Histology of skin and hair follicles
Human skin is a complex organ that performs a huge number of different functions (bactericidal, secretory, protective, metabolic, immune, etc.).
The total weight of the skin and subcutaneous tissue is, on average, about sixteen percent of the total body weight. The thickness of the skin ranges from one to four millimeters. Skin thickness varies in different parts of the body.
Children's skin thickness is less than that of adults, so the clinical picture of dermatological diseases in children always has its own specific characteristics.
For reference. Most of the inflammatory processes develop in areas with thin skin (face, neck, chest, etc.) or a thick layer of subcutaneous fat (buttocks, abdomen).
Human skin is represented by three layers - epidermis, dermis and hypodermis (subcutaneous fat).
The epidermal layer of the skin also consists of 5 layers:
- basal, ensuring reliable adhesion of the epidermal layer to the dermis. When this adhesion is disrupted, detachment of the epidermis occurs (toxic necrolysis of Lyell, congenital pemphigus, etc.);
- the spinous layer, characterized by the greatest reactivity, since most of all pathological processes affecting the epidermis occur in it. The spaces between the cells of the layer are filled with lymph and tissue fluid, which is responsible for cellular nutrition and utilization of cellular metabolic products;
- granular layer containing keratohyalin, from which the horny substance of the skin is formed - keratin (sulfur is also involved in the formation of keratin). In young children this layer of skin is absent; in older children, the granular layer is thinner than in adults. In some pathologies (psoriasis), this layer is also absent, which leads to disruption of the full process of keratinization of the skin;
- stratum lucidum containing eleidin (precursor of keratin);
- stratum corneum, the outer epidermal layer that lacks blood vessels. The constant, physiological rejection of cells of the stratum corneum is manifested by the appearance of peeling and promotes the renewal of the skin.
The dermis is represented by two layers: the papillary layer, which is responsible for nutrition of the epidermal layer, and the reticular layer. The dermis includes cellular elements (mast cells, monocytic, lymphocytic cells, etc.) and fibers.
For reference. The dermis also contains a large number of vascular formations (blood and lymphatic), glands (sebaceous and sweat), nerve fibers, etc. In this regard, all true inflammations in the skin always affect the dermal layer.
The subcutaneous fat layer (hypodermal layer) consists of fat lobules separated by connective tissue fibers. When the pancreas is involved in the inflammatory process, predominantly diffuse phlegmons or abscesses develop.
The development of boils occurs when pathogenic bacteria (usually Staphylococcus aureus) enter the hair follicles.
A hair follicle consists of hair roots and surrounding root sheaths.
The main components of hair follicles are hair:
- papillae, consisting of connective tissue fibers and blood vessels;
- funnels in which hair roots turn into shafts. Also, the ducts of the sebaceous and, sometimes, sweat glands open into the hair funnel;
- muscles (responsible for raising hairs under the influence of psychogenic, temperature, etc. factors);
- root sheaths involved in hair growth.
For reference. As a rule, two or three sebaceous and sweat glands open into one follicle. In this regard, if the bactericidal properties of sebaceous secretions are violated, the sebaceous glands are blocked, hypersecretion of sebaceous secretions, etc., Staphylococcus aureus can enter the hair follicles, causing the development of ostiofolliculitis, folliculitis, sycosis, boils, etc.
In superficial staphyloderma, only the mouth of the hair follicle is affected. Deep staphyloderma (boil that undermines folliculitis) is accompanied by damage to the entire hair follicle with its subsequent destruction.
Normally, intact skin has a high level of nonspecific resistance to the effects of many opportunistic and pathogenic microorganisms due to the secretion of the sebaceous glands. Also, skin cells are able to destroy (lyse) pathogenic bacteria and fungi (natural bactericidal and fungicidal protection of the skin).
Attention. The protective functions of the skin are realized only if the acidic pH of the skin is maintained.
Home remedies
To speed up the healing of wounds in the mouth, you can use:
- Rinsing wounds with saline solution - 2 teaspoons per glass of warm boiled water.
- Treat the wounds with a solution of hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexidine. To prevent the infection from spreading, apply a separate cotton swab to each wound.
- Apply ice to relieve inflammation.
Traditional medicine recommends:
- Wipe the wounds with a mixture of milk (100 ml), yolk and honey (1 dessert spoon) using a finger wrapped in a bandage.
- Rinse your mouth with a decoction of calendula flowers (1 tablespoon per 200 ml of boiling water) every 2 hours.
