anonymous, Male, 35 years old
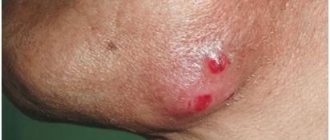
Hello. I am 35 years old. Bad habits include smoking. About two weeks ago, a burning sensation appeared on the left side of the throat in the area of the tonsil and palatine arch, or behind the tonsil on the wall of the pharynx; it is difficult to determine the exact location. There was pain there when swallowing food and saliva. There was no temperature. There was general weakness, pain in the head area above the temple on the same left side (highly localized pounding and aching pain). Something like a lump or bump about 1.5 mm in size appeared on the left tonsil, the same color as the tonsil. I don’t know whether it appeared at the same time as all these symptoms or whether it was there before. I haven’t examined my throat for almost a year. My left amygdala was healthier compared to my right. The right tonsil has been almost twice as large as the left for many years and has also been covered with tubercles since school. But it didn’t cause me much discomfort. The left tonsil is still smaller than the right one as before and the tubercle seems to be the same as on the right one, but the pain when swallowing and the burning sensation made me a little worried about this. In November 2014, I had a sore throat in the same place on the left for more than a month, no fever, general weakness, terrible dry mouth, and there was bloody discharge from the left nostril. There was no lump on the tonsil then. I visited three ENT specialists. A diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis and chronic pharyngitis was made. The treatment didn't help. The fourth ENT diagnosed rhinotonsillitis and chronic pharyngitis, and directed me to take a smear from the throat. Culture showed the presence of Staphylococcus aureus in the throat above normal. He was treated with bacteriophages and antibiotics. After two months of treatment, I finally returned to normal. Regarding the fact that the pain when swallowing began two weeks ago, now at the moment the pain has become much duller. There is no pain when swallowing or eating. But there was a feeling of numbness on the left side of the throat. Not strong but you can feel it. There is also a slight numbness of the skin on the left and right neck and on the back of the head. My hands are a little numb (the left one is more) in general, as I wrote above, I’ve been sick for two weeks now. For eight days there was pain and burning when swallowing, severe weakness and fatigue. For the last three or four days there has been no pain when swallowing and the feeling of weakness has gone away much. But there was a feeling of numbness. I didn’t take any treatment or take any medications. I hoped that it would go away on its own. I would really like to know your opinion, dear experts. Could it be pharyngitis or tonsillitis that I am suffering from, symptoms such as numbness like inside the throat on the left. And that there could be that tubercle on the tonsil. Could he be the cause of everything? Or is this again a manifestation of that Staphylococcus aureus? All sorts of thoughts come into my head. Thanks in advance.
The feeling of numbness has nothing to do with chronic throat problems. Therefore, it makes sense to consult a neurologist. Asymmetry and tubercles of the lymphoid tissue of the palatine tonsils often occur in completely healthy people. Don't pay attention to this! And staphylococcus, I am sure, has nothing to do with your current problems. In general, there is no such thing as a sterile oral cavity and pharynx!
anonymously
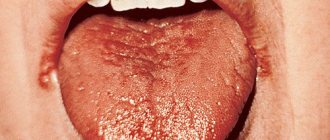
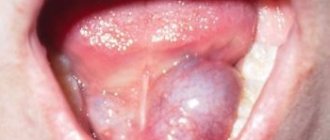
Male 36 years old. Hello dear Viktor Nikolaevich. Thank you very much for your answer. Yesterday I wanted to ask your opinion regarding some other problems related to the throat, but apparently my question was not accepted. I will try again to find out your opinion on one more issue. As I wrote in the previous question, about three weeks ago there was pain and burning in the area of the left tonsil, some kind of tubercle formed on the left tonsil, and pain appeared when swallowing. After two weeks the pain went away. The lump is still there. Now is the actual question. Yesterday, minor pain, not even pain, but discomfort in the left tonsil area reappeared, especially when eating solid food. What’s strange, but yesterday, while examining my throat, I noticed that the right tonsil had increased, although it was twice as large as the left one for many years, but now it has increased by about a centimeter, maybe more, but not in volume, but somehow in length, downwards. And it seems to have increased over the last two days. The tonsil became somewhat square and elongated. At the same time, I don’t feel any pain or discomfort on the right side of the tonsil at all, it’s just visually enlarged. I also forgot to write last time that at the very beginning of the pain on the left in the tonsil area, a yellowish or maybe light brown coating appeared on the tongue. It was especially pronounced on the left side of the tongue where the tonsil actually hurt. Now at the moment there is a coating all over the language. Do you think that, for example, an inflammatory process (if there is one) in the left tonsil can have such an effect on the right one, thereby enlarging it? And why the pain in the left tonsil again appeared slightly when swallowing. Is this normal? I'm very afraid of cancer. I read all sorts of symptoms on the Internet. Thanks in advance. Attached is a photo.
anonymously
Good afternoon 2 months ago, for a moment, my swallowing movements disappeared, as if the root of my tongue was numb, it scared me very much, but somehow it all went away and didn’t happen again for 3 weeks, then again, I had a headache all day and by the evening I felt again, that at some point I couldn’t swallow and my arms and legs began to go numb, as if I was losing myself. I got scared again, almost to the point of panic, my blood pressure rose to 140*100, I called an ambulance and went to the hospital. The therapist looked at me, talked, and said that no one except a psychotherapist could help me, don’t go to a neurologist. I immediately started doing massages at home for the head, neck, chest, and entire spine. I went to see a manual osteopath twice, and he said that he had removed a small blockage in the back of the head and in the chest. After a home massage, every evening different things happened to me: my lingual muscles hurt, I couldn’t eat, my throat was very choked a couple of times, then there were different vibrations in my throat. I also associate this with the fact that I am an alarmist, and I begin to get scared of everything. I took valeriac for a month, tenoten for 20 days, now my general condition is abnormal. I'm afraid to wake up in the morning, I'm afraid that it will become bad. I was also prescribed Grandoxin? - but I’m afraid to take it, there are side effects that block breathing - what if it gets blocked? Moreover, no one can tell me what exactly is wrong with me. I am 29 years old, I had a CT scan of the cervical spine, subluxation of C1, protrusion of C3C6 up to 2 mm. Now I’m injecting ALFLUTOP, so far I’ve done it 10 times, but my spine seems to be settled. I went to the ENT specialist and everything was fine. I still can’t get to the neurosurgeon - I have a question about C1, is there any pinching. Sometimes I sit at work and at some point my body goes numb, as if I don’t belong to myself, I feel like I’m either going to fall, lose myself, or even die. What is this? I must say that there were a lot of stressful situations during the current period. last year, some of them don’t leave my mind at all, and when I remember them, I feel really bad again. Maybe, really, see a psychotherapist?
