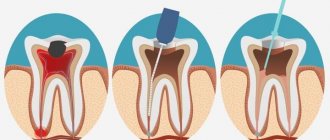
Is it possible to use Metronidazole and Tsiprolet together? This question worries many patients who are prescribed such combination therapy. To answer, it is necessary to compare Metronidazole and Tsiprolet, their mechanism of action and medicinal properties.
Treatment of some infectious and inflammatory diseases is effective only with the complex use of drugs that have different mechanisms of action. Thanks to this, it becomes possible to cover a wider range of pathogens. These drugs are Metronidazole and Tsiprolet.
The main active ingredient of Tsiprolet is ciprofloxacin, which is part of the group of fluoroquinolones. In the process of influencing the topoisomerase of harmful microorganisms, the drug suppresses their reproduction, which causes a decrease in the concentration of bacteria and their subsequent death.
The antibiotic is active against aerobic pathogens, including microbes that produce beta-lactamase.
Metronidazole is an antibacterial agent that exhibits active antimicrobial and antiprotozoal effects. By interacting with deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) found in bacterial cells, Metronidazole blocks the production of their nucleic acids, which causes the death of harmful microbes.
Shows activity against a large number of anaerobic microorganisms and protozoa.
Quite often, doctors prescribe Metronidazole along with Tsiprolet. This is due to the fact that compatibility enhances the antimicrobial activity of drugs.
The following indications exist for the use of drugs in combination:
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the gynecological area;
- severe infections caused by anaerobic microorganisms;
- infectious and inflammatory lesions of the peritoneum, severe, complicated by peritonitis.
- infection with protozoa causing mixed abdominal infections.
Combination therapy helps to increase the activity of the drugs used against a wide range of pathogens.
The combination of Tsiprolet with certain antimicrobial substances, for example, beta-lactam antibiotics, aminoglycoside drugs, as well as clindamycin and Metronidazole, significantly increases the effectiveness of the drug. That is why quite often doctors prescribe a treatment regimen in which it is necessary to take drugs at the same time.
For the treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases, joint therapy with Metronidazole and Tsiprolet is prescribed.
For vaginal infections, it is possible to use suppositories or Metronidazole gel and Tsiprolet tablets.
Suppositories and gel are used intravaginally. Usually one suppository is prescribed per day (at night). The duration of the therapeutic course is 10 days. The standard dose of the gel is a full applicator or 5 g of active substance twice a day. The duration of treatment is 5 days.
If Metronidazole tablets are used, the standard dosage is as follows: 1 - 2 tablets (250 - 500 mg) should be taken 2 - 3 times a day. Duration of therapy is from 5 to 10 days.
Simultaneously with Metronidazole, it is necessary to drink Tsiprolet in the following dose: from 250 to 500 mg twice a day. The duration of the therapeutic course is from 7 to 10 days.
At the end of treatment, it is necessary to conduct an appropriate examination to ensure the effectiveness of the therapy used.
Found a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter
Choosing the best antibiotic for cystitis
Doctors often recommend a broad-spectrum antimicrobial drug for acute symptoms even before determining the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms (if an infectious type of pathology is suspected). This type of diagnosis shows results in a few weeks. The pronounced symptoms of inflammation do not allow waiting. You need to act immediately. The antibiotic “Tsiprolet” for cystitis is prescribed precisely in such situations.
Pharmacologists offer a huge selection of antimicrobial drugs. Every year more and more new products come on sale. They are produced artificially, many are semi-synthetic. In infectious cystitis, these substances kill foreign agents and quickly relieve inflammation.
The method of short courses of antibiotic therapy is considered effective. This reduces the cost of treatment and the number of negative consequences. This tactic gives good results when the process is uncomplicated. Doctors take into account the spectrum of action of drugs.
The latest generation of fluoroquinolones have proven themselves better than others. Therefore, urologists are increasingly prescribing treatment for cystitis with Tsiprolet.
When choosing an antibiotic, specialists are guided by the following criteria:
- impact on certain microflora;
- tropism to the urinary system;
- combination with other medications;
- minimal negative reactions;
- ease of reception.