- Rinse with a decoction of calendula, linden, chamomile, linden bark and calamus, pour 500 ml of boiling water over the mixture.
Carrot juice, horseradish, and horse sorrel help heal wounds.
Why are abscesses of the body and root of the tongue dangerous? The disease is accompanied by high fever, pain and other very unpleasant symptoms. The patient can only sit almost motionless, since the slightest movement causes sharp pain.
A strong increase in the volume of the tongue impairs the patient’s speech and can block breathing! Advanced stages are fraught with serious complications!
Why do boils appear?
Bacteria, more precisely staphylococci, are to blame for everything. They live on the skin of each of us and in most cases do not cause much trouble. However, under certain conditions, a violation of the peace treaty is possible.
With injuries, mechanical damage (for example, constant friction) or decreased skin immunity (it is caused by a variety of reasons: from vitamin deficiency to diabetes), staphylococci can penetrate the skin. Specifically, the hair follicle is the sac from which hairs grow.
In response to aggression, the body sends leukocytes—white blood cells—to the same pouch, whose task is to absorb and digest insolent microbes. By destroying the infection, the leukocytes themselves die - this is how pus is formed.
When dying, defenders release substances that cause a local inflammatory reaction. Therefore, the skin around the battlefield swells, turns red and becomes hot.
Causes of ulcers on the tongue
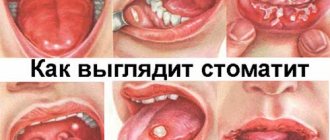
If sores appear on the tongue, this can be either an independent disease, the cause of which is, for example, mechanical damage to the mucous membrane, or a symptom of the pathology of any internal organ. Sores mean any atypical formations of various etiologies:
- pimples with watery or purulent contents;
- rash in the form of small blisters;
- ulcers and erosions;
- protruding cysts and seals.
In most cases, they do not pose a direct threat to the health and life of the patient. But they can cause a lot of discomfort in everyday life. If the ulcers are painful, a person cannot eat or talk, and sometimes it hurts even just to open his mouth. In addition, there is often bad breath and an unsightly coating on the tongue.
Diseases that often cause wounds, pimples and ulcers on the tongue:
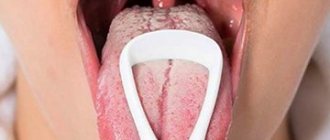
- Stomatitis of various natures is the most common cause of ulcers and rashes on the tongue. Aphthae look like small ulcers in diameter with a red bottom and rim, often covered with a white coating. Vesicular stomatitis manifests itself as small watery blisters, localized not only on the tongue, but also on the gums, cheeks, and sometimes palms and feet.
- Mechanical damage - biting the tongue, cuts with a knife or fork, injury from improperly installed dentures. In this case, the sore looks like a red abrasion, scratch, puncture or cut on the tongue, often with white edges (when the wound begins to heal).
- Infectious diseases. Tuberculosis, syphilis, chancroid - with all these serious diseases, a symptom such as the formation of sores on the tongue is often noted. They are usually crater-shaped, with a loose, bright red bottom and white edges. Purulent discharge may accumulate at the bottom.
- Vitamin deficiency often makes itself felt by various rashes on the tongue, painful spots and irregularities.
- Reduced immunity - in this case, the entire back of the tongue may be covered with red, painful wounds and ulcers.
- Cancerous formations - usually malignant cysts are located on the lateral parts of the tongue, very rarely on its tip and back. Visually, the sores look like rounded whitish or yellowish lumps protruding above the surface of the mucosa. As a rule, they are painful, secrete purulent or bloody contents, do not heal or dry out, and may increase in diameter.
The cause of the development of boils is Staphylococcus aureus; less commonly, the disease can be caused by opportunistic white Staphylococcus. The pathogen usually enters the hair follicle from the sebaceous glands.
However, it must be taken into account that staphylococci are a permanent component of the microflora of human skin.
Attention. White staphylococci are found in 100% of people and are part of healthy microflora. Staphylococcus aureus is constantly present on the skin of approximately forty percent of the population. And in most cases, in the absence of provoking factors, they do not cause an inflammatory process.
