Caries is the most common disease in the world, which is a pathological process of destruction of hard dental tissues due to a number of unfavorable factors. This dental problem, depending on the stage of the disease, is treated with a variety of methods - both innovative and gentle, and conservative, often very painful for the patient. How to prevent the development of caries and reduce the risks of its occurrence in the long term? You can read about this and much more below.
How to identify caries?
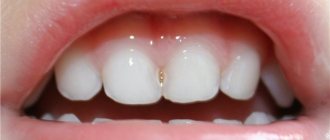
The simplicity and reliability of determining caries very much depends on the stage of its development, as well as the localization of foci of destruction on the dentition. At home, at the stage of a carious spot, when the pathology is located in the cervical, rib or root zone, it is almost impossible to visually notice the disease. Only a clear outer location on the visible part of the enamel suggests the presence of a small area of chalky color.
During the transition from the basic stage to classic superficial caries, the affected area acquires a more pronounced whitish tint, while the localization loses its shine compared to the rest of the enamel - active demineralization and destruction of the outer layer of the tooth begins, which is still focal. Over time, the diseased tooth begins to react to too cold, hot, sour, sweet foods and drinks, forming a temporary pain syndrome.
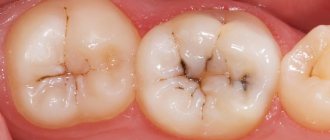
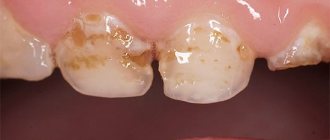
In medium and deep forms of the disease, the pathology is visible to the naked eye - these are darkening, holes and black cavities, partial tooth destruction, etc.
A particularly important stage in the effective fight against caries is considered to be the earliest possible diagnosis of the problem - only an experienced dentist can carry it out properly, through both a thorough visual examination using a special mirror and instrumental research techniques. Most often in modern dentistry, the following is used to solve this problem:
- Radiography. A photograph of the internal structure of the dentition and surrounding areas gives, with correct interpretation, a clear and unambiguous picture of the development of caries and the exact localization of lesions;
- Coloring. A simple method performed in a regular dental office. The procedure is carried out using fuchsin or methylene blue - areas of superficial damage to the enamel change their color;
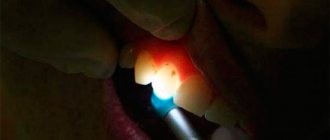
- Transluminescence. Illumination of the inside of the dentition using a powerful light source. Allows you to detect internal and hidden forms of caries inside the tooth;
- Cold thermal diagnostics and drying of the enamel surface. Two alternative methods involve treating potential affected areas with a cold reagent or drying them, respectively. In the first case, the patient will feel a slight pain syndrome, while in the second, the area of potential destruction loses its shine. Both methods are suitable for identifying superficial or medium caries, including in hard-to-reach places.
How can you stop caries at the spot stage?
The first stage, in which only a small light spot forms on the enamel, is the most favorable from the point of view of treatment prognosis. At an early stage of caries, it is possible to cure it without painkilling injections, preparation of the carious cavity, or filling.
How to stop caries is decided by the dentist in each specific case, but today there are several possible non-invasive methods.
- Remineralization of enamel.
Caries begins when tooth enamel loses minerals, loses its strength and cannot effectively protect the deep tissues of the tooth from the acid produced by bacteria. Remineralizing therapy is aimed at restoring the balanced composition of the enamel, strengthening its structure, and returning its strength and protective characteristics. The essence of the method is that the dentist alternately applies compositions containing phosphorus, calcium and other useful substances to the cleaned tooth surface. Another way is to attach special trays with remineralizing gel to the teeth.
- Fluoridation.
Using this method, you can increase the strength of enamel, its resistance to acid, eliminate microdamage, and reduce the pain reaction to cold/hot. Saturation of dental tissues with fluoride ions helps to achieve this effect. A simple or deep fluoridation procedure is possible. In the first case, the dentist uses fluoride varnishes or fluoride gels. They are applied to the teeth using trays or cover the surface of the enamel with a brush. In deep fluoridation, compounds are used to seal tooth enamel. The teeth are first cleaned, dried, isolated from saliva, deep fluoride is applied to them, dried again, and then treated with copper-calcium hydroxide. With this method, a fluoride-containing substance penetrates deeply into the pores of tooth enamel and helps preserve calcium.
