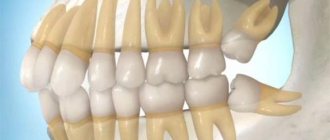
Types of teeth
There are four types of teeth. Normally, there are a total of twelve molars deep in the mouth, six on each jaw, including four wisdom teeth, which are the last to erupt. Molars are the flattest and widest teeth in humans.
Directly in front of them are the premolars. They are also called small molars or bicuspid teeth. Eight premolars - four above and below - have a flat occlusal surface designed for chewing food, and their vertical size determines the height of the lower part of the face.
Between the premolars and the teeth of the frontal group, on the left and right on the upper and lower jaws, there are four canines. They are easily distinguished from other teeth by their slightly pointed shape, which allows them to tear and hold food. In addition, the canines provide support for the lips.
There are eight incisors in front, four on each jaw. These flat, straight teeth are primarily used for biting food, but they are also responsible for articulation and lip support.
Distribution of chewing load, and teeth having antagonists (re
days), begin to perform a function unusual for them (not only biting
Not, but also chewing food). Moreover, they will bear the load like crazy
In both the vertical and horizontal directions, which is unfavorable for steam
Donta. When chewing this way, the lower jaw is in an extended position
Nii, and the articular heads carry out movement on the articular tubercle or its
Skate, which is unfavorable for all elements of the TMJ and causes their diseases
(dysfunction, osteoarthritis). Similar symptoms occur with one
End defects of the dentition. Note that TMJ is more common in patients with
Lancing side. For osteoarthritis of one TMJ, patients should be advised
Recommend chewing food on the “healthy” side, and in case of dysfunction, on the
The side of the affected joint. Corresponding changes (hypertrophy, atro
Fia) arise in the motor part of the masticatory unit, depending on the working
Or the balancing side.
Hodon's phenomenon should be differentiated from secondary partial adena
Tia in the absence of opposing teeth and a decrease in the height of the bite.
L.V.IlyinaMarkosyan and V.A.Ponomareva distinguish two forms of dental alveo
lar extension:
Displacement of teeth together with hypertrophied alveolar process
Jaws in the absence of periodontal pathology and maintaining the ratio
nia inside and extra-alveolar parts;
Displacement of teeth due to periodontal dystrophy and extra-alveolar enlargement
Lary part, accompanied by exposure of root cement, hyperesthesia
Hey, pathological mobility with visible alveolar hypertrophy
Leg process of the jaw.
These forms differ in morphofunctional characteristics, namely
They have a different clinical picture and require a differentiated approach
During treatment.
Orthopedic treatment of Hodon's phenomenon involves eliminating de
Formations followed by dental prosthetics. To eliminate deformation
tions apply:
grinding of hard tissues of displaced teeth;
hardware method (sequential disocclusion);
hardware-surgical method;
Surgical methods.
Grinding the hard tissues of a displaced tooth is possible if necessary.
The removal range is up to 1/2 the height of its coronal part. If necessary,
Some teeth are depulped before grinding.
For dental alveolar elongation of the first form, hardware is indicated
Tod treatment. Using special removable or non-removable devices (mo
Hundred dentures with a chewing surface made of plastic, removable mos
Toe dentures, supported dentures) separate the bite at the level of
Puppy teeth by 1 mm, subsequently carrying out weekly underlayering
Plastics in the area of the bite pad to a height of 11.2 mm, which ensures
Encourages the restructuring of bone tissue and the introduction of such teeth due to the function
National tension in the area of the bite pad.
With hardware treatment in older people, the prognosis becomes clear
In the first two months of treatment. If during this time it is not possible to achieve at least
Greater results, a more radical method should be used (E.I. Gavrilov).
Tooth extraction (with partial alveolectomy) is more often resorted to for dental
Alveolar elongation of the 2nd form and the inability to make it shorter
Not by grinding, as well as in elderly patients with serious
New deformities and the presence of severe cardiovascular diseases
And nervous systems.
It should be remembered that to speed up hardware treatment, first
Structure of teeth
At first glance, teeth appear to be hard, white, bone-like structures whose purpose is to grind food. However, they are more complicated than they seem. The popular dental information site provides visual diagrams and detailed descriptions of the anatomy of the tooth and surrounding oral structures.