As a rule, cystitis is caused by certain microbes. Not all antibacterial agents act on this range of foreign agents. In addition, these substances do not affect viruses and fungi. For such an infection, specific drugs are prescribed. Antibiotics are needed here as an addition to the main treatment, since a decrease in immunity entails the addition of bacterial flora.
Treatment of cystitis requires medications that target the tissues of the bladder. The active substance of such drugs quickly accumulates in the wall of the organ and is retained by it for a long time. This ensures maximum therapeutic results. In such a case, the medicine does not need to be taken frequently. This is important to consider when treatment occurs on an outpatient basis.
Antibiotics usually need to be combined with other medications. The prescribed drug must be compatible with certain substances, since the inflammatory process requires complex treatment.
The choice of remedy is influenced by its tolerability. Let it be gentle on the body’s native flora, so that there is no need for subsequent long-term treatment for dysbacteriosis. The drug should cause minimal allergenicity and not irritate the stomach and intestines.
Tsiprolet for gonorrhea and chlamydia
When treating chlamydia with ciprolet, there is a high possibility of having a bacteriostatic effect on the pathogen.
This drug is a representative of such a young group of drugs as fluoroquinolones, but differs from most of the first generation drugs in its higher efficiency. It often happens that a doctor prescribes ciprolet to a patient for chlamydia, but the pharmacy gives not the medicine that is written in the prescription, but one of the drugs such as ciprofloxacin, tsifran, citeral, afenoxime, ciprocinal, tsifobak, medociprin, ciprosan, cipropan, cypromide, ciproxin, ciproran, cyprinol, cyprobid, ciplox, cyprobay, aflox, quinlo, ciprolac, ciprova or cipro. The fact is that, in essence, all these drugs are the same medicine, the active ingredient of which is ciprofloxacin.
They strive to cure chlamydia with Tsiprolet, both at the stage of intensive proliferation of microorganisms, and in later periods of the disease, for example, in its chronic form. Tsiprolet, like other fluoroquinolones, does not allow chlamydia to divide unhindered in the cells of the mucous membrane of the genitourinary system, while being safe from attacks by the immune system and many antibiotics. The advantage of fluoroquinolones here is manifested in the high level of absorption by the cells of the human body, the unchanged structure of the drug in the blood, and most importantly, its ability, after penetration into the cell membrane, to significantly reduce the amount of DNA gyrase in the cells. Thus, in the affected cell, the binding of the enzyme necessary for chlamydia to duplicate the chromosome set during division occurs. No enzyme means no reproduction of chlamydia. That is, ciprolet for chlamydia deprives the disease of the possibility of progression, which means that by defeating the bacteria that are in the body, you can count on a complete cure.
However, despite all of the above, Ciprolet is never prescribed as the only drug for treatment. Usually it, like other fluoroquinolones, is combined with immunomodulators, enzymes, antimycotics and antibiotics, thereby starving out diseases without giving it the opportunity to adapt to any type of medication.
When prescribing this fluoroquinolone, you need to be sure that the patient is not pregnant, not breastfeeding, and is 16+ years old.
Based on materials from www.zppp.saharniy-diabet.com
Is Tsiprolet an antibiotic or not? You will learn the answer to this question from the materials in this article. We will also tell you about the purposes for which the drug mentioned is used, whether it has side effects and contraindications, what it can be replaced with, etc.
“Tsiprolet” is a group of antibiotics that contain the active substance ciprofloxacin. In addition, this medication also includes additional substances in the form of injection water, hydrochloric acid, disodium edetate, sodium chloride and benzalkonium chloride in solution.
In what form can the drug “Tsiprolet” be purchased? Antibiotics are produced in different forms. As for the mentioned medication, it is available in the form of a solution for infusion, eye drops and tablets.
Is Tsiprolet an antibiotic or not? Of course yes. Its main active ingredient is ciprofloxacin. This component is a fluoroquinolone derivative.
The principle of action of the drug in question is to suppress DNA gyrase in bacterial cells. This effect of the drug leads to a disruption of DNA synthesis, as well as a slowdown in the reproduction of microbes and their growth.
What to expect after treatment with Tsiprolet? Antibiotics cause pronounced morphological changes, as a result of which microbial cells die. The bactericidal effect of taking this drug manifests itself not only during the division period, but also during the dormancy of gram-negative microorganisms.
