, requires periodic consultation with a dentist. In case of weak enamel, the doctor recommends fluoridation and sealing of fissures in the primary occlusion. This will be the best way of local prevention.
Acute caries
The main symptom of the development of this form of caries is the appearance of acute short-term pain. As a rule, pain occurs as a result of exposure to cold or hot substances; if the cavity is filled with food debris, the duration of the painful sensations may be prolonged.
In addition to painful sensations, acute caries has other symptoms:
- smell from the mouth;
- rapid appearance of plaque;
- loss of fillings;
- saliva becomes more viscous and ceases to effectively clean teeth.
Timely prevention makes it possible to detect the disease at an early stage and effectively treat it.
The most useful products
What can you eat to keep your teeth healthy and strong for many years? First of all, to maintain a beautiful snow-white smile, the body needs calcium, and in large quantities. This microelement is very important for the entire skeletal system.
You may consider taking special nutritional supplements and vitamins, but only after your mouth has been examined by a dentist. In addition to calcium, vitamin D and some elements of group B are required. They prevent bleeding and inflammation of the gums. There should also be a constant supply of substances such as copper, iron, potassium, zinc and iodine.
Products good for teeth
Many of them are found in raw vegetables and fruits, others enter the body with animal food and fish. Therefore, for the health of teeth and gums, various foods are necessary and, as a rule, diets do not help strengthen them, but rather disrupt the normal functioning of physiological processes.
Foods high in calcium are:
- low-fat milk and yogurt;
- salmon;
- sardines;
- spinach;
- bakery products;
- rhubarb;
- beet;
- mineral water rich in calcium.
Vitamin D plays a huge role in the mineralization of enamel. It ensures normal absorption of phosphorus and calcium.
Most of it is found in:
- fatty fish (herring, halibut, mackerel, salmon, tuna);
- corn;
- cocoa;
- fish oil;
- egg yolks.
To maintain healthy gums, vitamin A is required. It provides reliable protection against pathogenic bacteria, caries and plaque.
Vitamin A can be found in the following foods:
- spinach;
- carrot;
- gooseberry;
- apricots;
- cabbage;
- red meat;
- offal;
- pumpkin;
- chicken eggs.
To prevent gums from bleeding, you need vitamin C. It ensures the strengthening of all blood vessels in the body, primarily by affecting their wall. Vitamin C provides elasticity, which significantly reduces their fragility and the deposition of cholesterol plaques. In addition, it helps the body resist various infections.
To replenish vitamin C, it is recommended that the menu include the following products:
- kiwi;
- all citrus fruits;
- cabbage;
- tomatoes;
- celery;
- red paprika;
- potato;
- broccoli;
- some by-products.
Fluorine fights well against many microbes. It helps reduce acidity in the mouth after consuming any food and strengthens enamel. The intake of this microelement in large quantities can negatively affect the condition of the teeth.
It is found in sufficient quantities in:
- black and green tea;
- rice;
- mineral water;
- different varieties of fish;
- fluoridated salt;
- dairy products.
To protect your teeth from tartar, chewing sugar-free gum is a good option. It promotes increased salivation to naturally cleanse the crown of plaque. In addition, the chewing gum itself mechanically removes all deposits, even on contact surfaces.
The duration of administration should be no more than 15 minutes after consumption of food. Long-term use of chewing gum has a negative impact on the temporomandibular joints.
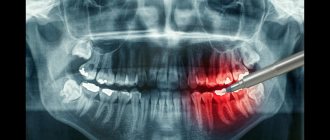
Panoramic shot
A dental panoramic photograph is a circular digital image of the entire jaw in a two-dimensional plane.
This examination allows you to:
- identify hidden caries;
- diagnose the condition of teeth under crowns and fillings;
- assess the health of canals and root tips;
- determine the presence of permanent tooth buds in children;
- establish periodontitis disease;
- monitor the condition of teeth during implantation and prosthetics.
An orthopantomogram, like a dental photograph, significantly increases the capabilities of dentists and allows them to see what cannot be detected during a visual examination.