anonymously
I saw an ENT doctor and everything was fine, but I went to see a neurosurgeon; they didn’t even prescribe an MRI of my head, they said that I was healthy (the question was about C1 subluxation; CT showed it, so the neurologist referred me to a neurosurgeon). I visited a psychotherapist, diagnosed with prolonged depression, prescribed Teraligen according to the regimen, Cipralex - long-term 10 mg. *1 per day. I’m afraid to take medications, I don’t know how the body will work further. Now I just feel physically ill, I don’t even know how to describe it, there’s a tightness in my chest all the time, or emptiness, palpitations, panic, my arms and legs feel incomprehensible inside, in general, the general condition is no lightness in the body, I’m constantly monitoring I tried to breathe a couple of times, so as not to lose my breath, and I almost died from fear. Something is wrong with me. And the other day I looked at my hands and thought, are they mine? I asked the psychotherapist if I was going crazy, he said that everything is fine, I’m healthy, I definitely won’t leave my mother’s side, because I’m strong, but nevertheless I’ve driven myself crazy. It already seems to me that I have all the diseases at the same time and that I am simply dying. My only wish is to go to bed quickly, because this is the only time when I feel good. As soon as I wake up, I’m afraid that it’s going to get bad. At night I wake up - I suddenly open my eyes - and I can’t fall back asleep, because I know that the alarm clock will ring soon, thank God that this happens soon after waking up, otherwise I would go crazy if I didn’t sleep at night. For 2 months I began to eat poorly - I just don’t want to, I quickly cram in as much as I can, because I’m afraid that food will cause a poor general condition of the body. I lost 7 kg - I dreamed about it, but not in this way. I was 57, now I’m 50. I’m 29 years old, I have a small child, 4 years old. I don’t want to do anything - neither cook nor play with the child - because I don’t feel well, I really like to knit, now even this makes me feel bad, it doesn’t calm me down at all, on the contrary, my husband says it’s all because of cervical osteochondrosis, the doctors answer -there is no such diagnosis. Answer me about the drugs. I understand that this is medical ethics, but I need to know WHAT could happen to me if I take them. It’s just that I’ve already felt bad a couple of times from Dramamine - maybe not from it, but against its background, although I took it more than once, many times - I’m very afraid of flying on an airplane, due to the fact that on the first flight in my life it was crazy I was sick of fear, to the point where I thought I was going to die!
If the tongue or lips go numb, this is not a disease, but only a symptom of the manifestation of some disease in the human body. Moreover, numbness can manifest itself in different ways:
- some feel like goosebumps running on their tongue;
- others feel a slight tingling sensation;
- Still others do not feel anything with their tongue - there is a dullness or absence of tactile and taste sensations.
All these signs indicate that it is time to undergo examination by specialists in order to identify the disease and overcome it.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Why does tongue numbness occur? There are a number of reasons that can cause this symptom:
- Visiting the dentist to have a tooth removed. Nowadays, such a procedure cannot be done without an anesthetic: the doctor gives an injection into the patient’s gum, and after a few minutes everything in the mouth goes numb. The duration of this effect lasts for half an hour to an hour (depending on the dose of the anesthetic). If the dentist has pressed or damaged the nerve of the tongue, its sensitivity is dulled, and numbness can last for a week, a month or even more. In this case, we recommend visiting a neurologist so that he can conduct a full diagnosis of the body and prescribe appropriate treatment.
- Iron deficiency anemia is a low level of hemoglobin (red blood cells) in the blood, as well as a decrease in the number of red blood cells.
- Diabetes mellitus, as well as endocrine diseases associated with a decrease in the hormone insulin in the human body. Such diseases indicate a violation of hydrocarbon, protein, fat, water-salt and mineral metabolism.
- Treatment with antibiotics or other drugs. This is the most harmless cause of tongue numbness. As soon as the use of antibiotics is stopped, the sensitivity of the tongue returns to normal. Advice: if such side effects have been observed, then be sure to tell the attending physician who prescribed this type of medication about it.
- The specific structure of the skull, which provokes compression of the IX pair of cranial nerves (glossopharyngeal nerve). In this case, surgery is necessary.
- Osteocondritis of the spine. It has been noted that damage to the intervertebral discs and cartilage leads to a number of diseases accompanied by pain and numbness in certain areas of the body. Cervical osteochondrosis can cause numbness of the tongue, dizziness, headaches, etc. This disease is quite common among people of all ages, even among young people who spend an excessive amount of time at their desks.
- Cardiovascular diseases, including stroke.
- Burns while drinking a hot drink (tea, coffee). In this case, not the entire tongue may become numb, but only its tip.
- Laryngeal cancer, which causes numbness in the throat, tongue, entire mouth and even the face. This disease often affects people who smoke for a long time.
Causes of the phenomenon
Reasons why the upper palate becomes numb:
- Severe stress;
- Eating food that is too hot, causing a burn to the oral mucosa, which leads to short-term paresthesia;
- Chronic fatigue;
- Poisoning with alcohol or toxic substances;
- Installation of dentures, which can interfere with the functioning of the palate if the procedure is performed incorrectly;
- Injuries, damage to the spinal or cranial nerves;
- Surgery to remove wisdom teeth.
Paresthesia of the palate area is caused by diseases - hypertension, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, inflammation of the tonsils, damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve.
↑
Take the Attention Test! Find 10 differences! (click right here!)
Diagnostic and treatment methods
Having felt numbness of the tongue, the question immediately arises, what to do? The best decision is to seek help from a specialist at the clinic. Consultation required:
- therapist;
- dentist;
- gastroenterologist;
- neurologist;
- nutritionist.
The attending physician will examine you, collect anamnesis, as well as information about previous diseases. He will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis to identify the causes of the pathology and prescribe treatment.
Often the patient:
- donates blood for analysis to exclude or confirm the presence of diabetes;
- examines the cardiovascular system;
- undergoes examination of the cranial nerves (glossopharyngeal and vagus);
- performs magnetic resonance and ultrasound diagnostics.
Instrumental methods for diagnosing this disease:
- Ultrasound diagnostics using a special ultrasonic emitter;
- Magnetic resonance imaging is performed to identify pathologies of the brain and spinal cord, which provoke paresthesia of the tongue.
Having determined the cause of the disease, the specialist prescribes:
- complex of vitamins;
- a number of medicines;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- diet.
So, if the patient:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia, then vitamins and minerals are prescribed to improve blood circulation;
- cervical osteochondrosis, it is recommended to undergo a course of special exercises and therapeutic massage;
- laryngeal cancer – surgical and medical treatment;
- neurology of the trigeminal nerve, damage to the nerves of the oral cavity and throat - medications, physiotherapeutic procedures and/or surgery in the form of pulsed currents, surgery, acupuncture, laser puncture are prescribed.
Traditional treatment methods include the following:
- meditation and yoga;
- Apply a cotton swab dipped in warm sea buckthorn oil to your tongue;
- Roll a clove of garlic in your mouth with your tongue, lightly biting it. The procedure should be done 10 minutes after meals 3 times a day, always at night;
- a strict diet excluding spicy, sour, salty and fried foods; period - 2-3 months.
- rinse your mouth daily with a tincture of oak bark and a small amount of honey.
In conclusion, I would like to note that self-medication of tongue numbness is unacceptable! Therefore, alternative treatment should be carried out only as a complement to the treatment prescribed by a specialist.
In the practice of an otolaryngologist, one hears both quite common complaints and not quite common ones. The latter may include a feeling as if the throat is numb. This situation can cause a lot of anxiety for patients, and you need to find out what is causing it.
Numbness is a type of sensory disorder, medically called paresthesia. It can occur in any area of the body where there are corresponding nerve receptors, including the oral cavity, pharynx and larynx. The reasons for this phenomenon are local or systemic in nature. The former are often associated with the following processes:
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane.
- Allergic reaction.
- Traumatic injury.
- Tumor lesion.
It is impossible not to mention the influence of external factors on sensitivity. Numbness in the throat may appear after eating spicy food, taking certain medications, or local anesthesia (at an appointment with a dentist or ENT doctor). But there are also general disorders in which paresthesia of the tongue and pharynx appears:
- Deficiency of vitamins and minerals (cyanocobalamin, iron).
- Neurological problems (transient ischemic attack, stroke).
- Endocrine pathology (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism).
- Diseases of the cervical spine (osteochondrosis, hernia).
- Psychogenic disorders (neuroses, depression).
As you can see, the causes of numbness in the throat are very diverse: from a local inflammatory process to a general disease. And each situation requires an individual approach to determine the origin of unpleasant symptoms.
Why numbness of the tongue or throat occurs will become clear only from the results of a comprehensive examination, which is impossible without the participation of a doctor.
The palate in the mouth goes numb: reasons, upper, what makes it numb
The palate in the mouth becomes numb because a number of provoking factors arise: from taking certain medications to injuries and vitamin deficiency. Sometimes an additional symptom occurs - the tongue goes numb. Numbness requires seeing a doctor.
