Many people have heard about the importance and necessity of preventing dental diseases. Most parents support the idea that it is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. Now there is no longer any need to convince patients of the need for preventive measures. Parents often ask questions about how exactly to carry it out, because it is so easy to get confused in choosing good hygiene products given the modern abundance. Which toothpaste or brush to choose, how to properly care for your teeth, what to pay attention to at different age periods? Hygienist Elena Smirnova in her work relies on many years of experience and a state prevention program developed specifically for these purposes. This article contains the main points of the program and advice from the Dial-Dent hygienist on the prevention of caries and periodontal diseases.
The immutable basis of any preventive measures is daily oral hygiene, proper and balanced nutrition, and the use of fluorides as directed. Let's consider prevention methods in different age groups:
Oral care for newborns and young children (up to 3 years)
Dental care for children should begin with the eruption of the first tooth. Before teeth appear, oral hygiene can be performed with special wipes or a clean cloth moistened with water. Once all the teeth have erupted, soft toothbrushes (Curaprox or Nenedent) and age-appropriate toothpaste can be gradually introduced. If the child is breastfed, then he receives a sufficient amount of fluoride from the mother's milk (if she eats a balanced diet and takes vitamin complexes). When breastfeeding is completed, fluoride comes from food and water.
Attention
, poor oral hygiene, frequent night feedings and constant drinking of sugary drinks between main feedings provokes the appearance of early caries!
At an early age, it is advisable to see the dentist once a year, starting from the appearance of the first teeth, unless the doctor prescribes a different schedule of visits.
Section 4. Prevention methods
Moscow, 1988
The program includes the following methods for the prevention of dental caries and periodontal disease:
- Health education (education of a healthy lifestyle) for the prevention of dental diseases.
- Correction of children's nutrition in relation to the frequency and amount of sugar consumption.
- Teaching children effective oral hygiene.
4.4. Local treatment of teeth with anti-caries drugs. These methods are applied differentiated depending on
from the contingent.
Moscow, 1988
from the contingent.
Moscow, 1988
from the contingent.
Moscow, 1988
from the contingent.
You should take care of your baby’s dental health from a very early age, namely from the 5th week of your pregnancy. A method of antenatal prevention has been developed especially for expectant mothers and the following are recommended:
- a complete diet for a pregnant woman, including foods high in calcium and phosphorus - milk, cottage cheese, fish and seafood;
- taking vitamin preparations as prescribed by a doctor;
- sanitation of the oral cavity in the second trimester of pregnancy, timely elimination of foci of carious infection.
How to clean
When the first teeth appear at the age of 5-7 months, it is necessary to clean the child’s oral cavity daily using rubber finger brushes. Hygienic procedures using toothpaste are carried out starting from 1.5-2 years.
Choosing a toothpaste
The first toothpaste should be fluoride-free, since young children swallow up to 30% of the product due to lack of teeth brushing skills, which threatens the development of fluorosis (damage to tooth enamel as a result of excess fluoride intake).
For preschoolers, the maximum permissible concentration of fluoride in toothpaste will be 0.05%; children over 8 years of age and adolescents can use a product with 0.09-0.15% - for example, ROCS baby.
From the age of 3, young patients are given caries prevention on an outpatient basis.
One of the common techniques used in dentistry is
silvering
: The doctor treats baby teeth with silver nitrate, which tends to settle on the surface of the enamel and is active against cariogenic bacteria.
To avoid an allergic reaction, the child’s gums are treated with Vaseline oil.
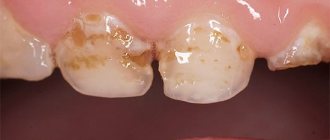
If chalky spots are already visible on the surface of the enamel (stage I of caries), which indicates a lack of calcium and fluoride ions, the dentist will recommend remineralization - for example, applications with Diplen-Denta F film. The composition of the medicine that the doctor sticks to the surface of the teeth:
- chlorhexidine, which has bactericidal properties;
- sodium fluoride, which strengthens tooth enamel.
The course of treatment consists of 8-10 applications applied at one-day intervals. To consolidate the results of therapy, the procedure is repeated after 1-1.5 months.