- Clinical crown. This is the name of the upper, visible part of the tooth.
- Enamel. Enamel covers the crown of the tooth and is the hardest tissue in the human body. Since it is exposed daily to the negative effects of acids produced by plaque bacteria, caries prevention plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the enamel.
- Pulp chamber. This is a cavity inside the tooth, which is filled with pulp, consisting of connective tissue with blood and lymph vessels, as well as nerve endings.
- Root canal. Nerves and blood vessels pass through it.
- Root. The root is the part of the tooth located in the alveolar socket inside the jaw.
- Neck. The neck is the narrowed part of the tooth between the crown and the root.
- Cement. Cement is a specific tissue that covers the surface of the root and neck of the tooth. The cement is less durable than the enamel on the crown of the tooth.
- Dentine. Dentin makes up the majority of the tooth and is located under the enamel and cementum. It is penetrated by microscopic tubules that provide innervation and nutrition to hard tissues. Enamel wear leads to exposure of dentinal tubules and increased tooth sensitivity.
- Alveolar bone. The alveolar bone, or ridge, is the part of the jaw that supports the roots of the teeth.
- Periodontal ligament. The periodontal ligament consists of connective tissue and collagen fibers. With its help, the tooth root is fixed in the alveolar socket.
- Gums. Part of the crown, the neck of the tooth, and a small portion of the root are surrounded by gum, which helps hold the tooth in the jaw and protects teeth that have not yet erupted.
Indications and contraindications
Most often, the procedure is prescribed when it is necessary to correct tooth deformation, which was obtained as a result of mechanical stress or as a consequence of periodontal disease. However, there are other indications that require a procedure. Among them are the following:
- displacement of the dentition or serious malocclusion;
- gingival tissue, which is subject to a pathological process, which is accompanied by bleeding gums;
- non-standard arrangement of teeth;
- exposed tooth root;
- multiple hard deposits
On this topic
- Operations
Why do you need a retraction thread?
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- July 7, 2020
Under the influence of the procedure, the teeth are aligned and acquire an aesthetic appearance.
However, the technique may be contraindicated under the following circumstances:
- the likelihood of an allergic reaction to the material used during the procedure;
- poor quality oral care
- inflammatory processes that have a severe course;
- high sensitivity;
- multiple gum pockets with purulent contents inside.
Before prescribing the procedure, the dentist must carefully examine the oral cavity and conduct an x-ray examination. Only after this is a decision made on splinting, if there are no prohibiting factors.
Knowledge is power
A person has only one set of permanent teeth, which means they need to be protected. Getting to know the structure of teeth helps you better understand what is needed to properly care for them. You should brush your teeth at least twice a day: in the morning after breakfast and at night before bed. Using a fluoride toothpaste, a soft-bristled toothbrush, and a mouthwash will not only keep your breath fresh, but also prevent the development of tooth decay and gingivitis. Daily cleaning of the interdental spaces with dental floss will also have a beneficial effect on the condition of the teeth and gums. Finally, every six months it is imperative to undergo preventive examinations at the dentist, which, coupled with timely treatment and professional teeth cleaning in the clinic, will be the key to maintaining oral health for many years.
Kinds
Splints that are placed on the dentition come in two types - removable and non-removable. Each of them has certain advantages and indications for use.
Removable structures are presented in the form of mouth guards and plates. They allow you to connect several teeth, even if some are missing. In addition, using removable splints, it is possible to repeatedly carry out therapeutic measures.
Fixed splinting involves the use of a durable material that more firmly fixes the dentition. That is why these types of structures are prescribed in case of severe damage to the gingival tissue or significant loosening of the teeth, which significantly reduces the overload of the periodontium.
On this topic
- Operations
The whole truth about laser trimming of the frenulum of the tongue
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- September 30, 2020
Among the most common materials used in the permanent method are:
- fiberglass;
- aramid fiber (cable-stayed method);
- polyethylene thread.