- Infiltration method.
Another method will stop the development of caries at the spot stage without drilling and filling, and will prevent the formation of a carious cavity. First, the dentist treats the carious stain with a special etching composition; the next step is to apply a liquid composition to the cleaned, washed and dried surface to seal the pores of the tooth. The infiltration method helps stop the spread of the carious process, since the acid produced by bacteria cannot penetrate the sealed pores of the enamel and continue the destructive process. The method is completely safe, painless and suitable even for children over three years old. This treatment is usually not performed on a younger child, because during the procedure you need to sit still for about 20 minutes, which is not possible for small children.
In addition to the listed methods, ozone therapy and laser therapy are used today, which also help stop the carious process without tooth preparation. If a hole has already formed, then the only way to stop caries is surgical treatment. Using a drill, the doctor removes the affected tissue, prepares the cavity for filling and installs the filling there layer by layer, returning the tooth to its natural anatomical shape.
Prevention of caries in adults
Adult men and women who do not have serious chronic diseases are offered a full range of possible preventive measures aimed at counteracting the possible manifestation of caries.
Comprehensive prevention usually includes the elimination of a potentially dangerous cariogenic situation, as well as a significant increase in disease resistance of all structures of the oral cavity, both generally and locally.
Main activities include:
- Systemic oral care using toothpaste/powder, rinsing solutions, threads, etc.;
- Refusal of bad habits that can indirectly provoke caries - smoking and alcohol;
- Using special sugar-free chewing gum based on xylitol, which additionally cleanses the oral cavity;
- Significant correction of the daily diet with the exclusion of foods rich in sugar and simple carbohydrates from the diet;
- Dental methods for the prevention of caries - fluoridation and sealing of fissures with polymer compositions;
- Regular preventive examinations at the dentist, at least once every six months. Mandatory treatment of any non-carious diseases, pathologies and dental problems.
Features of caries
Before considering how dental caries can be prevented, it is important to say that it is not always possible to independently identify this disease, because the pathology can be localized in places that are difficult for the human eye to reach. Only a dentist can detect it most accurately during a professional examination.
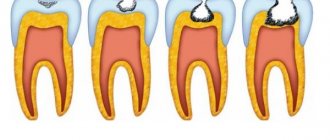
Advanced caries threatens the development of pulpitis.
Caries can be of different neglect, forms of progression (acute, chronic), as well as localization. In addition, dentists distinguish superficial, medium and deep types of this pathology, each of which is accompanied by its own characteristic signs.
The following are the most common symptoms that indicate the onset and progression of this disease:
- Increased sensitivity of teeth, which is expressed in discomfort and pain when exposed to chemical, thermal and other types of irritants.
- A change in the color of the affected enamel, which can range from pale yellow to dark brown.
- Loss of the natural shine of the tooth enamel surface (tooth clouding).
- Increased enamel fragility and roughness.
- The appearance of bad breath.
Important! When identifying the first signs of this disease, a person needs to immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment, otherwise the pathology will begin to progress and affect healthy teeth, thereby becoming a threat to the entire area of the hard tissues of the oral cavity.
Prevention of caries in children
Children from one to 14 years of age are at a special risk group for caries - as modern medical statistics show, it is they who most often quickly acquire this pathology, and the carious process itself on milk teeth develops rapidly - sometimes the transition period from the stain stage to deep damage to dentin takes just a few months.
When to start the first preventive measures? Dentists recommend paying attention to the potential risk after the baby’s first teeth erupt.
Where to begin? To begin with, introduce drugs with a high calcium content into the child’s diet, adjusting the diet in parallel, limiting the consumption of products based on simple carbohydrates as much as possible. Chips, carbonated water, inexpensive candies, industrial baked goods - all this negatively affects the condition of a child’s teeth. Be sure to include milk, cottage cheese, hard cheeses in your diet, and don’t forget about vitamins - it’s advisable to keep fruits that are not very sweet, and in the autumn-winter period it becomes mandatory to take vitamin-mineral complexes.