Dentists pay special attention to methods of endogenous and exogenous prevention, the use of which is already relevant in preschool age.
Endogenous measures are “directed inside” the body, their task is to compensate for the lack of microelements and enhance the mineralizing properties of saliva, which nourishes the hard tissues of the teeth and protects them from pathogenic microflora. As a preventive measure using this method, the pediatric dentist will recommend:
- take vitamin supplements for children (Multi tabs Baby calcium, VitaMishka calcium plus);
- limit food intake containing carbohydrates and polysaccharides - cariogenic bacteria “love” sweets and starchy foods;
- include hard fruits in your child’s daily diet: they remove food debris from the interdental spaces and increase salivation.
In some cases, medications containing phosphorus and fluorine and vitamin D are prescribed.
Exogenous prevention measures involve protecting baby teeth from external unfavorable factors - soft microbial plaque and the enamel-damaging effects of certain foods. This:
- daily oral hygiene using children's toothpastes, flosses and rinses (Den Tek, Cura Prox, Silca, Oral-B);
- choosing the right toothbrush - 1) medium hardness; 2) X-shaped arrangement of cleaning beams of different lengths; 3) timely replacement - once every 3 months;
- coating of teeth with fluoride-containing products.
Fluoridation of teeth and the use of toothpastes with optimal fluoride content strengthens tooth enamel by creating fluorapatite, a solid compound that fluoride ions form with hard tooth tissues.
Ages over 8 years and puberty in children are characterized by extensive hormonal changes in the body: the mineralizing properties of saliva weaken, and the dentin in the already emerging permanent teeth softens. Therefore, dentists strongly recommend that school-age children undergo a primary caries prevention procedure, which allows them to preserve the integrity of their first chewing teeth.
We suggest you read: Antibiotics used in dentistry
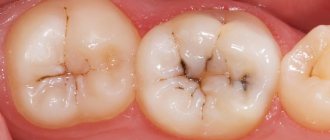
Primary prevention is aimed at protecting and strengthening the enamel of healthy teeth not damaged by caries. For this purpose, school-age children and adolescents undergo fissure sealing.
Dental sealants
The 6th and 7th teeth, which are the first permanent teeth to erupt and form the bite, are “sealed” with a composite or glass ionomer sealant. Sealants (dental sealants) are composites that contain fluoride and have a more fluid texture than a conventional filling. Once on the surface of the tooth, they spread and fill the fissure.
To control the safety of the coating, special colored sealants are used in pediatric dentistry.
The procedure is carried out by a dentist-therapist, takes no more than 10-30 minutes and includes the following steps:
- Cleaning teeth with a special abrasive paste.
- Apply a few drops of phosphoric acid and rinse with water.
- “Sealing” the fissure with sealant and “exposure” with a halogen lamp.
- Removal of composite residues by preparation (drilling).
Fissure sealing allows you to protect chewing teeth from caries for a period of 2 to 8 years. If carious lesions are observed not only on the enamel, but also on the dentin of the tooth, preparation, installation of fillings and secondary prevention of caries are carried out.
Secondary prevention involves identifying the disease at an early stage, eliminating the source of infection and protecting the teeth located next to the patient from caries.
Since the age of 8-11 years is a period of active development of the skeletal system of the body, in addition to infiltration and preparation of carious cavities, the doctor may prescribe medications. For example, tableted fluorine or sodium fluoride, calcium lactate, Phytin or Vitaftor.
Fissure sealing, silver plating and fluoridation are absolutely painless procedures, so this is where your child’s visit to the dentist should begin. And if you provide brushing your teeth and rinsing your mouth after meals in the form of a fun game or competition (“Who’s first?”, “Who has whiter teeth?”), then caries simply won’t have a chance.
Dental care for preschoolers (3-7 years old)
At this age, it is necessary to help the child brush his teeth; you need to control this process, checking the quality of brushing and the amount of toothpaste used. It is important to brush your teeth in the morning and evening (evening brushing should be done especially carefully). Recommended manufacturers of pastes and brushes: Curaprox, Rox, Splat. To check the quality of cleaning, you can use tablets or liquid to determine plaque "Curaprox", "Paro".