The specific material is selected by a specialist after an examination has been carried out and an x-ray examination has been carried out. In addition, the choice is influenced by such indicators as:
- age category of the patient;
- malocclusion ;
- existing solid deposits;
- treatment was carried out before
- severity mobility and others.
It is also important to remember that when choosing one method or another, it is necessary to strictly observe the biocompatibility of the material with living tissues.
Fiberglass tape
The fiberglass procedure is a relatively recent innovation. However, despite this, the method has become widespread in the fight against dental pathologies due to its effectiveness, which ultimately ensures the reliability and aesthetic appearance of the oral cavity.
It is necessary to combine both mobile and stable teeth. Usually these are canines (in the case of anterior splinting).
If the procedure is carried out for the upper jaw, then it can be used not only in case of severe loosening of the teeth, but also if there is a fan-shaped divergence.
On this topic
- Operations
Everything you need to know about gum plasma lifting
- Olga Alexandrovna Novikova
- August 15, 2020
When there is no need for a fiberglass thread, it can be easily removed, and the resulting groove is filled, which allows not only to hide it, but also not to harm the appearance.
Other advantages of this method include the following:
- During installation of the splint, damage to the gums is minimal;
- there is a high probability of ensuring preservation of teeth that have an advanced degree of loosening;
- no need to grind teeth;
- nothing interferes with hygienic
- the load on the combined group is distributed evenly;
- the risk of atrophy is minimized.
Fiberglass splinting allows not only to reliably fix the mobile dentition, but also to eliminate or significantly reduce the gaps that have formed in it.
Cable-stayed method
This is also a well-known and popular method. But to make this material, a braided thread that contains aramid fiber is used. The main advantage of this method is the strength of the material and its better compatibility with the enamel coating of teeth.
In addition, aramid fiber does not react chemically with food or human saliva. Thanks to this, this procedure is the most physiologically compatible and effective compared to others.
Advantages:
- stopping further increase in loosening, but natural mobility is preserved;
- invisibility to others;
- high aesthetics;
- uniform distribution of the load on all teeth and elimination of gaps between them that have arisen unnaturally;
- prevention of further atrophy of bone tissue;
- reduction to a minimum of carious lesions, since the grooves are filled with composite material;
- additional prophylaxis or treatment is not contraindicated;
- full implementation of hygiene measures in the oral cavity;
- the ability to use instead of prosthetics;
- maintaining not only functionality, but also an attractive appearance.
The effectiveness of the cable-stayed method remains for many years.
Removable structures
This procedure is used in the presence of serious diseases and their severe forms, in which not only the mobility of the teeth is lost, but also their loss occurs.
To preserve the dentition, the dentist makes a special structure designed not only to fix healthy teeth, but also to restore fallen ones using artificial crowns.
The removable method is indicated after mechanical exposure to the teeth. This could be a fracture or bruise of the jaw. Using this technique, the dentition is fixed, which prevents changes in the natural position of the teeth during the recovery period.
On this topic
- Operations
All about jaw resection
- Olga Alexandrovna Novikova
- August 15, 2020
To make such tires, metal or plastic is used.
The main removable structures include:
- One-piece mouth guard system . Secures the front teeth with special protective caps. This model allows you to protect the dental arch from the effects of uneven and increased load distribution during chewing.
- Circular tire. It can be presented in the form of a regular form or with claw processes. Quite often used during splinting. It is effective in the absence of pronounced loosening. This method is not used if there are obvious deviations of the teeth from the axis.
- Elbrecht system . To make this design, a special alloy is used, which provides increased comfort when wearing them, as well as a long service life. Helps eliminate mobility in all directions. However, this method cannot fully protect against increased chewing load. For this reason, the model is effective only at the early stages of pathology development. Tires can be positioned differently (at the top, in the middle or at the bottom). In addition, the design can have a standard or extended version. This depends on what anatomical features the patient has.
- Elbrecht model with clasps, used on anterior teeth. Promotes reliable fixation of the dentition. It is used in the early stages of loosening and provided that there is no periodontal inflammation.
The structures are made in dental laboratories using a jaw cast made for each patient. In this case, such parameters as the number of missing teeth, degree of deformity, age, bite, type of disease and others must be taken into account.