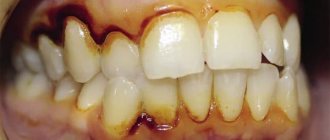
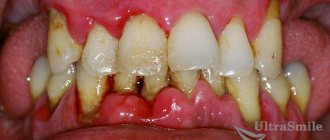
In Russia, all age groups of the population are susceptible to caries. As patients get older, the prevalence of the disease increases. The intensity of caries is determined by a calculation method. The calculation includes people with a diagnosed disease, the number of teeth or locations of inflammation.
general information
The prevalence of caries can be calculated in numbers using the formula. This value is expressed as a percentage; it is not difficult to determine if we know the number of patients who have treated or extracted teeth. The obtained indicators must be divided by the total number of patients and multiplied by 100%.
There is a concept of the intensity of caries damage in one patient or the intensity index of the KPU, where P is the number of teeth with fillings, and Y is the number of teeth removed.
When calculating the dental CP index, we take the indicator of affected teeth from an individual patient and divide this number by the number of people examined. A filled tooth with inflammation detected during examination is also classified as carious and is taken into account.
In children, in addition to regular ones, there are dairy ones. Therefore, when calculating the CP intensity index, the sum of temporary and permanent teeth is taken.
Prevalence of caries.
| Caries prevalence = | Number of people with teeth affected by caries | x 100% |
| Number of people examined |
The intensity of caries damage in one examined person is determined by the index of dental CP of teeth and CP of cavities. The CPU index of teeth is the sum of carious (C), filled (P) and removals due to complications of caries (U) teeth in one examinee. When determining this and other average values of intensity indices for a significant number of the population, their sum is divided by the number of those examined.
Caries statistics and its objectives
Statistics on the frequency and course of caries under certain conditions in different age groups makes it possible to:
- Study the etiology and pathogenesis, causes and factors influencing the occurrence of the disease.
- Planning for caries prevention in different patient groups in the future.
- Determine the effectiveness of preventive measures taken.
- Planning medical care for different groups of patients in the future.
You can choose the scale for calculating the intensity index depending on the goals of the statistics.
The number of caries patients is also counted because the prevalence of the disease reaches 100% of the adult population. Therefore, qualified specialists are in demand in dentistry, who have begun to use the latest methods of treatment and diagnosis. Improving the quality of dental care also depends on disease statistics.
Data on the course and nature of the disease are stored in the medical record for up to 75 years. Thanks to the archive, it is possible to collect information about the health status of people at different ages.
Main tasks of statistics
Dental research relies on statistical data on caries, its prevalence, intensity and duration in different patients. When collecting information, the following tasks are set:
- studying the mechanism of origin and development of the disease in its individual manifestations;
- studying the origin of the disease in general: the conditions and causes of its occurrence;
- division of the population according to the degree of risk of developing the disease;
- drawing up future forecasts of the development of the disease for planning preventive care and adequate provision of dental services to the population;
- assessment of the effectiveness of created preventive and therapeutic methods;
- determining the degree of development of the disease in the examined group of patients in order to correct errors that have appeared and plan new directions in methods of prevention and treatment.
Information collection and important indicators
When collecting information on caries, several important indicators are taken into account. First of all, pay attention to the age of the patient. Children belong to a separate group of patients because baby teeth are more susceptible to caries compared to permanent teeth. Therefore, cases of the disease are observed at an early age. Adult patients are divided into the categories of young, adult and elderly.
Internal and external factors also influence statistics:
- Place of residence.
- Climatic conditions.
- Length of daylight.
- The composition of drinking water in a region affects disease statistics.
If the patient's diet is not balanced, a deficiency of certain vitamins and microelements appears in the human body. This leads to further tooth decay.
Research and its statistics
As mentioned above, in our country the prevalence of caries reaches enormous values. This is due to the fact that at an early age children develop caries in their baby teeth. Some parents do not consider it necessary to brush their baby teeth, since they will still be replaced by permanent ones. This is a big mistake.
If a baby tooth is affected by caries, an equally carious permanent tooth will grow in its place. It is important to start teaching children about oral hygiene from an early age. As people grow older, the degree of caries damage to the population only increases, approaching 100% of the indicators.
By the age of 6, a child with caries may have damage to his first permanent teeth, which can lead to their loss in the future.
Much attention should be paid not only to treatment, but also to the prevention of caries. The child must:
- Brush your teeth twice a day.
- After eating, it is advisable to rinse your mouth.
- Avoid consuming large amounts of sweets, which can damage children’s baby teeth.
- For cleaning, a special thread is used that removes plaque.
- It is mandatory to visit the dentist at least 2 times a year for timely treatment.
- Your toothbrush should be changed at least once every 3 months.