Loading... Use search Are you having a problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease.
↑
Reasons why the upper palate becomes numb:
Source: https://GidPain.ru/nemeet/nebo-rtu-prichiny.html
Symptoms
Each pathological process has its own clinical picture, and clarifying it is the primary task of the doctor when a patient seeks medical help. From complaints and anamnestic data I receive subjective information about the disease. It is important to note the characteristics of the symptom called numbness:
- Where is it located?
- Disturbs constantly or periodically.
- Is it related to any factors (colds, emotional stress, local anesthesia, taking certain foods, medications, etc.).
The doctor details the complaints and purposefully identifies additional symptoms that the patient could simply not pay attention to. And after the interview, a physical examination is carried out, including inspection, palpation and other methods (percussion, auscultation).
Inflammatory pathology
A feeling of numbness may occur in patients suffering from chronic inflammatory diseases: pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis. In such cases there will be other symptoms:
- Sore throat and sore throat.
- Dry cough.
- Hoarseness of voice.
Upon examination, signs of inflammation are visible - swollen and reddened mucosa. Plaques are noticeable on loose tonsils with tonsillitis, and the palatine arches are compacted. The atrophic process is accompanied by thinning of the epithelium, through which the vessels are visible.
Allergic reaction
Numbness of the throat is one of the symptoms of stenosing laryngotracheitis (false croup), which can appear as a reaction of the body to an allergen. In other words, the laryngeal mucosa swells, and the lumen of the airways narrows, which causes ventilation problems. Then the clinical picture will have the following signs:
- Barking cough.
- Stridorous breathing.
- Inspiratory dyspnea.
At the same time, other allergy symptoms may appear in the form of itching in the throat, hives, watery eyes, and nasal congestion. A severe hypersensitivity reaction is accompanied by anaphylaxis with vascular insufficiency (shock).
Having noticed the first signs of an allergy, there is no time to waste, because there is a risk of serious consequences.
Injuries
A feeling as if the tongue or throat has become numb can occur after injuries or operations that damage the fibers that innervate them. In such situations, most likely, we are talking about open injuries with a violation of the integrity of the nerve conductors. Additional signs may include pain, including when swallowing, bleeding, hematoma and swelling, and difficulty breathing.
Tumors
Oncological processes that destroy soft tissues are another local reason that may cause numbness of the tongue or pharynx. Clinical symptoms are determined by the size of the primary lesion, its location and degree of malignancy. Signs of a tumor include:
- Intense pain radiating to the ear, nose, neck.
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia).
- Feeling of a foreign body in the throat.
- Voice change (dysphonia).
- Bad breath.
- Ear congestion.
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
If the tumor grows into the bones of the skull, pain in the jaw and teeth and double vision occur. As tissue disintegrates, purulent discharge and severe nosebleeds appear.
Neurological disorders
Acute cerebrovascular accidents are a dangerous condition in which tongue numbness is likely. But this feeling usually extends to one half of the body. Hemiparesis is also accompanied by a weakening of muscle strength in the arm and leg, decreased sensitivity, speech disorders (dysarthria), and disorders of consciousness (from stupor to coma). It all depends on the area affected by ischemia or hemorrhage. In most cases, the patient's condition is serious and requires outside help and care.
Spinal diseases
A feeling of numbness in the hands and throat can occur with diseases of the cervical spine, when the corresponding nerve root is pinched or irritated. A similar symptom is characteristic of osteochondrosis or intervertebral hernia. At the same time, other signs attract attention:
- Pain in the neck of a shooting or aching nature, radiating to the head or shoulder.
- Limitation of mobility.
- Spasm of the paravertebral muscles.
- Soreness of the root exit points.
Damage to the cervical spine is sometimes accompanied by vertebral artery syndrome, when patients experience dizziness, noise in the head, and even short-term loss of consciousness (drop attacks). All this is associated with compression of the corresponding vessel and a decrease in cerebral blood flow.
Pathology of the spinal column can also provoke sensory disturbances in the throat area, which is associated with an effect on the nerve roots of the cervical spine.
Vitamin and mineral deficiency
Profile of the State and the Restoration of the World
The symptoms in question may appear with deficiency anemia, when the body does not have enough iron or vitamin B12. Then most patients note a perversion of taste, dry mouth and tingling of the tongue, a feeling of a foreign body and a sore throat. A detailed study reveals systemic problems:
- Dry skin.
- Hair fragility and loss.
- Flattening, separation of nails.
- Weakness and fatigue.
- Burning and itching in the vagina in women.
- Drowsiness and dizziness.
- Decreased attention and ability to work.
Atrophic changes affect not only the tongue, but also other parts of the digestive canal, which causes esophagitis or gastritis. These symptoms are associated with a decrease in iron in the blood and tissues (anemic and sideropenic syndromes).
Psychological problems
The feeling that there is a “lump” in the throat and the tongue is numb often appears with neurotic disorders or depression. Such disorders are functional in nature and are accompanied by polymorphic symptoms, which can masquerade as various somatic pathologies:
- Pain in different parts of the body (headache, heart, abdominal, joint).
- Cardiopalmus.
- Dizziness.
- Dyspnea.
- Skin itching.
- Anxiety and emotional lability.
- Decreased mood and irritability.
- Eating disorders (bulimia, anorexia), etc.
Taking this into account, many patients consult doctors for a long time, but they do not find organic pathology, considering them to be malingerers. However, with a targeted study of the psychological sphere, the diagnosis is not in doubt.
Causes of numb throat
Discomfort in the form of numbness cannot be causeless. There is something that causes this symptom. Doctors identify many factors that can lead to it. In most cases, such throat problems occur due to the following reasons:
- Received throat injuries.
- Infection with a bacterial or viral infection.
- Eating too spicy food.
- The development of spinal diseases that affect the cervical spine.
- The appearance of an allergic reaction to an irritating factor.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- The development of a cancerous tumor in the larynx.
A person can also experience such discomfort due to a lack of certain microelements in the body. In this case we are talking about iron and vitamin B12. Quite often, this kind of ailment worries pregnant women who carry a child for more than 15 weeks. A deviation can be identified by checking the functioning of the thyroid gland, as well as studying the results of certain tests.
If numbness occurs in the oral cavity, then you need to first try to figure out what contributed to this. It is possible that discomfort is just one of the symptoms of sore throat, a fairly common infectious pathology that affects the throat. It is usually caused by pathogenic bacteria that end up on the mucous membrane of the affected area.
Statistics show that infectious diseases most often cause numbness in different parts of the oral cavity. Another common cause of the development of the pathological process is various injuries.
People who have a cold often complain of throat discomfort. This is because it primarily affects the organs of the nasopharynx. Numbness spreads to almost the entire area of the oral cavity. If you bite your tongue in this state, the pain will not be severe.
With colds, there is no point in trying to treat an unpleasant symptom separately. It is necessary to fight the reason that caused it. After recovery, the numbness will completely disappear.
Other factors that lead to a strange symptom are constant stress, nervous disorders and lack of sleep. Therefore, it is encountered by people who forget about proper sleep and rest, and also do not try to avoid stressful situations in their lives.
With such disorders, numbness in the oral cavity can be a periodic phenomenon or constant. A light neck massage will help quickly solve the problem in this case. It also wouldn't hurt to drink a glass of warm water. These measures will help relieve tension. If numbness occurs too often and nothing helps get rid of it, then the person will have to consult a neurologist.
Infections caused by bacteria are not always to blame for throat discomfort. It is not so rare that this happens because of the food that a person eats. Certain foods cause not only numbness, but also constriction in the larynx. Also, a person may begin to feel as if there is a lump in his throat that he cannot get rid of.