At this age, as a preventive measure for caries, on the recommendation of a doctor, you can use a paste with a fluoride concentration of 500 ppm to 1000 ppm. The dentist may recommend prophylaxis with Tuss Mousse gel (not suitable for children with cow protein intolerance) or coating the teeth with special varnishes containing fluoride, as well as remineralizing gels, for example, Rox.
Attention , poor dental care, snacking, drinking sugary drinks, eating disorders, a large proportion of food containing carbohydrates in the diet provoke the occurrence of caries!
In preschool age, it is recommended to visit the dentist 2-3 times a year. During this same period, it is advisable to see an orthodontist, especially if there are doubts about the correct development of teeth (the child sucks fingers or tongue, places the jaw incorrectly, teeth grow crooked, etc.).
Dental diseases
When developing a prevention program, it is necessary to include the following sections:
- identification of dental problems among the population of the area (city, region, etc.);
- setting a common goal and measurable (generally accepted criteria) program objectives;
- selection of methods and means of prevention;
- provision of personnel;
- material support;
- Information Support;
- evaluation of program effectiveness.
1.1. Identifying Dental Problems
The World Health Organization recommends the introduction of problem-oriented programs aimed at solving
current or predicted problems. Therefore, the first stage of program development (planning) is to identify problems. It is very important not only to detect dental diseases (for example, dental caries), but also to study their prevalence and intensity, as well as evaluate (based on existing experience) the real possibilities for preventing diseases (for example, are they available, are they accessible, are they effective, etc. .
means and methods of caries prevention). As a result of identifying problems and analyzing the situation, it is then possible to meaningfully set measurable goals and objectives of the program and, therefore, an objective assessment of the effective program. It should be kept in mind that if the first stage of planning is ignored, then management and evaluation of the program will not be possible.
In the conditions of the USSR, where in different regions the intensity of dental caries varies from low to very high (according to WHO classification), careful orientation of the prevention program on local conditions is especially important.
According to the WHO Collaborating Center and publications in dental publications in the USSR, currently the most common dental diseases are moderately intense dental caries (on average 3.4 KPU of teeth of 12-year-old children) and periodontal disease (100% of adolescents and adults).
Until recently, the USSR occupied an intermediate position between the low intensity of dental caries in the population of developing countries in Africa and Asia and the high intensity of dental caries in the population of Western Europe. Since the mid-seventies, the situation has changed dramatically: in developing countries, especially Latin America and the Middle East, the intensity of dental caries is increasing, and in Western Europe, the USA, Australia, Canada, Japan, and Scandinavian countries it is decreasing.
In a number of cities of the USSR, where fluoridation of drinking water was introduced (Leningrad, Moscow, etc.), there was a tendency to reduce the intensity of caries, at the same time in other cities, as well as in rural areas, especially in the regions of Siberia, the Far East, and the Baltic republics , the intensity of caries is increasing. Thus, in general, the problem of dental caries in the population of the USSR remains relevant.
We suggest you read: A child has a white spot on the tip of his tongue – Teeth
Information about the prevalence and intensity of periodontal diseases in the USSR is contradictory due to the use of different approaches in diagnosing diseases. In 1982-1983 Studies have been conducted using the WHO periodontal index. Was
a high intensity of periodontal diseases was discovered in the Armenian SSR, Uzbekistan, Riga, Moscow and Kaunas.
Dental care for schoolchildren (8-17 years old)
Children this age can care for their teeth on their own, but parents or a hygienist can periodically check the quality of brushing using plaque tablets or liquid. It is good to use mouth rinses or special foams. Fluoride-containing pastes (1000-1500ppm) and Tuss Mousse gel applications can be used to strengthen tooth enamel (as prescribed by the dentist). At this age, it is necessary to pay attention to the condition of the gums: it is important to teach a teenager to use dental floss and an irrigator. Proper oral hygiene is especially important if you have braces. It is better to visit a hygienist to learn how to properly brush your teeth with braces. To help with self-hygiene, you can have your teeth professionally cleaned by a hygienist.
Attention , eating disorders, as well as poor hygiene when wearing orthodontic equipment worsen the condition of the oral cavity, increasing carious lesions!
At school age, it is advisable to see the dentist every six months, unless the doctor prescribes a different schedule of visits.