Risk factors contributing to the development of boils are:
- hormonal imbalances, excess androgens, endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus);
- skin contamination;
- contact with chemicals, industrial oils, resins, etc.;
- living in regions with an excessively humid climate;
- the presence of foci of chronic infection;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- improperly selected skin care;
- unhealthy diet (abuse of fast foods, alcohol, fatty foods, sweets, flour products, carbonated drinks, etc.);
- severe intestinal dysbiosis;
- frequent stress, depressive disorders, psychosis;
- overwork, chronic sleep deficiency;
- exhaustion, vitamin deficiency;
- the presence of scabies, pyoderma or fungal diseases of the skin;
- overweight;
- the presence of concomitant dermatoses (psoriasis, eczema, atopic dermatitis, neurodermatitis, etc.);
- long-term therapy with glucocorticosteroids, immunosuppressants, cytostatics;
- severe anemia;
- pregnancy (boils in pregnant women may be associated with decreased immunity, changes in hormonal levels, or the development of gestational diabetes mellitus);
- immunodeficiencies of various origins.
Diagnostics
https://youtu.be/cckZDjeiLG4
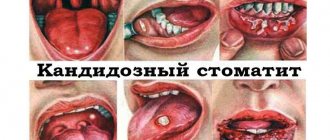
Aphthous stomatitis
The causes of aphthae in this type of stomatitis are decreased immunity and an acute lack of vitamins B and C. External signs of aphthae due to stomatitis are the appearance of ulcerative-type erosive formations on the tongue, palate and inner side of the cheeks.
These structures are characterized by a grayish-white color and a highly painful course of the disease, especially when eating salty and sour foods. Recurrent stomatitis of this type is characterized by a pink tint of the aphthae, a high probability of developing an abscess on the surface of the tongue and the appearance of pus on the tongue with a transparent color structure.
Other types of stomatitis
The herpes type of disease is distinguished by a white-pink type of ulcers formed, having clear contours and small sizes. Ulcerative stomatitis is formed when infection enters wounds and places of injury on the surface of the tongue, and is characterized by painful course and frequent bleeding.
Often the cause of the disease is bacterial stomatitis, as a result of which single ulcers are formed on the surface of the mucous membranes, the tubercles of which are covered with a layer of film, under which there is a site of damage that has a yellow-gray color.
Syphilis
First of all, the doctor asks everything from the patient. He is interested in the circumstances under which the tongue injury was sustained. Blood tests are then ordered. As a rule, with an abscess the level of leukocytes and ESR increases.
Diagnosis of the disease consists of examining and clarifying the circumstances under which the tongue injury was sustained. The doctor will prescribe a general blood test. With an abscess, leukocytes and ESR will be significantly elevated. To identify the pathogen, bacterial culture is performed.
X-ray examination is also indicated. The doctor’s task is to differentiate an abscess from similar pathologies and prescribe adequate treatment. Similar symptoms may appear with Ludwig's angina, lymphadenitis, and lymph node abscess.
READ MORE: Boil on the leg. How to treat a boil on the leg
The photo shows a lateral abscess on the tongue
The first visit is to a dermatologist. In many cases consultation is required:
- surgeon;
- endocrinologist;
- otolaryngologist;
- pulmonologist;
- gastroenterologist.
The diagnosis is made after a general examination. Additionally required:
- bacterial culture of the contents of the pustule;
- dermatoscopy of the affected area.
First of all, the doctor asks everything from the patient. He is interested in the circumstances under which the tongue injury was sustained. Blood tests are then ordered. As a rule, with an abscess the level of leukocytes and ESR increases.
Why is a boil dangerous?
The hair follicle is closely connected with blood vessels. If you damage them carelessly (for example, by trying to squeeze out pus from an immature boil, where leukocytes have not yet defeated the microbes), bacteria can enter the bloodstream. And this is fraught with blood poisoning.
Together with the blood, microbes enter the internal organs, which is why they begin to malfunction.
Boils on the face, neck or scalp are especially dangerous in this regard. The infection quickly enters the brain and can lead to meningitis, cerebral vein thrombosis and other extremely unpleasant conditions.
Tongue abscess: causes, symptoms, differential diagnosis, treatment
A tongue abscess is an inflammation that forms in the thickness of the tongue with the formation of an abscess. This is a rather serious pathology, accompanied by elevated body temperature, general malaise, and difficulty eating and speaking. How dangerous is this disease? What causes it? How to treat?
To get answers to these and other questions related to this pathology, you need to familiarize yourself with the clinical picture of the disease, its symptoms and signs.
Features of the development of boils
The formation of boils occurs in three stages: infiltration, abscess formation and resolution.
At the stage of infiltration with a boil, the appearance of limited hyperemia (inflammatory redness) and slight swelling is noted. The pain of the inflammatory infiltrate at the infiltration stage is moderate.
