Causes
A hematoma on the mucous membrane of the throat and palate can be of the very nature. Usually the hemorrhages are small and multiple, this is due to the peculiarities of the blood supply to the mucosa.
- Mechanical damage to the palate or pharynx.
- Acute and chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane.
- Various infectious diseases accompanied by enanthem.
- Hemangioma is a congenital benign tumor of vascular origin.
- Oncological diseases, often malignant.
From the above we can conclude that there are many reasons for the formation of bruises. It is not always possible to determine the cause on your own, so if new symptoms that are unknown to you appear, you should consult a doctor.
Treatment of bruises differs in each specific case and depends on the cause of their occurrence.
Injuries
A single hemorrhage on the mucous membrane of the palate or pharynx is most often a symptom of ordinary mechanical or thermal damage:
Such hematomas do not require special treatment. After an injury, the mucous membrane heals quite quickly, vascular tone returns to normal and hemorrhages disappear.
Pharyngitis
Acute and chronic pharyngitis are very common diseases in any population on our planet. Acute pharyngitis is called a sore throat and can be caused by both viruses and bacteria. The chronic form of the disease develops with insufficient treatment of the acute form or with the peculiarities of local immunity.
Both variants of the disease can be accompanied by bruising in the throat. The mechanism of their formation is as follows:
As a rule, such manifestations disappear along with the underlying disease. Antibacterial and symptomatic agents should be used correctly to treat pharyngitis.
Infectious diseases
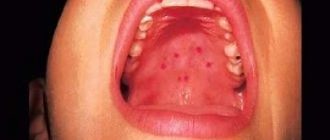
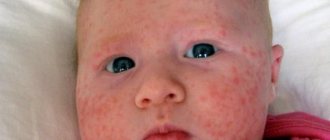
Sometimes enanthema, a rash on the mucous membrane of the palate and throat, is mistaken for a bruise. It can occur with a variety of diseases, most often of an infectious nature:
The appearance of enanthema is associated with dilation of the vessels of the mucous membrane (with measles and scarlet fever in children), less often with the direct presence of the pathogen on the palate and pharynx (herpes and syphilis). Less commonly, enanthema can be a manifestation of systemic diseases, for example, lupus erythematosus.
This symptom requires examination by a doctor, since it is impossible to independently determine the cause of the rash. Treatment depends on the causative agent of the disease.
Hemangioma
Hematomas on the mucous membrane of the throat and palate can also be caused by cancer. Among them, hemangioma, a benign vascular tumor, is absolutely harmless.
Hemangioma is most often of congenital origin, does not require treatment and is a proliferation of blood vessels under the mucous membrane.
There are methods for removing such a tumor, but operations are performed solely for cosmetic purposes.
Oncological pathology
Malignant neoplasms can also manifest as hemorrhages in the throat. Pharyngeal cancer is a tumor that is located on the mucous membrane and gradually grows inward.
This pathology can cause dilation and even destruction of blood vessels, which is manifested by hematomas. Other symptoms that should alert a person:
- Difficulty swallowing food.
- Pain when swallowing.
- General weakness and malaise.
- Unmotivated weight loss.
- Lack of appetite and aversion to certain foods.
Frequent damage to the mucous membrane and chronic diseases of the pharynx can be factors in the development of the oncological process.
Treatment uses surgical techniques, radiation and chemotherapy. The treatment method is selected individually by the oncologist for each patient.
source
The child has bruises in the throat
Clarithromycin - children 20-30 mg per kilogram of body weight per day (divided into 2-3 doses).
On the 3rd day, when the temperature subsided, a rash appeared... there was a slight rash on the face. But in the groin, it was very strong, right in the crust and armpits, on the neck.. In the morning, my daughter discovered a bruise in her throat, like an abrasion, dark. We recently had a sore throat, it was just the things in my throat... We recently had the same thing. My eldest daughter (3 years old) discovered a crescent-shaped, dark red bruise in her throat on the upper palate. The pharynx is the beginning, but at the same time it is the “crossroads” of two systems – the respiratory and the alimentary. The pharynx is the “entrance” to the pharynx from the oral cavity. Anatomically, it is located between the soft palate, the root of the tongue and the palatine arches.