An unpleasant symptom develops due to food that contains too many different spices . Unfortunately, even if you drink a large amount of water after eating, you are unlikely to get rid of the problem. You will just need to wait until the mucous membrane, which was undoubtedly burned by spicy dishes, heals and is completely restored.
The throat is numb due to allergies. But in this case, the person will be disturbed by other signs of malaise that are characteristic of this painful condition. With numbness, skin rashes and itching will occur. Redness of the body and face, as well as swelling of the tongue, are possible.
To accurately understand whether an allergy caused discomfort, it is necessary to remember whether the patient ate, drank, or simply came into contact with a product or object unfamiliar to him recently.
There are also more dangerous factors that lead to numbness in the oral cavity. We are talking about the following diseases:
- Vascular dysfunction.
- Stroke.
- Vegetovascular dystonia.
- Malignant processes.
Studying the entire clinical picture of the disease, as well as standard diagnostics in the hospital, will help to accurately diagnose the patient and understand what exactly led to the development of the symptom.
Additional diagnostics
The origin of the symptoms is determined on the basis of a comprehensive diagnosis. As a rule, a clinical examination alone is not enough, so the doctor, taking into account its results, will refer the patient to laboratory and instrumental procedures:
- General blood and urine tests.
- Biochemical analysis (indicators of inflammation, coagulogram, immunoglobulins, iron, cyanocobalamin, etc.).
- Analysis of pharyngeal mucus (cytology, culture).
- Allergy tests.
- Pharyngoscopy.
- X-ray of the cervical spine.
- Tomography of the head.
- Rheoencephalography.
- Cerebral angiography.
- Tumor biopsy with histology.
Having received a complete picture of the pathology and knowing its causes, it becomes possible to establish a final diagnosis. And this, in turn, allows you to begin treatment that will relieve the patient of unpleasant symptoms.
Neuroses form a huge group of diseases that are psychogenic in nature. Laryngeal neurosis is one of the varieties of this type of pathology, which in most cases is reversible, but may require long-term treatment. It is worth taking a closer look at the symptoms, signs and causes of the disease in order to seek help as quickly as possible and bring your health back to normal.
Which doctor should I contact if my tongue goes numb?
Paresthesia is observed in pathologies of the cardiovascular system, changes in the brain or thyroid gland, sclerosis, diabetes mellitus and a number of other diseases.
You need to visit a general practitioner, who will prescribe further consultation with the right specialist. If the victim is a minor, you must first contact a pediatrician, who will then refer you to the right doctor.
The problem of paresthesia is dealt with by a neurologist, to whom a general practitioner will refer you. First, a neurologist identifies the patient’s complaints, analyzes the medical history, and asks about bad habits and past illnesses. Blood tests and instrumental methods are prescribed.
↑
Features of neuroses
Pathological changes in the sensitivity of the larynx can appear in various diseases of this part of the body. As a rule, they are all associated with impaired nerve conduction of the laryngeal mucosa. Throat neurosis as a process leading to a change in the sensitivity of the organ may be caused by damage to the nerve plexuses of the larynx, or by pathology of the central nervous system.
Throat neurosis can manifest itself in three forms:
- Hypostesthesia, or anesthesia. It is the absence of the pharyngeal reflex, manifesting itself at different periods and in varying degrees of severity.
- Hyperesthesia. This disease consists of increased sensitivity of the larynx due to the influence of various etiological factors. It is one of the characteristic components of many neuralgic diseases, including neurasthenia and hysteria.
- Paresthesia. Experts include all abnormal sensations in the larynx that are not associated with organic damage (lump in the throat, itching, burning and other symptoms) to this pathology.
Causes of the disease
The most likely cause of any form of laryngeal neurosis is hysteria. This mental disorder leads to changes in the fields of consciousness, accompanied by disturbances in sensory and motor function. Other neuropsychic disorders can also manifest themselves as neurosis of any part of the body, including the pharynx and larynx.
Organic lesions of the body can also cause disturbances in the sensitivity of the throat in the direction of its increase or decrease. So, the reasons for anesthesia of the larynx can be:
- syphilis;
- a brain tumor;
- post-stroke and other types of paralysis;
- multiple sclerosis;
- past infections (influenza, diphtheria, typhoid, measles, etc.);
- cervical osteochondrosis.
Increased sensitivity of the pharynx may be due to:
- acute inflammatory process in the larynx, trachea, pharynx;
- chronic tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis;
- long-term bad habits (alcoholism, smoking);
- working in hazardous industries.
Paresthesia is more typical for suspicious people prone to irritability (usually women), and often intensifies during menopause. Paresthesia can also occur after severe stress, shock, against the background of chronic insomnia, VSD, etc. Once a sensation in the throat occurs, it leads to the person concentrating attention on it, and as a result, against the background of excitement, anxiety, and the search for the causes of an imaginary problem, the signs of paresthesia can only intensify.
What does dizziness and numbness of the tongue mean?
Dizziness and numbness of the tongue are frightening symptoms for many, as they primarily suggest an impending stroke or heart attack. However, most often this condition passes quickly and does not pose a threat to health. The article outlines both serious and harmless causes of these symptoms.
What sensations may accompany
Depending on the factor that caused this combination of symptoms, impaired sensitivity of the organ is manifested by either mild tingling or absolute numbness. Partial or complete loss of taste is often observed.
Sensitivity loss can affect the root, tip, half of the tongue, or the whole tongue. Sometimes unpleasant sensations spread to the lips, gums, cheeks, neck, and arms.
The head may not only feel dizzy, but also hurt, and in some cases the condition is aggravated by nausea and vomiting.
What triggers symptoms
Among the common causes of paresthesia (loss of sensitivity) of the tongue and dizziness, the following are noted:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- stress, depression;
- migraine;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- diabetes;
- deficiency of iron and vitamin B;
- hormonal imbalances (especially during menopause);
- a brain tumor;
- taking certain medications;
- thyroid diseases;
- consumption of alcohol, drugs;
- snake bites, insect bites.
Temporary numbness of the oral cavity and dizziness are possible after dental procedures. When a tooth is removed, for example, the nerve of the tongue is damaged.
If it has been subjected to compression, the numbness will go away within two weeks; Once a rupture occurs, healing will take several months.
Dizziness and paresthesia of the tongue and gums may be a reaction to anesthesia during dental treatment. When the injection wears off, the symptoms disappear.
Loss of sensitivity of the speech organ or part of it, combined with a bitter taste in the mouth, can be caused by taking antibiotics. Allergies, especially drug allergies, are expressed by a rash and numbness of the lips and tongue.
Rarely, such a reaction can develop into Quincke's edema, accompanied by low blood pressure, dizziness and difficulty breathing if it affects the larynx.
This condition requires immediately calling an ambulance.
Paresthesia of the limbs, fingers, lips and tongue is a common symptom of diabetes mellitus. An imbalance in blood glucose levels destroys the walls of blood vessels, arteries and nerve fibers, impairs blood flow and causes stagnation. This provokes burning and stiffening of the taste organ and other parts of the body.
Multiple sclerosis causes paresthesia of parts of the body, weakness, and dizziness. Migraine can also cause headaches and numbness of the tongue, lips, and hands. Neurological diseases, in addition to the above, are often accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Such signs may also indicate a skull injury.
If your tongue goes numb, and your head hurts and feels dizzy, you can suspect osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. A person suffers from tension and lumbago in the neck, high blood pressure, tingling in the fingers, which develops due to pinching of nerve endings by the vertebrae.
If you have pain and dizziness due to vegetative-vascular dystonia, there is nothing to worry about, since in this condition vascular spasms often occur, which do not pose a threat to health. Because of them, the blood supply may be temporarily disrupted, leading to a crawling sensation, burning and cramping of body parts.
If a headache and numbness of the lips are accompanied by weakness, trembling and hunger, this most likely signals an attack of hyperinsulinism. Sweet tea or foods rich in carbohydrates will help relieve the condition.