Disease intensity
To solve statistical problems, it is necessary to take into account not only the fact of the development of the disease. To improve the level of dental services, an assessment of the intensity of caries is needed.
To calculate the degree of intensity of the disease, scientists from WHO came up with a special index of the sum of damaged teeth - SPU, where K - teeth affected by caries, P - filled teeth, U - teeth removed. The intensity of dental caries is calculated according to the formula: ((K+P+U)/(total number of examined)).
Children with temporary (baby) teeth are given the index kp, where k is teeth affected by caries, p is filled teeth. For children whose temporary teeth are being replaced by permanent ones, the intensity of the disease is calculated using the index KPU+KP.
In mass studies of the intensity of the disease in children, it begins to be calculated from about 12 years of age, when the replacement of temporary teeth with permanent ones has ended. Such restrictions are considered the most informative, since the level of caries damage to primary teeth is a relative concept and not a constant one. WHO identifies five degrees of disease intensity, which can be found in the table:
Table of caries intensity according to WHO
Prevalence
The prevalence and intensity of caries increases depending on the age category. In patients aged 12 years, the disease progresses from 61% to 96%. In older age categories, caries occurs in 100% of cases. All Russians suffer from damage to tooth enamel.
Research shows that the coating on the upper teeth is more likely to be damaged. The disease occurs in people, regardless of age.
Based on the intensity of carious formations, the following classification is given:
- Short – 0-30%.
- Average – 31-80%.
- High – 81-100%.
Changes in the prevalence of caries in the world over a twelve-year period:
To determine the intensity of caries, the following indicators are used:
- Intensity of inflammation of temporary milk teeth:
The index kp (z) corresponds to the sum of teeth with damaged enamel and fillings installed by one dentist.
Kp index (n) is a set of inflammation points.
To determine the average index of kp(z) and kp(p) among several subjects, you will have to find out the individual indicators for each patient, summarize all the data and divide the result among all group members.
- Intensity of caries of molars:
The indicator KPU(z) is a set of teeth with damaged enamel, filled by a dentist.
Index KPU (n) - the sum of all damaged areas with carious formation or filling. If a tooth was pulled out, in this classification it is considered 5 surfaces.
When calculating such indices, the first stages of caries and light spots are not taken into account.
To determine the average number for the above indices for a group, you should find the sum of personal indices and divide it by the number of people surveyed in this group.
Analysis of the intensity of caries in the population. To compare indicators between regions or states, the average values of the KPU index are used.
All about the intensity of caries
According to WHO, caries occupies a leading position among oral diseases, surpassing cases of periodontal disease. The most famous pathology in modern dentistry is becoming increasingly widespread among the entire population, although hygiene means and techniques are constantly being improved. Due to the frequency of visits to clinics, diagnostic and treatment methods are familiar to all adults.
Caries is widespread due to modern attitudes to nutritional principles, consumption of many sweets, and fast food products. Such products do not provide the body with the necessary minerals that are beneficial for teeth.
Among Russian residents, the intensity of dental damage is high among both adults and children. Recent studies have shown that young children are the leaders in the incidence of caries.
The intensity of damage to dental tissue is assessed by the caries index, which is calculated as an individual indicator of the development of the disease for each individual person:
- in adults , the index is expressed by the total number of missing teeth, living teeth with caries and with fillings;
- in children, the index is expressed by the number of affected teeth and with fillings installed.
After determining the individual index, an arithmetic mean is calculated, showing the index of caries intensity in the group of subjects. Using the same principle, the prevalence index of dental tissue damage is determined.
At the same time, experts believe that this method of calculating indices does not express the true state of affairs, since it does not take into account teeth at the initial level of the disease - superficial or in the form of a primary stain.
Because of this, the statistics look more optimistic than the actual state of affairs. Expert assessment proves that among the Russian population the index of prevalence and intensity of caries reaches 100%.
Epidemiological indicators
Cases of caries incidence when conducting examinations of citizens must take into account age categories. This is due to the different susceptibility of the disease in children and the presence of temporary teeth. They should also be taken into account in adults. According to WHO recommendations, adults are divided into several age groups.
The prevalence and intensity of caries in the population depends on a number of factors. Geographical factors are considered significant: climate, mineral content in soil and drinking water, solar activity indicator.
The main cause of caries formation is nutritional problems. Typically, the diet contains many refined components with carbons. When food is thermally processed, a large amount of substances necessary for the body is lost. An unbalanced diet leads to a lack of nutrients in the body and a weakened immune system.
The importance of rational nutrition is confirmed by data from epidemiological, clinical and experimental studies. The prevalence of caries depends on the age of the person, which is due to the different number of teeth in children and adults and the susceptibility of tissues to caries; temporary teeth are more easily affected than permanent teeth. This is taken into account during the study.