We mentioned above that it is incredibly rich in capillaries, therefore, viruses or bacteria quickly enter the bloodstream and lead to inflammation and dilation of local blood vessels. The following table shows the “classic” signs of any inflammation, “translated” into symptoms of pharyngitis.
Once in the bloodstream, it destroys red cells in the capillaries of the larynx. Clinically, this manifests itself as small bruises on the pharynx, soft palate, and sometimes on the tonsils.
All these symptoms appear due to inflammatory swelling and irritation of the nerve endings of the oropharyngeal mucosa by viruses, bacteria or allergens. If necessary, the doctor also takes a culture: runs a long stick with a cotton swab at the end along the oropharynx and tonsils. There is also a quick analysis, which, unfortunately, is not available in our country due to its high cost.
The patient must remain in bed for at least 5 days and drink plenty of fluids. The diet will meet the nutritional and vitamin needs of each age. A single dose of 10-15 mg per kilogram of body (children) and 500 mg for adults. Adults – 25 mg (one tablet) twice a day. For children - according to age.
ATTENTION! The information on this site can be used for reference or educational purposes only. The text of the articles is not a guide to the treatment and diagnosis of diseases, but contains only educational information.
Good afternoon Yesterday I discovered red spots like bruises on the mucous membrane of the soft palate. Tell me, is it worth rushing to the clinic? Hello. I have been worried about plugs in my tonsils for many years and they come out periodically. Hello! A week ago, the child began to have a sore throat, runny nose, and cough. I thought that the child had a cold, so I began to treat it.
Girls, yesterday the child was 38.5 without any complaints about anything in particular, his throat was slightly red. The doctor said it was a viral sore throat and prescribed antiviral, antihistamine and streptocide. The opinions expressed in this topic represent the views of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the administration. As far as I understand, 'bruising spots' are a grainy throat, which means infection. Read how to treat a sore throat, maybe you can give something for immunity today, gargle..
Treatment is almost the same for both sore throat and scarlet fever - antibiotics. Yes, the tongue is coated and the papillae on the tongue are a little larger than usual. But with scarlet fever, the doctor said it rashes on the face (cheeks) and sometimes on the chest and neck. Our face is clean. Does stomatitis cause ulcers on the throat? Well, we went to the ENT specialist today (he said it was a viral sore throat.
See the dentist and you will be sure of at least one thing. This is our second day and our skin is clear everywhere. Sore throat and common ARVI gave us such a sore throat. It’s been 3 weeks since I had scarlet fever. And if a rash does appear and a diagnosis is made, you will need to check your kidneys after the illness, take an OAM, because this is a common complication. Yesterday I complained about my throat, my papillae were enlarged, a slight swelling was visible in my throat. The temperature is normal (35.9 in the morning). The daughter says that yesterday she screamed loudly and loudly in the garden, like a seagull.
The boy at the entrance was sick, but four weeks ago, and at that time we had chickenpox. On the trail. During the day the bruising became smaller, and by Monday it had completely disappeared. They didn't go to the doctor. So, I don’t know what it was... I found out, I went to an ENT specialist, this is when the blood vessels are weak, for some reason at night, or before going to bed, blood flows down the throat, along the back wall, and in the morning we see a bruise, and this is a stuck clot.
Everyone got sick in two doses. Ilyushon is wearing a T-shirt, or at best a turtleneck... It looks like a bruise. I can't even imagine what it is. Naturally, I'll go to the doctor tomorrow. But I can’t calm down, and I’d like to hear the opinions of different experts.
When I asked if her throat hurt and if she shoved anything into her mouth, my daughter said - no, it doesn’t hurt, she didn’t shove anything... Because... In the morning there is fever, rash spots on the throat, under the tongue and on the roof of the mouth, near the throat. Rashes like bruises. 4 months ago, in addition to bruises on the throat, one day there was a high fever and red pimples on the palms and soles of the feet; we went to the doctor - Diagnosis: Enterovirus infection.
Blood streak on the back of the throat
With inflammation of the tonsils and the entire throat, everyone recognizes these symptoms as a sore throat. However, if not the entire larynx begins to hurt, but only the back wall of the throat, doubts arise in determining the diagnosis. Most often, after such complaints, doctors give a verdict: pharyngitis.
This disease is no more dangerous than a sore throat, but it may well provoke complications if treatment is not started in time. That is why it is so important to know about all the symptoms and types of this disease.
Based on this knowledge, you can choose a suitable treatment method, both medicinal and non-traditional.