Numbness of the tongue and part of the face, accompanied by a headache, is observed with Bell's palsy, an infectious disease characterized by inflammation and blockage of nerves.
When your lips and tongue go numb, your head hurts and feels dizzy, your speech and coordination of movements are impaired, you should urgently call an ambulance, as these symptoms may be harbingers of a stroke.
If numbness is accompanied by shortness of breath, chest pain, and rapid heartbeat, this may be a manifestation of myocardial infarction.
Which doctor should I contact?
It is extremely difficult to independently determine the cause of dizziness and numbness of the tongue. To do this, you will need consultations with a neurologist, therapist, endocrinologist, as well as certain studies and examinations:
- tomography of the brain and spine;
- blood sugar test;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels.
Source: https://cefalea.ru/golovokruzhenie/nemeet-yazyk-prichiny.html
Symptoms of pathology
The symptoms of different forms of throat neuroses are also different. Hypostesia is characterized by such a symptom as a violation of the pharyngeal reflex in the direction of its decrease, or a complete absence of the reflex. On the contrary, with hyperesthesia, the clinical picture is based on an increase in the pharyngeal reflex and includes the following symptoms:
- feeling of a coma, film in the throat;
- the presence of tickling, itching;
- the presence of attempts to cough, which cause nausea and vomiting.
With paresthesia, patients most often experience numbness, goosebumps in the throat, tingling, pressure, itching, and the severity of these symptoms can vary throughout the day from almost imperceptible to very strong and irritating. With long-term paresthesia, a person may have a feeling of the constant presence of a foreign body in the throat. Sometimes there is a sore throat that can radiate to the ear and tongue.
All types of throat neurosis in different people are often accompanied by common symptoms - increased sweating, tachycardia, tearfulness, insomnia, irritability. Headache, decreased memory, attention, excessive excitability, and appetite disturbances are often present. Sometimes laryngeal neurosis is combined with migraines, as well as painful reactions to sounds and light.
Complications of pharyngeal neuroses most often occur during such a form as anesthesia. If the neurosis is severe, it can cause aspiration of saliva and food, which provokes serious consequences for the lungs or can cause asphyxia.
Causes of severe headache and numb tongue
Who will take care of our health if not ourselves? The body of each of us is a multifunctional complex mechanism that is capable of informing us about its malfunctions. Distress signals - symptoms sent during the development of any disease, are vitally important and necessary, because it is thanks to their appearance that it is possible to promptly suspect and treat the disease.
There are symptoms, such as headache or fever, that do not cause much concern for a person. Your head may hurt from fatigue, and a high temperature may indicate a common cold. But why the tongue goes numb is a question that requires due attention.
Paresthesia is one of the variants of sensitivity disorder, in which a feeling of numbness, crawling and slight tingling appears.
It often happens that after anesthesia during the removal of a tooth in the lower jaw, for some reason the tongue becomes numb. However, discomfort may persist even several days after dental procedures. As a rule, this is due to partial damage to the nerve endings of the tongue located near the root of the extracted tooth.
If you are sure that the reason why your tongue is numb is directly related to a trip to the dentist, you don’t need to do anything. Within a few weeks, the sensitivity of the tongue will be completely restored.
In people with diseases of the cardiovascular system, numbness of the tongue may be accompanied by paresthesia in another part of the body, for example, an upper limb.
In this case, the appearance of such sensations may be associated with an increase in blood pressure and indicate the development of cerebral circulation.
The most life-threatening conditions in which the tongue can become numb are cerebral stroke and myocardial infarction.
The presence of cardiovascular pathology significantly increases the risk of stroke. To avoid serious complications, if you experience tingling or numbness in your tongue, you should immediately report it to your doctor.
A crawling sensation or a feeling of numbness in the tongue area often occurs after brushing your teeth. Toothpaste contains components that can cause an allergic reaction.
Use your usual toothpastes. You should not be influenced by advertising when experimenting with various pastes to cleanse your mouth. Try to buy toothpaste after studying its composition.
A symptom such as numbness of the tongue may indicate the development of many unrelated diseases. The most common reasons why the tongue begins to go numb include:
Osteochondrosis in the cervical spine: paresthesia of the tongue develops against the background of an exacerbation of the disease, when the pinched vertebrae compress the main vessels, causing a disruption of the blood supply;
Long-term use of antibiotics;
Metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus);
Tumor-like formation in the brain;
Pregnancy: lack of vitamin B 12, iron deficiency anemia can also provoke the development of paresthesia in the tongue;
Smoking: Cigarettes contain nicotine, which has a vasoconstrictor effect. For heavy smokers, tongue numbness is a common symptom;
Poisoning by poisons, exposure to radioactive radiation, alcohol poisoning;
Hormonal disorders (thyroid pathology);
Stress, hard work, emotional overstrain: in this case, numbness of the tongue is one of many neurological symptoms, which may include fear of eating solid food, speech impairment, dizziness, etc.;
The presence of vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD).
The first step if numbness occurs in the tip of the tongue or the entire organ should be a visit to the doctor.
First, consulting a specialist will help rule out some of the diseases that cause paresthesia. Secondly, the doctor will draw up an examination plan.
The local therapist can handle this task quite easily, so you should not disturb the endocrinologist or neurologist unnecessarily.
If you suspect you have diabetes, it is enough to take a general blood test to determine your glucose level. For people suffering from hypertension, electrocardiography (ECG) and cardiac ultrasound (ultrasound) will not be amiss.
As for cases where, in addition to numbness of the tongue, there is dizziness, loss of coordination, incoherence of speech, etc.
a more thorough and expensive examination will be needed, which includes magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography of the brain (MRI, CT).
There is no need to waste time independently finding out the reason why your tongue began to go numb; you need to seek help from specialists as quickly as possible, who will make an accurate diagnosis and select the most effective treatment for each case.
Tongue numbness or tingling, which patients most often describe as prickles, pins, or needles in the tongue, is not unusual. This symptom is medically called paresthesia of the tongue and is usually accompanied by a slight burning sensation or pain.
Numbness of the tongue may occur along with muscle weakness, cramps, pain or twitching of facial tissues, and blurred vision.
With complete numbness of the tongue or partial numbness (only the tip of the tongue may become numb), its sensitivity and ability to sense taste are lost.
There are many reasons why the tongue goes numb.
A fairly common cause of tongue numbness is nerve damage from botched dental procedures (wisdom tooth removal or root canals), oral surgery, brain damage, or trauma.
A stroke is an example of brain damage and can result in a numb tongue. Blunt head trauma or a broken jaw can cause nerve damage, which can also lead to numbness of all or part of the tongue.
Allergies are another common reason why the tip of the tongue goes numb. Food allergies often cause the tongue to become swollen or numb. Numbness of the tongue can be a side effect of antibiotics, and if this occurs, you should immediately consult your doctor.
Numbness of the tongue can also occur during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester as a side symptom of high blood pressure (hypertension) and edema (late gestosis).
Sometimes the cause of tongue numbness can be a number of diseases, the symptom of which is tingling of the tongue:
- multiple sclerosis, a neurological disorder that can cause numbness in many parts of the body, including the tongue;
- hypothyroidism - dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- migraine;
- transient ischemic attack - a temporary sequence of symptoms that may be a warning of an impending stroke;
- Lyme disease is a disease caused by a tick bite;
- cerebral aneurysm;
- spinal cord cancer;
- a brain tumor;
- syphilis;
- Bell's palsy is a disease directly related to facial numbness.
The risk of tongue paresthesia increases due to excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, deficiency or excess of minerals in the body (calcium, sodium, potassium), vitamin B12 deficiency, radiation and radiation therapy in the treatment of cancer, heavy metal poisoning.