Almost every child does not like brushing their teeth too much - try to organize this monotonous process in a playful way, carefully monitoring the brushing time (it should not be less than 3-4 minutes). Teach your child the correct treatment of the cavity with manipulation of all parts/elements of the dentition.
As an addition, for children over 5 years old, regular rinsing of the mouth with fluoridated water is allowed - this will speed up the process of natural mineralization of enamel and protect not too resistant milk teeth from the potential negative effects of bacteria.
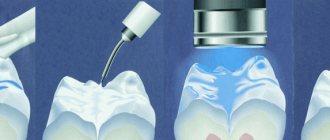
A fundamental method of combating caries in children is non-invasive fissure sealing. It is on the chewing surfaces that teeth are most susceptible to caries, since food debris enters small spaces and microflora actively multiplies. The procedure itself consists of a number of stages:
- Complete cleaning of the dentition and oral cavity from any remaining food and plaque, as well as drying;
- Fixation and isolation of the treated teeth from the penetration of saliva;
- Application of orthophosphoric acid solutions to working surfaces;
- Washing the oral cavity and dentition;
- Drying the surfaces to be treated and applying a special sealant to them;
- Crystallization and hardening of the applied material using a photopolymerization lamp;
- Removing unnecessary residues, grinding, cleaning the cavity from dirt.
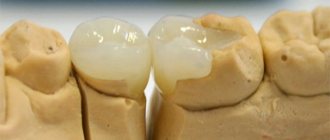
Sealing practice
Fissure cavities are uneven channels on the surface of teeth that are most often affected by caries. This happens due to the accumulation of food in such fissures, which provokes the activity of pathogenic bacteria.
With the help of professional fissure sealing, the doctor will be able to protect them from germs and also saturate the enamel with fluoride.
This is what the result of fissure sealing looks like.
This method of prevention can be practiced only in the absence of caries on the teeth. Otherwise, the doctor must first fix the problem and place a filling, and only then carry out the sealing.
Prevention of caries in pregnant women
Prevention of caries in the fair sex during pregnancy has a double meaning - first of all, a woman’s teeth, which are losing their resistance due to changes in hormonal levels and a lack of essential minerals/vitamins, are protected from potential carious processes, and preventive measures are also taken to reducing the risk of developing pathology in the unborn child during the antenatal period.
The basic principles include the following:
- Regular oral hygiene as carefully as possible;
- A proper diet with the exclusion of simple carbohydrates, as well as a significant increase in products containing calcium and fluoride - these are dairy and fermented milk dishes, vegetables, fish, unsweetened fruits;
- Mandatory cleaning of teeth from plaque and tartar at the dentist;
- Intensive intake of vitamin and mineral complexes;
- Carrying out therapy and rehabilitation of carious teeth as quickly as possible, even at the initial stage of the disease;
- Regular dental examinations;
- Timely treatment of any third-party acute and chronic diseases, especially gastrointestinal pathologies.
Exogenous prevention
It is mostly associated with external factors and includes the use of hygiene products for oral care. These can be toothbrushes, rinses, toothpastes and flosses for cleaning the spaces between the teeth. This is what the next conversation will be about.
Toothbrushes. According to the experiments conducted, scientists concluded that removing plaque with a toothbrush is considered an excellent prevention of caries. When choosing it, you need to correctly focus on one of the types of this “tool” of hygiene, because they can be soft, normal hardness and hard. If the patient has completely healthy teeth and gums, then you can use a hard brush. When there are problems with the gums and when their users are small children, it is recommended to brush the teeth with a soft one. A brush with medium hardness is generally considered optimal for most cases.
The size of the brush should be such that it does not overlap more than three teeth - this is approximately two and a half to three and a half centimeters in length. The beams should be different in length and arranged in an x-shape - then this will be considered an ideal version of this device. The head should have a flexible connection, and the handles should be such that pressure can be adjusted, thereby preventing damage to the gums and enamel.
The brush cannot be used for more than three months, since during this time it is already very mechanically worn out and is no longer able to effectively rid teeth of plaque. In addition, a huge number of microorganisms begin to accumulate in the bristles.