Within one to two days, an inflammatory nodule forms around the hair follicle. Unlike ostiofolliculitis or folliculitis, the node with a boil is large, and the tissue around it is noticeably swollen. As the disease progresses, the rim of hyperemia, swelling, and severe pain appear.
The abscess formation stage of boils is accompanied by the appearance of highly specific symptoms of suppuration and necrosis (the appearance of a necrotic core is a mandatory symptom of a boil).
For reference. The process of spontaneous purulent melting of tissue begins by the third or fourth day of illness. The opening of the boil is carried out precisely at this stage.
The surgeon must open the boil. Squeezing boils is strictly prohibited.
A boil on the lip, chin or nasolabial fold is the most dangerous, as it can be complicated by thrombosis of the cavernous sinus, meningitis, sepsis, brain abscess, etc.
Attention. If the boil has opened on its own, after the purulent contents have drained, it is necessary to treat the resulting defect and the skin around it with hydrogen peroxide. It is impossible to press on an opened boil to speed up the discharge of pus.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WFA7Shgczsg
If the necrotic core (purulent core with hair remains) has come away along with pus, the resulting defect is treated with chlorhexidine. Next, a bandage with levomikol, etc. can be applied.
Treatment of boils in the area of the nasolabial triangle should be carried out only by a surgeon. Such boils are called malignant, due to the high risk of developing severe complications.
For reference. Before the “era of antibiotics,” the mortality rate from complications after malignant boils reached 65%.
After opening the abscess boil, a bleeding ulcer occurs. Subsequently, the bottom of the ulcer is lined with granulation tissue. Swelling, hyperemia and tissue tenderness quickly decrease.
The stage of boil resolution is manifested by gradual healing of wounds (usually within two weeks) with the formation of a hypotrophic scar (pit).
Boils in women and men proceed in the same way. The disease can affect any part of the body except the palmar and plantar surfaces. Depending on the location of the boil, some specific features of the inflammatory process may be noted.
Most often, boils appear on the skin of the face and back. In areas with a large amount of subcutaneous fat, the boil can quickly reach large sizes, due to the involvement of the loose base in the inflammatory process and the formation of massive infiltrates.
A boil in the nose can be accompanied by severe pain, swelling of the nostrils and impaired nasal breathing (due to the blocking of the nasal passage with an inflammatory infiltrate).
For reference. A boil in the ear is characterized by a sharp, throbbing pain that radiates to the lower jaw and temple. The pain may intensify during chewing.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H1yN4m3MUz8
A furuncle under the armpit rarely develops; as a rule, in the armpits the inflammatory process occurs as hidradenitis. In addition to the formation of a specific inflammatory infiltrate, the symptoms of the disease will be severe pain, aggravated by moving the hand.
Attention: Boils in intimate areas are most often associated with shaving these areas, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, or the patient having sexually transmitted diseases.
A boil in a child most often develops on the face or nose. In children under 12 years of age, boils are extremely rare, usually with severe concomitant staphyloderma.
Prognosis of inflammation of the root of the tongue
Abscesses of the body and root of the tongue in the mouth should not be neglected; the success of treatment directly depends on a timely visit to the doctor. Cure occurs within 14 days if the disease is not advanced and adequate treatment is provided. Otherwise, serious complications may occur.
A very dangerous complication is phlegmon. This purulent inflammation of fatty tissue quickly spreads into the surrounding tissues, muscles, and tendons. Difficult to treat. Mediastinitis is inflammation of the mediastinum. Sepsis (“blood poisoning”) – infection of the body, infection entering the blood. In such cases, there is a serious threat to life.
How to treat a boil at home
As was said, there is no need to peel off the sore, much less squeeze out the abscess and cauterize it with an alcohol solution. Thus, a banal irritation from a fish bone or a displaced tooth crown can be turned into an inflamed, giant fistula in the tongue.
To quickly get rid of a sore, you need to establish the cause that triggered its development. Until it is eliminated, the sore will not disappear.
- Syphilis, tuberculosis and other infectious diseases are treated comprehensively with drugs of various actions. Usually, as the main illness is cured, its symptoms also go away – including ulcers and pimples on the tongue. Additionally, to reduce discomfort and speed up the healing process, it is recommended to lubricate them with antiseptic solutions or ointments.
- Thrush or herpes are treated with special antiviral and antibacterial drugs. These are Acyclovir, Zovirax, Chlorhexidine, Chlorophyllipt, Miramistin, Givalex.