If your tongue goes numb, regardless of whether there are other symptoms of disease (weakness, sudden headache, loss of vision or its deterioration, speech defects), immediately consult a doctor to rule out more serious disorders in your body or to treat them in a timely manner. Before visiting a doctor, to better diagnose your condition, determine the answers to the following questions:
- When did you first notice tongue numbness?
- Have you ever had a head injury?
- Have you had oral surgery recently?
- Do you have other symptoms associated with tongue numbness?
- At what time of day does the tongue become more numb, and at what time less?
- What medications are you taking?
We hope our article helped you answer the question of why your tongue goes numb and what you need to do in this situation.
Many people who feel this symptom are interested in whether their hands can go numb due to osteochondrosis.
The answer is affirmative and categorical. Moreover, this is a sign of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. This causes compression of nerve endings and blood vessels. As a result, the face and hands go numb. But if a diagnosis of osteochondrosis has not been made, and such a symptom accompanies a person, then you should immediately visit a specialist. Treatment of this pathology must be carried out immediately.
IMPORTANT! ADVICE OF ORTHOPEDIST DIKUL: A SIMPLE CREAM WILL RELIEF FROM PAIN IN THE BACK AND JOINTS. READ MORE
Hands begin to go numb at an early stage of development. But this can bother men and women at the moment when the symptom becomes regular. In this case, other symptoms may occur, discomfort in the upper extremities.
Numbness often develops against the background of headache, dizziness and may precede loss of consciousness.
Doctors say that numbness in the hands is a rather alarming symptom that indicates the presence of serious pathologies with the spine. Any discomfort or concern should prompt people to seek medical help, and should never attempt to treat themselves.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is characterized by dystrophic-degenerative changes not only in the vertebrae, but also in their joints. Each vertebra is surrounded on the sides by nerve endings.
With dystrophic-degenerative changes, compression of the nerve endings occurs, and bone osteophytes (growths) appear.
Compression of the nerve roots leads to numbness of the face, arm, and leg.
The first signs of pathology (numb hand, pain) appear at the age of 30-45 years. At the same time, doctors say that the disease is getting younger every year. This pathology is the cause of headaches in 40%. If not treated in a timely manner, it will lead to intervertebral protrusion and hernia.
With osteochondrosis, pain occurs in the neck area, radiating to the shoulders, arms, sometimes to the heart area, and legs. The pain in the upper extremities with osteochondrosis is aching. With minimal exertion, during coughing and sneezing, they intensify, while the face becomes numb, and the tongue may become numb.
- When turning or tilting the head, a crunching sound is heard in the neck, accompanied by pain, and the neck goes numb.
- Arms and legs go numb, a tingling feeling appears on the back.
- Regular headaches are observed, starting from the back of the head and spreading to the parietal, temporal region, and these parts of the body may become numb.
- If you turn your head suddenly, you may lose consciousness.
- A person suffering from osteochondrosis not only has numbness in his arms or right or left leg, but also develops rapid fatigue.
- There is noise in the ears, hearing deteriorates, and visual acuity may decrease.
If the little finger and ring finger are numb, this is a sign of osteochondrosis. At the same time, you feel a tingling sensation, goosebumps, and a burning sensation between the middle and ring fingers.
If the thumb, index and middle fingers alternately on the right hand go numb and hurt, it means that the person has osteochondrosis of the sixth cervical vertebra.
- sedentary lifestyle (drivers, office workers);
- disrupted metabolic processes in the body;
- against the background of salt deposition in the cervical region;
- unbalanced diet, lack of a healthy lifestyle.
- genetic predisposition;
- mechanical damage to the neck;
- hypothermia;
- disrupted hormonal levels;
- rheumatoid arthritis.
Numbness of the limbs with osteochondrosis is the minimum discomfort that may occur.
The cervical form is the most dangerous form of the disease. The cervical region is small in size. Nerve channels and blood vessels pass through it. The task of the latter is to supply the brain with necessary substances and oxygen. The vertebrae adjacent to each other, with the slightest changes, compress the nerves and blood vessels. This can lead to irreversible consequences.
Poor circulation in the brain causes migraines, vegetative-vascular dystonia, hypertension, and cardiovascular problems. A person may lose hearing and vision. Many people develop loss or incoordination. Lack of oxygen in the brain (hypoxia) makes a person disabled.
An advanced form of the cervical disease leads to compression of the artery. In medicine, this condition is called vertebral artery syndrome. Its main function is to supply blood to the medulla oblongata and cerebellum. Compression of the artery leads to ischemia of the brain, spinal cord, spinal stroke (the main symptom is the tongue begins to go numb).
Dystrophic-degenerative changes affect the nerve roots (therefore the hand begins to go numb). As a result, partial or complete loss of mobility develops. One of the most severe consequences of this disease is compression of the spinal cord. In 99% of cases this change ends in death.
But all this can be prevented and prevented if you start timely treatment of osteochondrosis and at the first symptoms, such as numbness of the limbs, immediately go to the hospital.
Self-treatment of this disease cannot be called a reasonable activity, taking into account all the possible complications and consequences. Complete recovery can occur only at the first stage of development of the pathology. Advanced stages of osteochondrosis cannot be treated. The main task of doctors in this case is to relieve the patient of severe pain and prevent exacerbation of the disease.
Self-medication for osteochondrosis gives absolutely the opposite effect. Traditional medicine can be used as an auxiliary method, but not as the main one. Herbs and decoctions will not get rid of osteochondrosis and numbness in the hands! You need to remember this well. Treatment is carried out comprehensively.
- Joint pain limits your movements and full life
- You are worried about discomfort, crunching and systematic pain
- You may have tried a bunch of medications, creams and ointments
- But judging by the fact that you are reading these lines, they did not help you much
Source: https://fiwap.ru/golovnaya-bol/silno-bolit-golova-i-nemeet-yazyk-prichiny/
Diagnosis of throat neuroses
The examination for suspected laryngeal neurosis should be very thorough. If the patient initially sought help from an otolaryngologist, a neurologist should be involved in making the diagnosis. Research is being conducted on the functions of the pharynx, adjacent organs, and the brain.
The main types of examinations for throat neuroses:
- X-ray or CT scan of the cervical spine;
- MRI of the brain;
- laryngoscopy, microlaryngoscopy;
- FGS of the esophagus and stomach;
- X-ray of the lungs and mediastinum.
Neuroses are differentiated from osteochondrosis of the spine, as well as from other diseases of this part of the body associated with irritation of the roots of the spinal cord, or with disruption of the sympathetic nervous system in the cervical spine.
What to do in a situation when your entire throat is numb
Throat diseases are one of the most unpleasant in terms of their discomfort. The bad thing is that they can leave behind many complications. Among these manifestations there are those that are essentially very similar to spasms. And if during them your throat begins to go numb, this is a serious cause for concern.
Independent attempts to diagnose what is actually happening are unlikely to be crowned with success. Consultation with at least two specialists is required to understand the underlying problem. Because everything can actually turn out to be very serious. The spectrum of diseases may range from otolaryngology to neurology.
Signs of numbness
Most often, the throat becomes numb as a result of a sensitivity disorder. Doctors call this condition paresthesia. Such a manifestation can be enhanced by the following symptoms:
- numbness;
- tingling;
- goosebumps.
Moreover, each of these signs can transform into another. Sometimes they are accompanied by a feeling that there is a foreign body stuck in the larynx.
Such manifestations most often occur in those people suffering from increased irritability. They may also have a history of hysteria and neurasthenia. Such phenomena are also common in women during menopause.
The patient can concentrate his attention on these sensations, which significantly impairs the possibility of healing.
Check with specialists
Before declaring a particular diagnosis, you should seek help from the appropriate doctors. Attempts to cope with the disease on your own very often do not bring any results. The doctors you can contact can do the following medical examinations:
- The otolaryngologist must confirm or deny the presence of chronic laryngitis or pharyngitis. The fact is that both of these diseases can create similar symptoms.