Definition of disease
The main difference between pharyngitis is damage to the larynx. Translated from Latin, pharynx is designated by the word “pharynx,” which gives the name to the disease. The ending with “itis” indicates an acute inflammatory process.
Therefore, pharyngitis is not a simple difficulty swallowing or irritation of the back of the throat, but a serious condition that must be treated with the help of doctors.
Pharyngitis is very similar to the similar disease tonsillitis, but if you study these pathologies in more detail, significant differences can be identified between them.
With tonsillitis, the side walls become inflamed, and pharyngitis most often occurs only with damage to the back wall of the throat. This type of disease cannot be treated carelessly. If treatment is not started in time, the entire body may suffer from complications.
Therefore, when the first signs of pharyngitis appear, you should immediately go to an appointment with an otolaryngologist. An experienced specialist will always determine the type of disease and prescribe the appropriate treatment regimen. You should not try to identify the disease yourself, much less treat it.
All manipulations, and especially traditional methods of treatment, must be agreed with a doctor.
Types of disease
Pharyngitis, according to its symptoms and causes of occurrence, is divided into several types: acute granulosa, chronic, catarrhal, atrophic, hypertrophic. Of these, the following types of origin should be distinguished:
- Fungal infection of the throat wall.
- Traumatic.
- Allergic.
- Bacterial.
- Viral.
The simplest forms of pharyngitis are: atrophic, hypertrophic, and mixed varieties. This disease can also occur in a chronic form. However, in this case, the blame partly lies with the sick person. If you treat the symptoms inattentively and neglect to visit a doctor, even the mildest form of pharyngitis can develop into a serious complication.
Chronic pharyngitis
Predisposition to colds, polluted environment, weak immunity - these factors influence the chronic course of pharyngitis. In addition, those people who work in industries can acquire pathology.
A polluted and dusty environment causes enormous harm to the body, provoking not only the development of pharyngitis, but also many other diseases.
Also, chronic inflammation in the throat occurs more quickly in smokers and those who abuse alcoholic beverages.
The chronic form of pharyngitis occurs without fever. However, the patient suffers from a constant cough, as well as a sensation of a foreign body in the throat. The person gets the impression that snot is running down the back of the throat. These symptoms are directly related to the accumulation of pus on the back wall of the larynx. Because of them, a person has an uncontrollable urge to cough and clear his throat.
Mucus and purulent growths cause a lot of discomfort; the patient tries to spit out the secretions from the throat, but he cannot do this without the help of medications.
After each expectoration, mucus again flows down the back of the throat, renewing the unpleasant sensations. These symptoms affect the emotional and mental state and affect the quality of sleep.
A person suffering from chronic pharyngitis becomes nervous, irritable and aggressive.
Granular pharyngitis
This form of inflammation most often occurs in those who live in humid climates. It also manifests itself in people whose professional activities involve working in conditions of high humidity. Those who are prone to allergic reactions, smokers or alcohol abusers are susceptible to the granular form of pharyngitis.
This type of disease manifests itself when pathogenic microorganisms enter the walls of the throat, causing swelling and redness. After this, the mucous membrane begins to become covered with a film, and then nodular granules form on the back wall. The diagnosis of this disease can be quickly determined by taking a photo of the back of the throat.
Granular pharyngitis is accompanied by certain symptoms:
- Severe cough. The patient constantly coughs, and unpleasant mucus is released from the throat. Poorly discharged and viscous secretions irritate the walls of the larynx and intensify the inflammatory process. It is produced especially strongly at night. This is why patients often suffer from insomnia. In the morning the cough becomes even more uncontrollable and severe.
- There is a sore throat and dryness. It becomes difficult for the patient to swallow. In this case, the back wall of the throat is white or slightly pinkish, with small red nodules and dots.
The disease is diagnosed fairly quickly by an otolaryngologist. Therefore, it is better not to delay your visit and, at the first symptoms, contact the hospital to draw up a treatment plan. If treatment is not started on time, granulosa pharyngitis quickly develops into an atrophic form.
Catarrhal pharyngitis
This form is different in that it appears at the very beginning of the disease. Catarrhal pharyngitis is the mildest stage. So
same, as in other forms, it is characterized by a sensation of a foreign body, as if snot is running down the back wall of the throat, tickling, itching and discomfort in the oral cavity. Sometimes it becomes difficult and painful to swallow. This symptomatology provokes frequent expectoration, as well as coughing.