- In case of vitamin deficiency, to prevent inflammation of wounds, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with decoctions of medicinal herbs, be sure to take vitamin complexes and adjust your diet, enriching it with fresh fruits and vegetables. If iron deficiency anemia is diagnosed, you should eat meat, fish, liver, eggs, various greens, and buckwheat.
- Wounds caused by mechanical damage, with normal immunity, quickly heal on their own. To avoid initiation, you can rinse your mouth with a soda solution, unsweetened green tea or chamomile decoction after each meal. The ointment with the freezing effect Kamistad will help reduce pain.
- With reduced immunity, you need to ensure proper nutrition, a stable daily routine with mandatory walks in the fresh air, and avoid hypothermia, overwork and stress. The course of taking immunomodulators in this case lasts at least 2-3 months. If the cause of the sores is an exacerbation of a chronic disease, appropriate therapy is prescribed.
If cancer is suspected, therapy is prescribed only after a comprehensive examination. Cysts and benign formations are most often removed using liquid nitrogen. The tissues are first cauterized, after which after some period of time they die and peel off. For malignant tumors, treatment tactics are always selected on an individual basis.
Nothing better. If you have a boil, the most thoughtful solution would be to go to a doctor - a therapist, dermatologist or surgeon. The specialist will examine the abscess, assess its location and size, analyze your state of health and, based on the results, give recommendations on how best to treat the boil specifically for you. These are the recommendations that you will need to diligently follow at home.
If you have not yet seen a doctor, home treatment can only consist of the following:
- Use warm compresses. They will help reduce pain and speed up the maturation of the boil. Gently apply gauze soaked in warm water 3-4 times a day for 15 minutes.
- Apply antiseptic ointments with a pulling effect to the boil: ichthyol, heparin, synthomycin (which one to choose, it is better to consult a doctor)
- If the boil opens on its own, thoroughly wash the wound with antibacterial soap, then treat it with any antiseptic - possibly alcohol-based. Apply an ointment with a local antibacterial effect, such as levomekol or tetracycline, and apply a bandage. Wash the wound with warm water 2-3 times a day and apply warm compresses until it heals.
Prognosis and prevention
How successful the therapy will be depends on the condition in which the person was admitted to the hospital. With timely treatment, the prognosis is very favorable - the disease can be cured in two weeks. When the pathology is significantly advanced, it all ends with mediastinitis, phlegmon, and sepsis. In these cases, there is a threat to life.
Remember, it is easier to prevent such complications than to treat them. Therefore, do not forget about oral hygiene, be careful not to injure the mucous membrane. If you notice pain, discomfort, or your condition is deteriorating sharply, you should not sit and wait for improvement, immediately go to a specialist.
Pay close attention to your health. Very often, an accidentally bitten tongue causes a lot of discomfort.
When such a nuisance happens to you, immediately buy an antiseptic solution and rinse your mouth. You will also have to give up hot, salty, spicy foods for a while.
A diet is required that includes soups, thin cereals, jelly, weak tea and other products that do not irritate the oral mucosa. But you will have to categorically give up coffee and alcohol.
Be healthy.
When you need to see a doctor urgently
If you have any of the following symptoms in addition to a boil, seek medical help immediately:
- Fever (body temperature rises above 38.5 °C).
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- The skin around the boil is distinctly red and hot, and the diameter of the inflammation exceeds 2–3 cm and is growing.
- The pain becomes too strong, you cannot forget about it.
- New boils appear.
These symptoms indicate that the infection has entered the blood. To prevent the consequences from becoming dire, it is necessary to start taking antibiotics as soon as possible. Only a doctor can select them.
Also, special medical attention is required for people whose boils develop due to diabetes, problems with the cardiovascular system, iron deficiency anemia, any problems in the immune system, or taking drugs that suppress the immune system. In this case, the body's defenses may not be enough to defeat the infection on its own. Therefore, you will most likely need additional therapy.
Treatment of an inflamed tongue
Treatment of uvulitis consists of eliminating the underlying disease that caused it. After conducting the necessary examination of the patient, the doctor prescribes treatment with various medications.