- If there is no confirmation for such diagnoses, you need to go to an endocrinologist. Problems in the endocrine system can also cause such sensations. The doctor must make sure that they are not a sign of dangerous and complex diseases that the throat may have.
- Numbness in the throat may be a reason to visit a neurologist. As mentioned earlier, such a formulation of the question justifies the occurrence of the disease due to disorders of the nervous system. But to make sure of this for sure, you need to do a number of special tests. This sign is the most common.
- Signs of numbness in the throat, combined with dryness of the tongue and entire mouth (as well as the notorious lump in the throat) can cause serious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. There is definitely a direct path to a gastroenterologist.
And although most people believe that such signs are trifles, it is worth reassuring them that this does not go away on its own. Self-medication is even more likely to damage the laryngeal mucosa and only aggravate what is happening.
Symptoms of pharyngeal paresthesia
Numbness in this case will not be the result of any damage to the throat. Most often it is localized closer to the ear openings, located in the lower part of the pharynx. Others feel as if a foreign body has entered their throat.
How to cope with laryngeal neurosis
If laryngeal neurosis has been diagnosed, then the cause is the human nervous system itself. The body can react in this way to something stressful. The doctor’s task will be to normalize the functioning of the nervous system. But nothing can be done without the participation of the patient himself.
A person should consult a professional psychologist.
A specialist will help you learn how to react correctly to what is happening in life and stressful situations (the throat will also “rebuild” its reaction). Something will have to change.
However, at the same time, it is very important to eat right. Here you can, for example, advise consuming more natural antidepressants - bananas and chocolate.
Diagnosis of pathology of the pharyngeal process
In order to detect or refute the presence of pathology, it is now simply necessary to conduct a special examination. The objects of research will be the throat (pharynx) itself and nearby organs. Attention will also be paid to the entire central nervous system.
Usually, the results of an X-ray of the cervical spine are taken as a basis - this measure can exclude pathologies in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system (they can cause irritation in the roots of the spinal cord). For a more accurate and reliable picture, they may prescribe either a tomography of the spine or a magnetic resonance imaging study (the latter turns out to be more informative).
How to get rid of such a disease
Treatment to relieve the feeling of numbness in the throat will, of course, be complex:
- If diseases are detected in the upper respiratory tract, they should be excluded through comprehensive treatment.
- An urgent measure would be to eliminate those factors that may contribute to the development of pathologies (quit smoking, alcohol abuse, eating hot or too spicy food, or, possibly, with a lot of spices).
- In cases where the problem is located in the ongoing organic changes in the skull or the spine itself in the neck area, it is necessary to contact the appropriate specialists.
Treatment methods
The treatment algorithm for the disease largely depends on its cause. To eliminate the etiological factor, the following types of treatment may be needed:
- antibiotic therapy under the supervision of a neurologist to eliminate the causative agents of syphilis;
- surgical, chemotherapy, radiation treatment of tumors;
- carrying out a number of rehabilitation and therapeutic measures after a stroke;
- massage, spinal traction, reflexology to normalize the condition of the neck with osteochondrosis;
- complete therapy of chronic pharyngitis, laryngitis;
- quitting smoking, drinking alcohol, etc.
To completely get rid of laryngeal sensitivity disorders, treatment must be comprehensive and necessarily include various measures recommended by a neurologist or psychotherapist. These include:
- novocaine blockades in the lateral part of the pharynx, or in the area of nerve bundles;
- electrophoresis with calcium chloride;
- hypnosis, special methods of psychotherapy (trainings, conversations, etc.);
- acupuncture, electrosleep;
- use of nootropics, muscle relaxants;
- taking tranquilizers, antidepressants, herbal sedatives;
- consumption of vitamins and mineral complexes.
Traditional medicine offers its own solutions to the problem, unless, of course, it is associated with organic pathology, but is caused by mental and nervous disorders. To eliminate the effects of stress, the following remedies can be used as strengthening, calming methods:
- Pour 300 ml of boiling water over 10 g of willow bark, bring to a boil, leave for 20 minutes. Drink a spoon four times a day.
- You need to add 1-2 mint leaves to any hot tea, take this drink 2-3 times a day every day.
- Any neurosis can be treated with thyme herb. To do this, prepare a tincture of 50 g of herb and 0.5 liters of vodka, leave in the dark for 14 days. Drink 10 drops three times a day.
My tongue goes numb and my head feels dizzy: why is it numb?
The tongue goes numb and the head feels dizzy due to osteochondrosis, which is accompanied by high blood pressure, pain between the shoulder blades, and in the lower back.
But don't rush to panic. First you need to figure out the origins of the warning symptoms. Loading …
Use search
Are you having any problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease. ↑
Possible development factors:
- Cervical osteochondrosis. The anatomical location of the nerve roots is next to the vertebrae. Aging of intervertebral discs, the appearance of hernias and other degenerative processes lead to pinching of the nerves of the cervical spine, and headaches develop. Characterized by numbness of the tip of the tongue. But at the same time, the person feels “lumbago”, overstrain of the muscles of the shoulder girdle and neck; blood pressure rises.
- VSD. Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a temporary phenomenon, especially acute in the off-season. It hurts, you feel dizzy from spasm of untrained blood vessels, and numbness of the tongue occurs in isolated cases as an additional symptom.
- Infectious diseases. Dizziness is a common sign of intoxication. Bell's palsy occurs as a result of inflammation of the facial nerve. The tongue and face on the affected side begin to go numb.
- Ischemic heart and brain disease. Myocardial infarction is accompanied by shortness of breath, pain behind the sternum, radiating to the left arm and left half of the face. Stroke is accompanied by additional symptoms - impaired speech and coordination of movements.
- Diabetes. Patients with this diagnosis know that after insulin injections, blood sugar levels decrease. Weakness, trembling, feeling of hunger are signals of a hypoglycemic state. Diabetics may experience tongue desensitization with dizziness.
- Treatment and removal of teeth. Temporary paresthesia and dizziness are possible after an appointment at the dentist's office as a reaction to anesthesia or damage to the lingual nerve. Paresthesia affects the root of the taste organ.
- Selected neurological diseases. Multiple sclerosis and migraines, head injuries are accompanied by these two symptoms. Differential diagnosis of conditions is carried out by a neurologist.
- Allergic reactions. A sharp drop in blood pressure, angioedema with difficulty breathing is a situation that requires immediate medical attention.
- Anemia. A whole group of diseases associated with a lack of hemoglobin or red blood cells. Disruption of normal gas exchange and tissue hypoxia lead to general weakness.
↑ //gidpain.ru/nemeet/yazyk-kruzhitsya-golova.html
What to do
First, consult a doctor who will collect anamnesis and prescribe additional tests. X-rays and MRI help identify problems with the spine; with blood vessels - Dopplerography, assess the work of the heart - ECG with echocardiography. The level of sugar, hemoglobin, and the number of blood cells are determined by appropriate tests.
Emergency conditions: stroke, immediate allergic reactions, myocardial infarction require calling service “03”. Reducing the concentration of glucose in the blood in diabetes is facilitated by eating sweet food or drinking, of course, if a coma has not developed, otherwise an “emergency room” is inevitable.
Anemia needs to be studied in more detail; it is often an indicator of disorders of the internal organs, and therefore stands out as a separate symptom. For vegetative-vascular dystonia, medications are prescribed to improve blood circulation and increase overall tone. A person has access to simpler means of training blood vessels: morning exercises and a contrast shower.
↑
Because paresthesia is related to circulation, initial diagnostic steps include measuring blood pressure. To identify the problem, sometimes a routine examination by a doctor is enough, but sometimes it is necessary to use more serious diagnostic procedures.