As for gram-positive flora, in this case the bactericidal effect is exerted only during cell division.
Can the drug “Tsiprolet” have a detrimental effect on a person? Antibiotics are always harmful to the liver, as well as other organs of the gastrointestinal tract. However, it should be noted that the cells of the macroorganism do not contain DNA gyrase. This fact completely eliminates the possibility of toxic effects of the drug on the body.
It must also be said that such a drug does not cause resistance to other antibacterial agents. “Tsiprolet” exhibits particular activity against aerobic flora, enterobacteria, gram-negative flora, chlamydia, listeria, mycobacterium tuberculosis, yersinia, campylobacteria, proteins, mycoplasmas and others. At the same time, the mentioned medication does not have a bacteriostatic or bactericidal effect on Treponema pallidum (that is, the causative agent of syphilis).
Is the drug "Tsiprolet" absorbed? Antibiotics of this group are absorbed quite quickly from the gastrointestinal tract. This medication is able to penetrate bone tissue, saliva, muscle corset, skin, lymph, bile, kidneys, lungs, tonsils, liver, pleura, peritoneum, seminal fluid and ovaries.
The drug is excreted through the kidneys (about 50-70%). The drug is also excreted in the feces (20%).
Why is the drug "Tsiprolet" needed? Antibiotics (reviews of the medication will be presented below) are prescribed for many diseases.
The drug in question is especially effective in the following cases:
- diseases of the ENT organs (for example, tonsillitis, otitis media, pharyngitis, mastoiditis, sinusitis, sinusitis);
- bacterial lesions of the respiratory system (for example, with cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis, bronchitis, pneumonia, sore throat);
- diseases of the genitourinary system (for example, with salpingitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, oophoritis, tubular abscess, adnexitis, prostatitis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, chancre, pelivoperitonitis, pyelitis);
- skin lesions (for example, with phlegmon, abscess, burns, infected ulcers, wounds);
- diseases of the digestive system (for example, peritonitis, typhoid fever, salmonellosis, intraperitoneal abscesses, yersiniosis, campylobacteriosis, cholera, shigellosis);
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system (for example, sepsis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis).
Now you know for what purpose the drug “Tsiprolet” can be used. It helps very well with angina. However, this medicine is often prescribed for the prevention of infectious lesions after surgery.
The medication in the form of eye drops is used for conjunctivitis, blepharitis and barley.
Does the antibiotic we are considering have any contraindications? Like any medicinal product, the drug "Tsiprolet" also has some prohibitions for use. It is not used in pediatric practice (that is, until adulthood). This is due to the fact that it is at this time that the child’s skeletal system and skeleton as a whole are formed.
Also, the antibiotic drug should not be taken by women during pregnancy, intolerance to ciprofloxacin, or during breastfeeding.
For atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, mental disorders, cerebrovascular accidents, epilepsy, epileptic syndrome, severe kidney and liver pathology, as well as for elderly people, this medication is prescribed only after consultation with a specialist.
How should I take the drug "Tsiprolet"? Antibiotics (an analogue of this medicine will be named below) are used only as prescribed by a doctor after a medical examination.
Tablets are taken orally three times a day, 250 mg. If the patient has a severe course of the disease, then the dose is increased to 0.5 or 0.75 grams.
For infections of the genitourinary system, the drug is prescribed twice a day, 0.25 or 0.5 grams for 7-10 days.
For uncomplicated gonorrhea, tablets are used once in an amount of 0.25 or 0.5 grams.
For gonococcal infections (with chlamydia and mycoplasmosis), the medication is taken every 12 hours, 0.75 grams (for 7-10 days).
For chancroid, the drug is used twice a day in an amount of 500 mg.
Tsiprolet tablets are swallowed whole and washed down with liquid.
If you have been prescribed medication in the form of eye drops, you should instill 1-2 drops every 4 hours. In case of severe damage, the drug is used 2 drops every 60 minutes.
As the patient recovers, antibiotic consumption can be limited in frequency and dosage.
As for the “Tsiprolet” solution, it is administered intravenously (0.2 g) over half an hour. Treatment of osteomyelitis can take about two months.
After intravenous use of the drug, they switch to tablet form.