Toothpastes. A good product for cleaning teeth and refreshing the oral cavity. First of all, when choosing it, you need to pay attention to whether it is intended to strengthen tooth enamel and prevent caries. As a rule, such toothpastes contain many useful substances that will help prevent dental disease. This number must include the following elements:
- fluorine;
- calcium;
- phosphorus;
- enzymes that help delay the appearance of plaque
- and others.
Very popular not only in the country, but also abroad, are toothpastes that contain fluorides such as fluoride ions. By enriching the enamel of teeth, they are able to form fluorapatite, which is a solid compound of a lattice of enamel crystals. This compound significantly strengthens teeth from the effects of microorganism acids and significantly reduces the occurrence of caries.
For example, for adult patients, such toothpastes are well suited for the prevention of caries, which contain all the necessary substances:
President Classic. In addition to sodium fluoride and xylitol, it also contains extracts of various herbs, such as sage, lemon balm and chamomile. It has an excellent effect in preventing caries and relieves gum inflammation.
Silca. There are several types of pastes (Herbal Complete and Natural Extracte) that contain sodium fluoride, but they differ in the herbal additives. Excellent means of preventing caries and relieving inflammation.
Elmex Protection against caries. By the name you can already determine the purpose of this toothpaste. It can be used every day, since the paste contains amino fluorides and does not contain components intended for use in courses due to the ability of microorganisms to adapt to them, for example, antiseptics, enzymes and antibiotics.
Methods and types of caries prevention
Modern medicine knows many methods and types of caries prevention. Their effectiveness in most cases is determined by a number of factors - from genetic predisposition to pathology to external influence. Basically, all activities can be divided into two large groups - endogenous (general) and exogenous prevention.
Endogenous (general) prevention of caries
It is the prevention of caries through general health improvement and increasing the body's resistance.
In turn, it is divided into prevention with medications and non-drug measures. Drug-free endogenous prevention is carried out in two directions.
- Rational balanced nutrition. The main task is to exclude from the daily diet foods rich in simple carbohydrates and sugar. It is these components in the oral cavity that create optimal conditions for the start of carious processes, especially in childhood. Along the way, it is necessary to control the intake of all necessary proteins, complex carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, amino acids and microelements into the body. You need to eat more unsweetened fruits and vegetables, meat, seafood and fish rich in fluoride, as well as dairy and fermented milk products containing natural calcium;
- Physical exercise. General strengthening of the body is impossible without moderate physical activity. Morning exercises, rest breaks during working hours, evening jogging, comprehensive hardening - all this forms the prerequisites for optimal body resistance to any disease, including caries.
Drug endogenous prophylaxis is carried out strictly under medical supervision. The dentist prescribes optimal doses of medications taking into account age, the current state of the body, and the presence of concomitant chronic and acute diseases.
Typical representatives:
- Calcemin, calcium glycerophosphate;
- Phytaftor, sodium fluoride;
- Fish fat;
- Natural spectrum immunomodulators - echinacea, eleutherococcus;
- Vitamins of groups D and B.
Exogenous (local) prevention of caries
By the term “exogenous caries prevention,” dentists mean local methods of preventing dental caries. Despite the high effectiveness of a systematic approach to reducing the risk of carious processes, due to economic, technical and physiological reasons, as well as the characteristics of the body, there is a need for additional direct treatment of the oral cavity and dentition.
Two main areas of exogenous prevention include oral hygiene and the use of direct-acting special means:
- Remineralization complexes;
- Fissure-sealing sealants;
- Fluorine-containing products for topical use in the form of pastes, varnishes, solutions, gels.
As modern medical statistics show, the trend towards a decrease in the incidence of caries diagnosis in developing countries is associated with the beginning of the total use of fluoride-containing pastes - about 90 percent of such products on the market contain this substance. Also, an important contribution is made by the use of additional hygienic oral devices - sugar-free chewing gum based on xylitol, organic and synthetic means of removing plaque from the enamel, under which carious processes are formed, and the increasing interest of the population in professional methods of cleaning the oral cavity in the dental office.
What is non-invasive fissure sealing?