In children, a rather low CP + CP index can be regarded as an indicator of an intense carious process due to premature removal of baby teeth. There are no recorded cases of a predominant number of caries patients among men or women.
During certain periods of life, for example during pregnancy, women have an increased tendency to caries, and the number of affected teeth may increase.
Dental caries is the most common human disease. It affects almost the entire adult and child population of the globe. In economically developed countries, out of 10 people, 8-9 need treatment for this dental pathology.
In the process of phylogenesis, human teeth have changed both in relation to their shape and size, and the resistance of the dental tissues themselves, and primarily enamel, to harmful factors of the external and internal environment.
The incidence of dental caries has increased especially sharply in the last two centuries, which can be associated with changes not only in the nature of people’s nutrition, but also in other working, living and environmental conditions. It must be taken into account that with the introduction of automation and chemicalization into modern life, the environment and nature surrounding humans also changes. The adaptive capabilities of the human body lag behind the rate of change in this environment.
In order to study the etiological factors of caries, extensive epidemiological studies are being conducted in many countries of the world, including Russia. Since the creation of the Central Research Institute of Dentistry in Moscow (1962), epidemiological expeditions have been conducted in our country to study the prevalence of caries in Russia. Studies have shown a significant frequency of this disease among the population of various medical-geographical and administrative zones of Russia, reaching 98% in some areas, as well as significant fluctuations in dental caries in children and adults in various agro-climatic zones. This can be associated with socio-economic, ethnic and demographic data, differences in biogenetic factors in the territory where the surveyed persons live.
To take into account the degree of dental caries, an indicator of the frequency, or prevalence, of the disease is used. This indicator determines the percentage of children (adults) of a given age and sex group with carious teeth per 100 and 1000 examined.
When analyzing the results of mass dental examinations of the population, WHO
in relation to age groups. Thus, in our country, the calculation of dental morbidity in children up to 15 years of age is carried out separately for each year, and then the group of 16–19 years old is studied. Among the adult population, age groups are formed at ten-year intervals (20–29 years; 30–39 years, etc.).
For a more accurate picture of the prevalence of dental caries in the population, a second indicator has been developed - the caries process intensity index, which is the average number of teeth affected by caries per person examined. When counting carious teeth, they should include not only carious untreated teeth (K)
, as well as filled for caries (P)
and removed as a result of carious destruction (U)
. This intensity index is abbreviated as KPU
. The caries intensity index of temporary (baby) teeth is denoted by lowercase letters kp
. Those removed due to caries and as a result of physiological changes are not taken into account.
Consequently, indicators of the intensity of dental caries are determined in children separately for temporary and permanent teeth, and in children with mixed dentition, i.e. when a certain number of temporary teeth are retained in the oral cavity, but some permanent teeth have already erupted, the sum is used to determine the intensity of caries indexes (KPU+kp)
.
When comparing the two above-mentioned indicators of the prevalence and intensity of dental caries damage, the intensity indicator should be considered more accurate and reliable. For example, with equal 100% prevalence of children or adolescents at two different administrative points, the level of intensity of dental caries may differ by 1 1/2 - 2 times or more.
To study the dynamics of the development of the carious process in children’s teeth, a third indicator is used - the increase in intensity, which reflects the number of teeth affected by caries that reappeared a year after the initial examination and treatment of children by a dentist.
G.V. Baziyan (1973) developed a simplified method for determining a standardized indicator of the prevalence of dental caries in schoolchildren aged 7–15 years. To determine this indicator, it is necessary to sum up the partial coefficients [percentage of dental caries prevalence in each age group (from 7 to 15 years) of each of the cities (districts) studied, etc.] and divide the resulting amount into nine surveyed independent age groups (7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 years old). As a result, the arithmetic mean of the age-specific indicators is obtained.
These standardized coefficients for the prevalence of caries only in permanent teeth in schoolchildren aged 7–15 years make it possible to very accurately and clearly compare the prevalence of the caries process in the permanent teeth of a large group of schoolchildren in a number of administrative zones, since these indicators are calculated based on the identical age structure of those surveyed.
Pages:
1
See also
Assortment management in a pharmaceutical organization Today there are a huge number of companies on the market. Each of them is engaged in some type of activity - production, trade, services, etc. The consumer presents...
Lupus erythematosus and the deceased child of the patient Patient Sh.H suffering from lupus erythematosus, a chronic autoimmune disease of connective tissue and blood vessels, accompanied by redness of the facial skin and inflammation of the joints, as well as ...
Healthcare reforms in the Russian Federation The purpose of my course work is to analyze the healthcare system of the Russian Federation at the present time, its work, the implementation of assigned tasks, priority areas of development, research into the problems of functioning ...