In this case, catarrhal pharyngitis is always accompanied by redness of the back of the throat. The cough in the morning can be so strong that there are attacks of vomiting. If adequate therapeutic treatment is not started in time, pharyngitis develops into a hypertrophic form.
Complications from this disease can spread throughout the body. Moreover, they quite often arise both due to lack of treatment and after illiterate use of medications. This is why it is so important to be treated under the supervision of a doctor.
Causes of pharyngitis
Mouth breathing is considered the main factor provoking the appearance of pharyngitis. During inhalation, polluted air enters the mucous membrane, which is filled with microbes, viruses, infections and other sources of inflammation. Among the main causes of inflammation of the back of the throat, the most common are:
- Polluted environment (cigarette smoke, smog and dust).
- Drinking cold drinks.
- Spending a long time in the cold or frost.
- Endocrine system disorders.
- Chronic pathologies, stomach disorders.
- Abuse of spicy and salty foods.
- Tendency to pharyngitis after removal of tonsils.
- Chemicals entering the body by airborne droplets.
- Constant drinking of alcohol.
- Infection.
- Viruses.
- Complication from ARVI.
- Abuse of nasal drops.
The throat can suffer due to untimely visits to the dentist. If caries develops on the teeth, the inflammatory process can spread to the mucous membrane.
Also, if signs of sinusitis, sinusitis or rhinitis appear, this may well result in pharyngitis. It is very important to be careful when treating a runny nose.
Drops in the nose constrict blood vessels, and this leads to a slowdown in blood circulation, which has a direct effect on the larynx.
About 70% of cases of pharyngitis are the result of viral infections. The back of the throat becomes inflamed due to the following types of viruses:
The most common cause of pharyngitis is rhinovirus.
Kids and their problems
If you once looked into your child’s throat and noticed ulcers or plugs there, you should definitely not be immediately alarmed by drawing your own conclusions about the development of a purulent sore throat, especially if with such a throat, the child’s body temperature remains normal.
It should be understood that there are many other diseases (conditions) that can cause similar symptoms.
Although, of course, practicing doctors are convinced that the likelihood of the rapid development of a purulent version of sore throat should not be discounted. When pustules or the same plugs are noticed in a child’s throat, only an experienced specialist can make an absolutely correct and accurate diagnosis.
Moreover, sometimes even the doctor’s experience may not be enough to make a correct diagnosis, and then strictly specific blood tests are used, which help the doctor determine the etiology of the disease.
In order for mothers to understand how many diseases are accompanied by symptoms including ulcers, ulcers or plugs that form in the throat, we will consider the reasons why children may have a purulent throat that is not accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
Diagnosis of the disease
The otolaryngologist diagnoses a small angioma in the pharynx against the background of other diseases with which the patient came. A large tumor is detected by palpation based on the patient’s complaints. For a more accurate diagnosis, pharyngoscopy is necessary.
An additional examination can confirm the disease - MRI, ultrasound, radiography, studies of the vocal cords. A biopsy is unacceptable, since excision of the slightest piece of tissue can cause significant blood loss.
To exclude infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract, oncology or the presence of a foreign body in the throat, the otolaryngologist can take a swab from the oropharynx and conduct a bacteriological analysis.
After surgery, a histological verification is carried out on the basis of the removed tumor to finally confirm the diagnosis and determine the type of benign neoplasm.
The main diseases in which plaque is noticeable on the laryngeal mucosa
Let us note once again that it is not possible to list absolutely all the diseases in which a mother will notice ulcers, whitish plaque, ulcers, or plugs in her child’s throat. We will try to highlight the most basic of these diseases. So, diseases, one of the main symptoms of which are ulcers or plugs in the throat:
- Sore throat or tonsillitis. Both its acute and chronic form. Moreover, it is the chronic form of this disease that leads to the fact that plugs are visible in the child’s throat, and the temperature remains normal.
- Pharyngomycosis is a condition when the baby’s throat is affected by one or another fungus. In this case, the lesions rather look not like plugs, but like ulcers or ulcers.
- Stomatitis is a condition in which lesions of the mucous membrane that only resemble pustules can be observed. Moreover, as a rule, such lesions accompany only the aphthous form of stomatitis.