This procedure is a fundamental method of combating carious lesions in baby teeth. It includes several stages:
- Comprehensive cleaning of teeth and oral cavity.
- Drying.
- Isolation of teeth from saliva.
- Then special solutions of orthophosphoric acid are applied.
- The oral cavity is thoroughly washed.
- The treated surfaces are dried.
- Then a layer of sealant is applied.
- The material hardens under the influence of a photopolymerization lamp.
- The teeth are polished and dirt is removed.
The procedure is aimed at reducing the risk of caries development on baby teeth.
Means for caries prevention
Any methods will not help get rid of the risk of caries if you do not use highly effective means to carry out basic activities. First of all, these include toothpastes - the most affordable consumer goods.
Modern toothpaste almost always contains fluoride compounds (fluoride). When this product is used correctly (using at least 2 times a day, 3 minutes of intensive cleaning of the entire dentition and adjacent areas), the risk of carious processes is reduced by 40 percent.
Prevention of caries with fluoride (fluoride)
Another effective method of local counteraction to the possible manifestation of caries is considered to be the treatment of teeth with fluoride compounds. This remedy is especially relevant for children over 5 years of age during the maturation of tooth enamel.
- Rinsing. A 0.025 percent solution of sodium fluoride in an amount of 10 milliliters is used. Rinse 3 times a day for 1 minute after brushing your teeth with toothpaste;
- Applications. The surface of the dentition is cleaned of dirt and plaque, dried and cotton swabs soaked in 0.2 percent sodium fluoride are applied. Keep the “compress” for about 3 minutes, then remove. Drinking and eating after the procedure is allowed for at least 2 hours. The course of preventive therapy lasts 5–7 days.
Drugs
Other typical drugs used as a means of preventing caries, modern dentists include:
- Fluoride varnish. A combined product of sodium fluoride, fir balsam, shellac, chloroform and ethyl alcohol. It has antimicrobial activity and saturates the enamel with essential ions. Used 4 times a year at the stages of regular sanitation of the oral cavity when visiting a dentist;
- Belagel. Organic topical treatment based on amino fluorides. In the form of a gel and special chemical activity, fluoride compounds stay on tooth enamel better and longer, inhibiting the potential formation of plaques and carious stains. Used once a week for six months. Reduces the risk of caries formation by 70 percent;
- Remodent. Multicomponent highly effective remineralizing preventive agent. Contains calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, potassium, sodium, chlorine, manganese, iron, zinc, copper and other trace elements adapted for local use and absorption. Significantly increases the resistance of the dentition to any carious destructive processes. Most often, a 3 percent solution is used for rinsing (at least 1 minute, 2 times a day), as well as applications using cotton swabs (for 15 minutes, a total course of 30 applications);
- Strontium chloride. A 25 percent aqueous solution of the substance is rubbed into dried tooth enamel. There are only 2 procedures, each of which is carried out after 2 days. Repeat prophylaxis - once every 6 months;
- Kaltsinova. Chewable tablets based on calcium, phosphates and a vitamin complex. The rate of consumption is 3 tablets per day for 3 doses in between meals, they must be chewed thoroughly, distributed evenly throughout the oral cavity;
- Sealants. They are used to seal fissures and radically prevent caries in children over 8 years of age and adults. Typical preparations are zinc chloride, silver nitrate, vitacryl, aluminosilicate polyacrylic, carbondent, silar, alphacom. There are both self-hardening and hardening under the influence of ultraviolet light, the sealing procedure is carried out only in a dental clinic.
Oral hygiene
The basic basis for local caries prevention, regardless of any circumstances, is comprehensive proper oral hygiene. It is in this localization that all carious pathologies begin and develop, and the disease itself originates under plaque and the action of the natural microflora of the mouth and teeth.