General condition of the body
Previous and concomitant diseases affect the susceptibility of teeth to caries. Cases of the disease are often recorded in children who have suffered infectious disorders or have problems with the functioning of internal organs. The state of the immune system also affects the development of carious processes .
Oral hygiene and dental care are one of the important factors in the occurrence of caries. Regular use of modern preventive and hygiene products is an effective method of preventing dental caries.
Uneven cleaning leads to an increase in the incidence of caries. This disease affects teeth whose crowns have a complex anatomical shape, a large number of fissures, pits, etc. The frequency of distribution on individual teeth can be distributed as follows:
- first molars;
- second and third molars;
- premolars;
- upper incisors;
- lower incisors;
- fangs.
Analysis of the CPP index of cavities allows us to identify tooth surfaces that are more often susceptible to destruction. In permanent teeth, caries appears at the contact points of the teeth and in the cervical areas.
Caries is also characterized by symmetrical damage to teeth. This is due to the peculiarities of their anatomical design. Susceptibility is affected by damage to hard tissues, often resulting from other disorders, disruptions of the body, etc.
Intensity waxing and waning
The increase in caries activity is studied for each patient individually. Dentists examine how many healthy teeth have been affected by the disease over a certain period of time. Typically, the doctor examines the patient every two to three years, in case of sudden deterioration - every three to six months.
The increase in morbidity is the difference in the indicators of the PCI index between the last examination of the patient and the previous one. Thanks to these studies, the dentist can plan a treatment method and a method of prevention based on the needs of each patient.
Based on this, scientist T.F. Vinogradova identified three types of disease development activity, which can be found in the article “Classification of types of caries.”
If prevention and treatment help, the activity of caries lesions begins to weaken - the disease is reduced. This information is measured using the formula: ((Mk-M)/Mk))×100%.
Mk is the increase in the disease in patients before preventive and therapeutic work, M is the increase in the disease after undergoing dental procedures.
Method for determining reduction
Reduction means a decrease in the intensity of caries. For a certain group of patients, preventive and control measures are carried out. Dental fluoridation procedures are often used. After some time, the level of reduction is determined.
To do this, from the increase in the number of cases of the disease in the study group, you need to subtract the increase in the group in which the patients adhered to old bad habits.
In the presence of numerous carious formations and complications, sanitation of the oral cavity in a young child often has to be performed, guided by Tokarev’s manual.
This treatment does not eliminate the causes of the disease, so children often have to undergo repeated sanitation. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a suitable algorithm for the treatment and prevention of dental caries in young children.
KPU index.
It is a fairly informative indicator that allows one to judge the level of caries intensity. According to WHO recommendations, there are five levels of caries intensity: very low, low, medium, high and very high.
| Intensity index (IPU) | ||
| Caries level | in children 12 years old | in adults 35-44 years old |
| Very low | 0,0-1,1 | 0,2-1,5 |
| Short | 1,2-2,6 | 1,6-6,2 |
| Average | 2,7-4,4 | 6,3-12,7 |
| High | 4,5-6,5 | 12,8-16,2 |
| Very tall | 6.6 and above | 16.3 and above |
Sometimes, for a more complete and accurate assessment of the condition of the teeth, the CPP (cavity) index is calculated, which takes into account the number of carious cavities and fillings. Unlike the tooth index, the total number of carious cavities and fillings is calculated, regardless of the number of affected teeth. That is, if one tooth has three separate carious cavities, then in the CP index of teeth it is counted as one, and in the CP index (cavities) - as three units. This index is especially indicative at low intensity of caries damage.
Morbidity (increase in caries and its intensity) is the average number of new teeth affected by caries, which are determined over a certain period of time, based on one examined person. Typically, the increase in caries is determined after one year, and if the pathological process is active, after 6 months.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Tartar Remedy: professional and folk removal methods
Clinical examination
Patients undergoing treatment in dispensaries are divided into 4 subcategories according to the level of distribution of carious formations:
- Almost intact teeth.
- Mild carious process.
- Subcompensated caries.
- Decompensated disorder.
For subgroup 1, a scheduled annual examination is carried out. Category 2 patients are examined every six months. 3rd visits the dentist once every 3-4 months. 4th comes to the dentist every month.
Treatment of carious formations on teeth in young children involves difficulties. Today, dentists use the silvering method instead of traditional cleaning with a drill, since when treating children, doctors are faced with the following problems: increased salivation, frequent gag reflex, small volume of the oral cavity.
Children get tired quickly and cannot sit in the dental chair without moving for a long time. The silvering method has a significant number of disadvantages and is not used in a number of Western countries.