It must be said that sometimes there are relatively safe (non-pathological) reasons for the development of plaque in the larynx, similar to pustules. For example, on the mucous membrane of the larynx there may be a plaque resembling ulcers, which, upon closer examination, turns out to be banal food debris. Often, parents may mistake the remains of dairy products on the tonsils for purulent plaque.
Sometimes parents mistake ordinary fibrinous plaque for pustules or plugs in the throat.
This phenomenon can occur as a result of injuries (most often burns) of the pharynx. Such a plaque simply covers all affected surfaces of the mucous membrane of the larynx, and may partly resemble the symptoms of a developing sore throat.
Naturally, each of these conditions requires strictly specific treatment, or does not require treatment at all. An experienced doctor, usually by the appearance of ulcers or plugs, can determine which disease led to such symptoms. Although sometimes even a doctor needs additional research to confirm the alleged diagnosis.
But a mother, even the most experienced and most wonderful, but who does not have a medical education, is unlikely to be able to find out the causes of the problem.
This is why, once again, we note that if you see ulcers in your child’s throat, you should not rush to start treatment.
Before carrying out any medical procedures, it is advisable to consult a doctor.
General information
The pharynx is the organ where the upper respiratory and digestive tracts intersect. It connects the nasal and oral cavities with the larynx and esophagus, respectively. The inside of the pharynx is covered with a mucous membrane lined with ciliated and stratified squamous epithelium. Next comes the connective tissue base, containing lymphoid accumulations (follicles), glands and blood vessels.
Thanks to this structure, the mucous membrane performs important functions, primarily protective. Being the entry gate for various infections, the pharynx must have a developed system to counteract foreign agents. Its first component is the tonsils, and the second is the mucous membrane. The glandular secretion contains antimicrobial substances (lysozyme, interferon, immunoglobulins).
Sore throat, pharyngomycosis and stomatitis - how to treat?
The problem can be treated only after the doctor has made an accurate diagnosis, and not earlier. It is quite possible that the plaque that reminded you of tonsil plugs will turn out to be banal food debris that accidentally stuck to the mucous membrane. Of course, such a condition will not require any treatment.
Also, definitely, the condition when the mother mistook fibrinous plaque for purulent lesions of the larynx will not require any specific treatment. If this phenomenon was the result of an injury or burn, soon the mucous membrane of the larynx will be able to fully recover, and completely independently.
It’s a different matter if the plugs on the tonsils are a consequence of the development of tonsillitis (acute or chronic tonsillitis). Sore throat is a pathological condition that is most often caused by bacterial pathogens (streptococcus). Unfortunately, today there are more and more cases where sore throats are asymptomatic, without fever (increased temperature to high levels), without cough, etc.
Moreover, chronic forms of tonsillitis are often accompanied by the formation of dense purulent plugs on the tonsils, against the background of the patient’s apparent complete health. Treatment of angina, as a rule, consists of the use of antibacterial drugs, and quite powerful ones.
When treating sore throats, it is important to constantly maintain adequate drinking regimen. Sometimes, purulent plaque with a sore throat needs to be rinsed out with medications of various compositions.
If a doctor diagnoses a child with pustules on the mucous membrane of the larynx as pharyngomycosis, the treatment will be radically different. Most likely, the doctor will be forced to do additional tests to determine the causative agent of mycosis; the treatment will actually depend on this.
By the way, it is pharyngomycosis that often develops against the background of improper use of antibiotics or other medications, when parents of children self-medicate a sore throat.
As a rule, therapy for this disease involves the use of special antimycotic agents, which the doctor will select in accordance with the identified causative agent of mycosis. Such drugs are often used both locally and as systemic (general) therapy. If the causative agent of mycosis of the pharynx was fungi of the genus Candida, the doctor may prescribe drugs such as miramistin, clotrimazole, or hydroxyquinoline topically, and fluconazole for oral administration, in a strictly individual dosage.
If the ulcers noticed in the larynx are caused by stomatitis, then the treatment will have its own specifics. Ulcers caused by stomatitis are usually located throughout the oral cavity, they often cause significant pain, and can cause a lot of inconvenience to the baby.
Almost the main role in the treatment of stomatitis today is played by the restoration of the child’s body’s own defenses. Treatment of stomatitis, in most cases, is still carried out by dentists, and includes only local therapy (rinses, lotions, treatment with solutions, etc.).