Basic hygiene techniques:
- Brushing your teeth with a brush and toothpaste. Every day, 3 times a day, as thoroughly as possible;
- Using dental floss. This device allows you to get rid of food debris between teeth and in hard-to-reach places. Recommended for use at least once a day;
- Rinse solutions. Used after brushing with toothpaste and floss, they contain antiseptic and antimicrobial components. Regular use is recommended at least 2 times a day for 3–5 minutes;
- Using sugar-free chewing gum with xylitol as a supplement between basic dental cleanings;
- Professional cleaning at the dentist. Getting rid of stubborn plaque or tartar at home is quite difficult. Contact your dentist on a regular basis, who will be able to carry out a comprehensive deep cleaning procedure using instrumental and innovative techniques - from an irrigator, Air Flow and laser treatment, to ultrasound and classical conservative dental techniques.
Quite often, people who think they practice oral hygiene on a regular basis still develop tooth decay. Why is this happening? Most often, the cause is banal errors during procedures, which constantly increase the risk of carious processes. The most famous and typical:
- Insufficient cleaning time. Complete oral care involves daily procedures, preferably 3 times a day for 3–5 minutes. Many people devote only a minute to this process, sometimes even less, which does not adequately provide local protection against caries;
- Incorrect cleaning technique. The correct technique is thorough “sweeping.” The dentition of the upper jaw is cleared towards the bottom, the lower - vice versa. Attention must be paid to the lateral, internal and posterior surfaces, as well as areas of direct contact when chewing. In addition to brushing your teeth, you should also brush your gums and tongue;
- Replacement of tools. Rinsing, chewing gum, and flossing are not replacement procedures, but rather complementary procedures to classic teeth cleaning. Under any circumstances, the brush and toothpaste should remain the basis;
- Wrong choice of tools. A high-quality brush should suit your hardness and be synthetic. In addition, it is necessary to select the correct size of the working head - a tip 2 teeth wide is considered ideal. Once every 3 months, do not forget to change the main cleaning tool, store it in a dry place with the head up and do not pour boiling water over it - the product should be washed with warm water after the procedures;
- Features of the paste. The paste must be of high quality, contain fluoride, and be approved by local health organizations. Pay attention to the expiration date of this product, do not use too much or too little material (the best option for an adult is a volume the size of a large pea).
Proper dental care -
Unfortunately, all people understand the term “good oral hygiene” differently, believing that everything is fine with their hygiene, and that all dental problems are to blame (hereinafter on the list) - water, bad heredity, pregnancy, etc. . Below we have described in detail for you how often and how to brush your teeth correctly, as well as what hygiene products are best to use.
How many times a day should you brush your teeth?
Most people know that they need to brush their teeth twice a day. Everything is correct, but this is only the minimum value. Normally, teeth are brushed after every meal, i.e. 3 times a day. If you are afraid that your colleagues at work will call you a cleaner if they see you brushing your teeth in the toilet during your lunch break, then you need to make a choice - between clean teeth, the absence of caries and bad breath, and the respect of dirty-toothed colleagues.
If a toothbrush and toothpaste at work are unacceptable to you, then the minimum amount of hygiene that will allow you to remain homo sapiens is dental floss + chewing gum. The most important thing in this combination is the use of dental floss, because... food gets stuck between the teeth (and we are not talking about stuck pieces of meat, but about soft food residues, which cause much more damage to the teeth, because they consist of quickly digestible carbohydrates and therefore are most quickly processed by bacteria into acid).
Diet – effective prevention of dental caries is impossible without following a diet. For example, it is very good if you brush your teeth 3 times a day after each main meal. But, if you decide to eat chocolate, cookies, sweets, nuts between main meals... the carbohydrates stick to your teeth again and bacteria immediately begin to convert them into acid. Therefore, all snacks should be eaten at the end of the main meal, and after that, immediately brush your teeth.
It is the wrong diet and frequent snacking on cookies and other carbohydrates that are the root cause of caries in children (this also applies to sugary drinks - juices, soda, liquid mixtures). Children often develop so-called bottle caries, which affects almost all teeth (when parents, to prevent the child from crying, give him a bottle of formula for the whole night or day). And without solving the problem with diet, no prevention of caries in children is simply possible.
If you are asking yourself how to get rid of caries at home, then following the recommendations of this article can almost completely save you from the appearance of new foci of caries. It's up to your willpower and motivation, because sometimes you are too lazy to get up and go straight away to brush your teeth, or finally start regularly using dental floss after every meal.