Depending on the nature of the numbness, diagnosis includes the following methods:
- Tongue mobility tests;
- MRI of vessels;
- Identifying other worrying symptoms;
- Ultrasound of blood vessels, which determines the movement and stagnation of blood;
- Electromyography is a method for recording muscle activity.
A neurologist may prescribe an ultrasound scan of the neck vessels and an ultrasound scan of the cervical spine. Diagnostic methods help the specialist to correctly identify the cause of the discomfort and prescribe adequate therapy.
Sometimes paresthesia is a manifestation of another disease, which is detected during a comprehensive diagnosis. There is no specific theory for the appearance of paresthesia, so the prescribed therapy depends on the accuracy of the diagnosis. After identifying the location of the lesion, further research focuses on searching for concomitant diseases.
More research will be needed to determine the exact causes of the symptom. For example, allergen tests.
For diagnostic accuracy, it is necessary to be examined using magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and cervical spine. If all diagnostic methods have been passed, and paresthesia is still not eliminated, sedatives may be prescribed.
Any proper treatment begins with the elimination of all factors that irritate the organ. There is therapy that includes sedative medications that correct blood circulation. If paresthesia turns out to be a sign of a disease, therapy is prescribed by the appropriate doctor for the current pathology.
↑
Prevention of tongue numbness
To reduce the chances of paresthesia occurring, it is advisable to follow the recommendations for preventing the problem:
- Regularly attend scheduled medical appointments;
- Avoid traumatic factors and stress;
- During pregnancy and menopause, consultation with a gynecologist is important;
- Monitor pressure indicators;
- Take care of your oral cavity;
- In case of the first warning symptoms, seek help from a clinic.
For prevention, it is advisable not to have bad habits and to be aware of your allergic reactions. It is recommended to analyze your daily routine, diet, food and medications consumed, and pay attention to diseases suffered during the last year.
Loss of sensation occurs due to certain components of food and drinks. Even chewing gum or smoking, or animal hair can cause it. For prevention, you need to review your diet and exclude from it foods that irritate the mucous membrane.
A lot of spices and seasonings, overly spicy, salty dishes and foods can provoke irritation of the mucous membranes and the surface of the tongue, causing numbness and discomfort.
A harmonious daily routine and the absence of psycho-traumatic factors are the prevention of many pathologies and uncomfortable phenomena.
↑
Folk remedies
Treatment is prescribed by a specialist in accordance with the cause of the unpleasant symptom. Non-traditional treatment options are not recommended and lead to complications. If the patient is sure that the numbness is caused by overload of taste buds or other irritants, you can relieve the discomfort yourself at home.
When paresthesia is not a symptom of a more complex disease, then traditional methods will help eliminate the unwanted symptom:
- 3 drops of iodine are mixed with 1 teaspoon of baking soda. The mixture is stirred in 250 ml of warmed clean water. Rinse your mouth 2-3 times a day.
- 1 tablespoon dried chamomile, 1 tbsp. A spoonful of oak bark is mixed and poured with boiled water. Cool the liquid, filter and rinse your mouth 2 times a day.
- 1 teaspoon of St. John's wort herb is mixed with 1 teaspoon of celandine. The mixture is poured with boiling water in a volume of 250 ml and left for half an hour. Rinse your mouth 2-3 times a day.
- Apply sea buckthorn, peach or rosehip oil to a cotton pad. Apply to tongue 3-4 times a day.
It is recommended to rinse your mouth with a solution of soda and salt in a 1:1 ratio. The described methods help relieve inflammation and paresthesia. But these remedies are not aimed at treating the underlying disease, the symptom of which is numbness.
To restore sensitivity and relieve swelling, cold compresses are used - an ice pack that is applied to the tongue for 15-20 minutes.
If there is no swelling, you can apply a warm compress to improve blood circulation.
To normalize blood flow, you can massage and knead the numb area. Before such a massage, you should wash your hands.
If paresthesia is caused by an allergic reaction, antihistamines are taken.
If an unpleasant symptom occurs more than 2 times a month or does not go away within 2 days, it is important to immediately consult a doctor.
We must not forget that even traditional methods can be harmful if their use is not approved by a doctor. Before carrying out self-treatment procedures, it is important to consult with a specialist, undergo diagnostics and identify the causes of the disorder.
↑
Consequences if you do nothing
It is difficult to say what is better - inaction or self-medication. Loss of sensitivity as a symptom is not life-threatening, but if it is a sign of pathology, then the lack of treatment leads to unpredictable consequences.
Without the intervention of a doctor, the first manifestations of the disease lead to severe complications:
- Allergies lead to angioedema, a life-threatening condition;
- A stroke or sclerosis contributes to the patient’s disability or subsequent death;
- Possible development of Bell's palsy, trigeminal neuralgia;
- The presence of inflammation, neoplasm of the oral cavity or larynx cannot be ruled out.
Intoxication is possible if loss of sensitivity is caused by poisoning with chemicals. Numbness in diabetes mellitus without treatment leads to diabetic coma and loss of consciousness.
Numbness of the tongue is a harmless, uncomfortable phenomenon that may be a symptom of a serious illness. Sensitive nerve endings are located on the mucous surface of the organ, and it itself is heavily supplied with blood, its reaction to changes occurring in the body is indicative. Inaction leads to unpredictable consequences.
Numbness manifests itself initially as a slight tingling sensation on the surface of the tongue. Then you feel unpleasant goosebumps.
Afterwards, the tongue completely loses sensitivity: the victim cannot distinguish taste, temperature, and there is no way to move the tongue. In the presence of serious internal pathology, the symptom is accompanied by a number of other manifestations.
As a result of tick bites, uncomfortable paresthesia is accompanied by impaired nerve conduction, which contributes to the development of Lyme disease.
In diabetes mellitus, in combination with loss of sensitivity in the oral cavity, the following are observed: a strong feeling of hunger, increased sweating, and hand tremors. If these phenomena occur, it is important to immediately measure the glucose level in the body and consult a doctor.
If paresthesia of the tongue is observed in combination with difficulty breathing, problems swallowing, numbness of other parts of the body, an urgent call to emergency care is required. These symptoms are signs of a stroke, which is life-threatening for the patient.
Numbness of the tongue is not a disease, but a symptom that cannot be ignored. Such an uncomfortable phenomenon is possible for harmless reasons, but sometimes it is a sign of serious disorders in the body that require urgent medical attention.
Source: //GidPain.ru/nemeet/yazyk-kruzhitsya-golova.html
What not to do
If a person does not have serious illnesses, as confirmed by a thorough examination, and the whole problem lies in the influence of psychogenic factors, only lifestyle changes will help cure throat neurosis. The patient must understand that it’s all about his nervous system, and there are no serious disorders of the body’s functioning. However, some actions only make the problem worse. Not worth it for neuroses:
- smoking, drinking alcohol;
- expose yourself to unnecessary stress;
- ignore the effects of stress;
- put up with insomnia;
- work in hazardous industries;
- eat incorrectly, abuse heavy, floury, fatty foods.
If you have throat neurosis, you need to devote as much time as possible to rest, quiet time, and, if possible, leave a job you don’t like and do something that will bring you pleasure.
Disease prevention
To prevent laryngeal neuroses it is necessary:
- treat viral diseases in a timely manner, prevent chronic diseases of any localization, or regularly undergo treatment courses;
- avoid severe overwork and stress;
- in the presence of nervous shocks, visit a psychologist and take medications prescribed by him;
- exclude poisoning, intoxication, smoking, alcohol abuse;
- Healthy food;
- devote time to sports;
- spend more time in nature, in the air;
- have hobbies, interests;
- visit a specialist to learn how to control neurological disorders.
Neurosis, panic attacks, VSD? In such conditions, we usually turn to psychotherapy, but often do not feel progress... Try to pay attention to your lifestyle, your senses are your assistants that will help you establish balance and promote faster recovery