We hope that our publication has convinced all mothers that if their children have pustules or ulcers in the larynx, they should not engage in thoughtless self-medication. When you discover ulcers on your baby’s tonsils, the most logical thing to do is consult a doctor. After all, only an experienced otolaryngologist will be able to correctly determine the cause of such symptoms, and therefore be able to select an adequate treatment for it.
source
Blood on the tonsils with staphylococcal sore throat
Staphylococcus is the second most common causative agent of acute tonsillitis. This is an opportunistic bacterium that is present in small quantities on the skin and mucous membranes of many (including absolutely healthy) people. Staphylococcus can provoke an infectious process only under certain conditions - with decreased immunity, dysbacteriosis, during a viral infection, etc. Externally, inflammation of the tonsils caused by staphylococcus differs little from streptococcal sore throat - the patient is also bothered by pain and plaque in the throat, fever, swollen lymph nodes, etc. However, it is precisely with staphylococcal sore throat that hemorrhagic exudate, a plaque containing an admixture of red blood cells, may appear on the tonsils. The fact is that staphylococcal infection provokes the development of a strong immune response. At the same time, in the area of inflammation, the vessels dilate, and together with the leukocytes, a certain amount of red blood cell mass comes out to the surface of the mucosa. With staphylococcal sore throat, blood on the tonsils is not noticeable, but the plaque may have a pinkish tint as a result of the release of a small number of red blood cells from the vessels. A diagnosis of “staphylococcal tonsillitis” can only be made based on the results of laboratory tests (bacteriological culture of a throat smear, ELISA or PCR analysis).
Pharyngitis. Causes, symptoms, signs, diagnosis and treatment of pathology
Pharyngitis is an inflammation or irritation of the mucous layer of the back wall of the nasal cavity, mouth and larynx, or more simply, the pharynx. As a rule, this pathology accompanies respiratory infectious and inflammatory diseases.
Particularly dangerous is acute pharyngitis, caused by group A streptococcus (hereinafter referred to as GAS). Early diagnosis and correct treatment of this disease can prevent extremely unpleasant consequences - complications on the heart and kidneys.
Did you know?
- Acute pharyngitis is the most common disease of the “winter season” among children from 4 to 7 years old;
- In school-age children, the cause of pharyngitis in 15-30% of cases is GAS infection;
- In adults, 90% of pharyngitis is caused by viruses;
- The sudden onset of the disease with a sore throat is more likely to indicate a GAS infection;
- Pharyngitis, which appears after several days of runny nose and nasal congestion, is most likely viral.
When is surgery needed?
If your tonsils become inflamed regularly and frequently, your doctor may recommend removing them.
If drug treatments for inflamed tonsils do not produce a positive result, the doctor decides to prescribe the patient surgery on the diseased organ.
Important! Tonsil surgery is performed only if other methods of therapy do not help the patient recover.
Doctors identify a group of indications for surgery on the tonsils:
- Lack of results with conservative therapy based on medications.
- Increased risk of developing complications after inflammation of the tonsils.
- Frequent sore throats.
- Excessive proliferation of tonsils.
If possible, the doctor offers the patient cryodestruction. This is a gentle option for surgical intervention, during which the inflamed tissues are exposed to low temperatures.
If there are frequent otitis media and other hearing impairments, as well as in the presence of serious complications, the doctor will insist on surgery.
We must remember! If a patient is diagnosed with seasonal allergies, then surgery cannot be performed during the period of its exacerbation.
Removal of tonsils surgically is carried out under general and local anesthesia. Today the first option is considered more popular.
You need to know that any surgical intervention will have its consequences. If a patient trusts his health to a competent specialist and adheres to his recommendations, then he may be able to avoid such problems.
Due to the removal of tonsils, the immune system is primarily affected. In addition, the tissues in the area where the organ was located are injured. For this reason, after radical therapy, the patient complains of severe sore throat. It will take some time for them to pass.
After tonsil surgery, body temperature rises.
To speed up tissue healing, it is recommended to follow a menu that does not contain hot or solid foods for several days after surgery. It is best to spend all this time in bed and avoid increased stress.