Proper hygiene scheme -
After each meal, you need to follow the following sequence: 1) flossing, 2) brushing with a toothbrush and toothpaste. If you don’t have toothpaste and a brush, you should always have dental floss and chewing gum with you. Floss will remove food debris, and chewing gum works by stimulating salivation (saliva has a certain buffering capacity that neutralizes acids in the mouth).
It is very important not only how to brush your teeth, but also when to do it. In the morning, it is best to brush your teeth after breakfast (for people with a lot of plaque and carious teeth, this can be unpleasant, so it is recommended for such patients to brush their teeth both before and after breakfast). As for all other oral hygiene sessions, teeth should be brushed within the first 5 minutes after eating.
Using dental floss –
Let's be honest - without dental floss there can be no talk of good hygiene. What do you think: why is the most common location of caries in the interdental spaces? Precisely because food debris gets stuck there, which cannot be removed by any fancy toothbrush models or even irrigators. If the instructions for a brush or an advertisement tell you that it perfectly cleans the spaces between teeth, this is all untrue and is only a publicity stunt. And this equally applies to electric, ultrasonic, and other models of brushes and attachments for them.
It is very important that you understand the following - you should use dental floss not only when you feel that a piece of meat is stuck in your teeth. After eating, so much soft sticky food debris accumulates in the interdental spaces that will not cause you any concern, but it is they (and not pieces of meat) that are the root cause of caries, because... Such food residues consist predominantly of carbohydrates that are easily digestible by bacteria.
Dental floss should be used after every meal, cleaning absolutely all dental spaces. This usually takes about 1 minute, but at the beginning (while you learn to use it) it may take longer. The thread should always be in your pocket or purse. You can use it at a party, in the restroom of a restaurant, or even just on the street. Everything will depend only on your desire to have clean teeth and a pleasant breath.
How to use dental floss correctly: video
→ Types of dental floss, and which one is better
If there are bridges on the teeth, braces -
In the presence of braces and bridges in the oral cavity, conditions are created for the retention of food debris. In the presence of bridges, food is stuffed, as a rule, under the intermediate part of the bridge, which imitates the missing tooth. Therefore, for good hygiene, an ordinary toothbrush and paste, as well as dental floss, will no longer be enough in this case (24stoma.ru).
Special devices called irrigators are designed for these purposes. Such devices deliver under pressure a thin pulsating stream of water, saturated with air microbubbles, with the help of which food debris and microbial plaque are washed away (Fig. 6). Irrigators are also indicated for patients with chronic gum inflammation, because... They also allow you to wash periodontal pockets using special nozzles.
Important: any caries you develop, even a single one, is an indicator that there are defects in your hygiene. You must understand that there is no norm for the formation of a certain number of caries lesions per year. Normally, there should be no caries at all, and if it appears, then this is a question of how correctly you brush your teeth, how regularly, whether you are familiar with dental floss, and also how correct your diet is.
When caries develops, microbial plaque and food debris remain at the edge of the corner. Adequate oral hygiene allows complete removal of both. Predisposing factors, of course, also exist. For example, a low concentration of lysozyme in saliva (this is an enzyme that inhibits the growth of plaque) is of a genetic nature, but this factor is only secondary for the development of caries.
Or the buffering capacity of saliva is too low, which does not effectively neutralize acid in the mouth. This usually occurs in patients who consume too many carbohydrates. In patients with a balanced and protein diet, the buffer capacity of saliva is always normal. Those. here again questions about your diet. Often drinking wine or fruit juices (acid), sweet soda (carbohydrates) - all this also leads to demineralization of teeth and increases the risk of caries.
Preventing caries at home
What can be done to prevent caries at home, in addition to classic teeth brushing, correcting your diet, taking vitamin-mineral complexes and immunomodulators, and using floss? Most often these are folk remedies.
It should be understood that conservative medicine does not recognize “traditional methods” as an effective and reliable concept of prevention, although a number of recipes under certain circumstances can help counteract the development of carious processes if they are used as a supplement to the main approved methods. Before using any of the methods described below, be sure to consult with your dentist.