Medications
Medicines for the treatment of an inflamed uvula:
| Antibiotics | Anti-inflammatory sprays | Antihistamines | Diuretics |
| Flemoxin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. The active ingredient is amoxicillin trihydrate. | Hexoral - contains hexethidine as an active ingredient. The drug has a wide spectrum of antibacterial and antimicrobial effects. | Cetrin. The active ingredient of the drug is cetirizine hydrochloride. Has an antiallergic effect. Does not cause sedation. | Lasix is a fast-acting diuretic drug. The active ingredient is furosemide. |
| Macropen - has a bacteriostatic and bactericidal effect. The active ingredient is midecamycin. | Bioparox - the active ingredient of the drug is fusafungin. Local antibiotic. Has antibacterial and antimicrobial activity. | Tavegil. The drug contains the active ingredient clemastine hydrofumarate. Has antiallergic and antipruritic effects. | Indapamide. The active ingredient is indapamide. Has a mild diuretic effect. |
For ease of use, each package of drugs includes instructions. With its help you can easily calculate the required dose of medication. The prices of these drugs vary, so everyone can choose an affordable drug.
Traditional medicine recipes
If a small tongue in the throat is inflamed, how else can this disease be treated, besides the use of medications? Traditional medicine recipes can be used as additional treatment. But only after agreement with the attending physician.
The good thing about these recipes is that you can make them yourself from ingredients that are available to everyone. They are quite effective and easy to make.
Here are a few such recipes:
- Crush one hundred grams of garlic. Pour 150 milliliters of boiled water into the mixture. Leave for five hours. Strain and gargle three times a day.
- Boil fifty grams of dried viburnum fruits in a liter of water. Cool. Gargle with warm broth as often as possible.
- Pour two tablespoons of onion peel into 700 ml of water. Boil for five minutes. Cool and gargle up to five times daily.
If you find yourself with inflammation of the tongue in your throat, treatment should begin as quickly as possible. Otherwise, all the symptoms will appear more and more intense.
Only an experienced specialist can conduct the necessary examination and prescribe the correct therapy. Self-medication can lead to serious complications and sometimes death.
The throat is part of both the respiratory system and the digestive tract. Various microorganisms constantly pass through it and enter along with food or air. Various dental diseases can also cause pain in the throat. But everyone knows what to do if you have a slight sore throat. However, what needs to be done during the inflammatory process should be discussed.
Furuncle - symptoms
Important. The main symptom of the disease is the appearance of a painful purulent cone-shaped infiltrate with a black dot in the center (purulent-necrotic core).
There is swelling and hyperemia around the purulent infiltrate. The greatest swelling is observed with boils on the face.
There is also an increase in regional lymph nodes. The inflammatory infiltrate is sharply painful. At the stage of abscess formation it may be characterized by the appearance of throbbing pain.
The general condition of patients with a single boil is rarely impaired. Increased temperature, fever and symptoms of intoxication are observed with boils involving a large amount of subcutaneous fat or with complicated “malignant” boils.
Attention. The development of complications most often occurs with boils on the face in the “triangle of death.” Symptoms of the development of complications are purple skin around the boil, the appearance of fever, headaches, weakness, drowsiness, and the appearance of dense swelling spreading to the entire half of the face.
With timely treatment, the purulent infiltrate can dry out without entering the abscess stage. It is also possible to develop dry boils, accompanied by the formation of a slight purulent infiltrate and a minimal risk of complications.
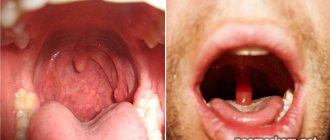
Symptoms and signs of uvulitis
What characteristic signs and symptoms can be used to identify uvulitis? It should be understood that many symptoms are similar to diseases such as laryngitis, tonsillitis (tonsillitis), cervical lymphadenitis, laryngotracheitis.
- Redness, swelling and an increase in the size of the uvula are the main symptoms indicating uvulitis.
- Temperature increase.
- “Lump in the throat” - a feeling that there is a foreign object in the throat.
- Weakness.
- Pain in muscles and joints.
- Difficulty breathing occurs due to an enlarged uvula, which blocks the nasopharynx.
- Pain when swallowing saliva or food.
- The uvula sags towards the base of the tongue.
- Inability to pronounce certain sounds.
- Vomiting attacks without subsequent regurgitation.
- Increased salivation.
- Possible appearance of ulcers or white formations on the uvula.
- Skin rash, cough, itchy throat, lacrimation, runny nose due to the allergic nature of uvulitis.
The nature of the disease is rapidly progressive and developing. It manifests itself very clearly, which cannot be attributed to a slight malaise. Prompt treatment should be started, since the uvula gradually increases in size, closing the airways, which can lead to asphyxia.