Causes of pharyngitis
Viruses that most often cause pharyngitis include:
- Adenovirus
- Herpes simplex
- Coxsackie group viruses
- Cytomegalovirus
- Epstein-Barr virus
The most dangerous cause of pharyngitis is group A streptococcus. Most often, this bacterium affects school-age children and, if untreated or improperly treated, leads to very serious complications.
Much less often, pharyngitis becomes a companion to allergies, cancer, or reflux of acid from the stomach.
In people with suppressed immunity (diabetes mellitus, chemotherapy, HIV), infection by fungi of the Candida family also occurs.
Why does my throat hurt?
An irritating factor (any of the above) comes into contact with the mucous layer of the pharynx.
We mentioned above that it is incredibly rich in capillaries, therefore, viruses or bacteria quickly enter the bloodstream and lead to inflammation and dilation of local blood vessels. The following table shows the “classic” signs of any inflammation, “translated” into symptoms of pharyngitis.
| Sign of inflammation | Symptoms of pharyngitis |
| "tickle" |
| "red throat" |
| sore throat that gets worse when swallowing |
| |
| Without clinical relationships, in case of pharyngitis |
Some differences are revealed in the picture of pharyngitis, the cause of which is group A streptococcus. This bacterium is also called hemolytic streptococcus. Literally translated from Latin, it means “destroying/dissolving” blood.
Once in the bloodstream, it destroys red cells in the capillaries of the larynx. Clinically, this manifests itself as small bruises on the pharynx, soft palate, and sometimes on the tonsils.
With the Coxsackie and herpes viruses, the connections between the cells of the mucous membrane are destroyed, and they “fusion” occurs. Clinically, it appears as fluid-filled blisters.
Types of throat angioma
Otorhinolaryngologists distinguish two types of such neoplasms depending on the vessels where the throat angioma forms:
If the tumor grows from blood vessels, it is called a hemangioma. Hemangiomas, in turn, are divided into simple (capillary), cavernous (cavernous) and branched.
All these types of hemangiomas differ in appearance from each other. Capillary ones look like red-blue spots filled with blood. Cavernoses look like nodular new growths of a blue hue. Branched ones look like bubbles consisting of pulsating vessels.
Lymphangiomas also have their own classification. They are divided into simple, cavernous and cystic. As with simple hemangiomas, simple lymphangiomas are composed of capillaries, but these capillaries are filled with lymph. Cavernous formations have several cavities, like a sponge, where each of the cavities is filled with lymph. Cystic, as the name suggests, is one cyst or several cysts fused together.
Laryngeal angioma may not manifest itself for a long time, remain dormant and appear, for example, already in adulthood.
Symptoms of pharyngitis
Examination by an ENT specialist
- Questioning (history)
- General medical examination - the doctor examines the skin for bruising or jaundice, lymph nodes (which can be enlarged with scarlet fever or mononucleosis), and the borders of the liver (also enlarged with mononucleosis).
- Special ENT examination. The pharynx is examined using a disposable spatula, pressing the root of the tongue down.
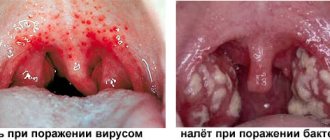
On examination, the following may be noted:
| Redness | The onset of any viral or bacterial infection |
| Redness and fluid-filled blisters | Herpes virus or Coxsackie group |
| Redness + pus spots | Any bacterial infection, including GAS |
| Redness and small bruises | SGA |
If necessary, the doctor also takes a culture: runs a long stick with a cotton swab at the end along the oropharynx and tonsils. This test is used to confirm streptococcal pharyngitis. Unfortunately, results can only be obtained within 4-5 days.
There is also a quick analysis, which, unfortunately, is not available in our country due to its high cost. Therefore, a general and special ENT examination is very important in diagnosing streptococcal pharyngitis. Based on this, a decision about treatment is made.
Other laboratory tests are rarely key to diagnosis. A complete blood count may show the presence of atypical monocytes, which are important for diagnosing mononucleosis. It is also possible that leukocytes and ESR may increase, which happens with any infection.
What to do?
There are a lot of reasons, it is almost impossible to find the exact one on your own. Therefore, you must definitely go to the hospital and take tests, which will be prescribed by the attending specialist. The doctor may order a general blood test and a throat smear, after which he will make an accurate diagnosis and select individual treatment.