- Sage tincture. Take 1 teaspoon of medicinal sage purchased at the pharmacy, pour a glass of boiling water over it and let it brew for an hour. Strain the product and regularly, 3 times a day between meals, rinse your mouth with it for 3 minutes;
- Propolis applications. Propolis perfectly removes plaque and strengthens enamel. Take a sufficient amount of it, wrap it in gauze and apply it to plaque-covered teeth for 30 minutes. 1 procedure before bed is enough;
- Collection of herbs. Take 1 spoon each of chamomile, St. John's wort and calendula herbs. Brew in 0.5 liters of boiling water and let steep for 15 minutes. Strain and rinse your mouth several times a day after meals;
- Cabbage. Be sure to eat raw white cabbage and, if possible, drink cabbage juice - this remedy strengthens dentin and enamel, and stops carious processes.
Nutrition rules
The following dietary recommendations can help reduce the risk of caries:
- Minimizing the consumption of sweets. It is better to replace them with honey and dried fruits. If you cannot completely give up your favorite treats, then after each use you must rinse your mouth and brush your teeth.
- Reduce consumption of sugary carbonated drinks.
- Enrich your diet with fermented milk products such as kefir, cheese and cottage cheese.
- Regularly consume fresh vegetables and fruits, especially apples, which act as a natural enamel cleaner.
- It is useful to eat fresh greens and nuts.
- It is important to avoid eating excessively hot or cold food, as it can injure the enamel and cause discomfort in a person.
- Additionally, you should take vitamin complexes.
- Several times a week it is important to eat fish and seafood that are rich in phosphorus.
The diet should include fermented milk products.
You should be especially careful when eating solid foods, which can easily cause enamel chipping or get stuck deep between teeth, thereby causing a buildup of bacteria and inflammation.
Nutrition to protect against caries
A proper diet is one of the important components of endogenous caries prevention in people of any age. It is the daily diet, if it is poorly chosen, that can provoke the formation of plaque and create an optimal environment for the growth of bacteria in the oral cavity, which, in the presence of a large amount of simple carbohydrates, produce organic acids that negatively affect the enamel.
What should you give up? First of all, limit as much as possible the consumption of sweet black tea and coffee, chips, salted peanuts, crackers, muffins, donuts, milk chocolate and other products that provoke the formation of plaque and contain a large amount of simple carbohydrates.
Add dairy and fermented milk products, vegetables and unsweetened fruits, as well as all types of meat to your daily diet. Eat a balanced diet (equal proportions of proteins, fats and complex carbohydrates), in small portions, at least 5-6 times a day. Try not to pass it on at night and, if possible, brush your teeth after each meal. If this is not possible, use sugar-free chewing gum with xylitol from time to time and rinse with fluoride-based antiseptic solutions (but do not replace brushing your teeth with them on an ongoing basis).
Oral hygiene
Insufficient oral hygiene is considered one of the most common causes of caries. This is justified by the fact that in this state, a huge amount of bacteria and food debris accumulate on a person’s teeth and gums, which negatively affect the condition of the enamel and spoil it.
Preventing this process through hygiene involves following these tips:
- You need to brush your teeth at least twice a day: morning and evening.
- The process of cleaning your teeth should be quite long - at least three minutes. It is also important to not only brush your teeth, but also your tongue, gums and the inside of your cheeks.
- For additional antibacterial treatment, dentists recommend using special mouth rinses.
- If it is not possible to brush your teeth after eating meat dishes, you should definitely use dental floss to remove any remaining food in the area between your teeth.
- Brushing your teeth should be done in a thorough circular motion. At the same time, it is important to make movements away from the gums so that plaque and microbes do not penetrate into the area of soft subgingival pockets.
Good hygiene is one of the components of caries prevention.
The most suitable for home prevention of dental damage are pastes with a high fluoride content. They will effectively strengthen the enamel and make it less susceptible to penetration by pathogenic bacteria.
If it is difficult for a person to choose a cleaning paste for himself, he can contact his supervising dentist with this question, who will recommend the most suitable option for his patient.
As for mouth rinses, experts advise using those products that do not contain ethanol.
Important! Due to the ability of caries to destroy the root of the tooth, the disease can lead to the entry of bacteria into it, which in turn can easily provoke inflammation, periodontitis, and neoplasms.