What to do at home? On your own, you can only alleviate the condition and create comfortable conditions for the sick person:
• provide bed rest;
• follow a diet (food should be soft, warm, without spices);
• drink more fluids;
• gargle with antiseptic solutions (the procedure is effective in all cases).
All other treatment measures are selected by the doctor. If the tonsils are constantly inflamed due to chronic tonsillitis, then the specialist may recommend surgery to remove the tonsils. An abscess is also often treated with surgical methods.
Well, that's all, dear readers. I hope you found answers to all your questions in the article. If it was interesting and useful for you, then subscribe to updates and share what you read with your friends. Good health to you and your loved ones!
Roman Kolmakov, Female, 4 years old
Hello, my child (4 years old) A month ago I had follicular tonsillitis, the treatment was as follows: treatment with chlorhexidine 4 times a day, inhalation with Bioparox 4 times a day for 7 days, aflubin 10 drops 6 times a day. After the treatment, the doctor wrote us a certificate to the kindergarten with a conclusion - healthy. Two weeks later, the child began to have a wet cough and runny nose, and an unpleasant purulent odor from the mouth and nose. When we visited the doctor again, we were told: “your throat is a little red, treat it with chlorhexidine, dissolve Lysobact, and drink ACC for cough.” At the moment, we were treated according to the prescribed treatment regimen for 5 days and I decided to look at the child’s throat, I didn’t like what I saw there at all! The tonsils are loose and swollen with red streaks, the uvula is also swollen, the tonsils occupy almost the entire space in the throat. I don't think that's what a "little red" throat should look like. Please help us determine whether we are being treated correctly, and if not, what is the diagnosis and treatment? There is no fever or sore throat. Just a wet cough and runny nose. Thank you in advance!
Young children are most susceptible to colds, especially in the autumn-winter period. When complaining of a sore throat or feeling unwell, parents often independently examine the throat and discover red streaks on the child’s tonsils. This picture can be observed both normally and indicative of various diseases.
Treatment of pharyngitis
General provisions
Treatment of streptococcus-positive pharyngitis
Treatment of streptococcus-positive pharyngitis will be more “solid” in order to prevent complications in the heart and kidneys.
Daily regime
The patient must remain in bed for at least 5 days and drink plenty of fluids. The diet will meet the nutritional and vitamin needs of each age. To maintain oral hygiene, you can use solutions of chamomile, furatsilin (1:5000), soda (2%), as well as any other antiseptics.
Medicines
Drug treatment will take center stage. The following groups will be used in the treatment of this type of pharyngitis:
| A drug | Mechanism | Drugs and doses |
Antibiotics
| destroy the “shell” of the bacterium, thereby destroying its main defense. As a result, streptococcus dies | Penicillin B (tablets) is used in a dose of 250 mg 2-3 times a day (for children), and 500 mg 2 times a day for adults. Should be taken half an hour after meals for 10 days. Clarithromycin - children 20-30 mg per kilogram of body weight per day (divided into 2-3 doses). Adults 600 mg per day in 2 divided doses after meals. Take for 10 days. Cefuroxime – 20 mg per kg of body weight per day for children in 2 doses, 250 mg twice a day for adults. Course 10 days. |
| Antipyretics – in case of temperature above 38 degrees (paracetamol) | Stops the action of an inflammatory “enzyme” called cyclooxygenase (COX), which causes fever | A single dose of 10-15 mg per kilogram of body (children) and 500 mg for adults. Use no more than once every six hours. |
| Antiallergic drugs | Blocks cells responsible for allergic reactions. | Adults – 25 mg (one tablet) twice a day. For children - according to age. Take 7-10 days |
| Vitamins | Stimulates the body's recovery | Vitamin C – 100 mg twice a day. |
Related and recommended questions
Pharyngitis? Good day! A little over two weeks ago I started having problems with my throat. Previously...Vessels on the throat For a long time (about a year) one tonsil was inflamed, and also visible...
Tonsillitis/pharyngitis I suffer with my throat all the time. The doctor diagnoses chronic tonsillopharyngitis...
Red blood vessels Troubles the throat. Three weeks ago I took a course of antibiotics because... Vessels in the throat A week ago my throat started hurting and became red. I started rinsing with chamomile...
Tonsillitis? I have had problems with my throat for a long time. Sometimes it hurts, sometimes it doesn’t. Yesterday I climbed...
Throat Doctor tell me about three months ago my tonsils became inflamed...