Absolutely all antibiotics, including Tsiprolet, have side effects. Therefore, they should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor.
Among the most frequently occurring undesirable effects are the following:
- increased sweating, insomnia, fainting, dizziness, thrombosis of cerebral arteries, anxiety, migraine, fatigue, various psychotic reactions, peripheral paralgesia, confusion, nightmares, depression, tremors of the limbs, hallucinations, increased intracranial pressure;
- vomiting, cholestatic jaundice, diarrhea syndrome, decreased appetite, flatulence, hepatonecrosis, epigastric pain, bloating, nausea, hepatitis;
- hearing loss, leukocytosis, tinnitus, granulocytopenia, impaired taste perception, development of anemia, diplopia, tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmia, drop in blood pressure;
- allergic response, arthralgia, urticaria, arthritis, tenosynovitis;
- polyuria, impaired nitrogen excretion of the kidneys, dysuria, interstitial nephritis, glomerulonephritis, hematuria, crystalluria.
There are many analogues of Tsiprolet. The following drugs are similar in composition: “Alox”, “Medociprin”, “Floximed”, “Ificipro”, “Ciloxan”, “Cipronate”, “Ciproxol”, “Cifran”, “Tsipromed”, “Ciprofloxacin”, “ Tsipropharm", "Tsiprol" and others.
As for the price, the medicine in question is not very high. Tablets of 500 mg can be purchased for 110 rubles (10 pcs.). The cost of eye drops and injection solution varies between 60-150 rubles.
Most reviews about the antibiotic "Tsiprolet" are positive. This drug helps treat many diseases. However, it should be remembered that it can only be taken in extreme cases.
Many patients leave negative reviews about this medication. As a rule, they are associated with the occurrence of side effects such as dizziness, weakness and difficulty breathing.
Based on materials from fb.ru
Today, the problem of treating chlamydia poses great difficulties for many doctors and patients, since often after treatment with antimicrobial agents, after a certain time, this insidious disease manifests itself again.
The problem is that most patients have chronic urogenital chlamydia, drug treatment for which is often ineffective.
Chlamydia trachomatis most often causes the following pathologies of the urogenital tract:
- urethritis in men and women (over half of all non-gonococcal urethritis),
- prostatitis and orchiepididymitis in men, cervicitis, salpingitis, endometritis,
- Combined organ damage is often observed (for example, urethritis, arthritis and conjunctivitis in the Reiter's syndrome program).
At the same time, there is a fairly extensive list of laboratory methods for diagnosing chlamydia, although the most reliable methods today are immunoassays with monoclonal antibodies (venous blood is used) and PCR diagnostics (usually scrapings of the endothelium of the urogenital tract).
In the treatment of chlamydial infection, as well as in the treatment of other infectious processes, the primary tasks are eradication of the pathogen and getting rid of acute or chronic inflammation of the genitals and urinary tract, which reduces the quality of life. Fortunately, a urologist, gynecologist or venereologist does not have a goal to reduce mortality from chlamydia, since dying from a chlamydial infection of the urogenital tract is very problematic.
An intermediate goal may be to avoid the chronicization of chlamydia, reduce the number of relapses of the chronic chlamydial process, as well as reduce the number of articular and ocular complications of urogenital chlamydia. We can also talk about the desire to reduce the number of complicated or miscarried pregnancies due to chlamydia and to avoid post-chlamydial infertility in both women and men.
With an active inflammatory process, a whole range of medications is required for a full course of treatment for chlamydia. The drugs used in treatment regimens are selected by the doctor taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, clinical symptoms of the disease, the severity of the inflammatory process and the results of all tests - immunogram, liver tests, general blood test, urine culture, PCR results, ELISA and other laboratory data.
Today, treatment standards do not require the use of immunostimulants or immunomodulators in the treatment of even complicated chlamydia. Drugs of these groups, with the exception of serious cytostatic drugs that have strict indications and are prescribed only after an immunogram, should not be used as drugs with unproven effects. The shamanism of a large number of urologists, venereologists or gynecologists in this area is more often explained by bonuses from pharmaceutical representatives or an attempt to lengthen and increase the cost of treatment for patients of paid clinics and medical centers.
All information about medications and treatment regimens is intended for informational purposes only. Treatment of chlamydia is prescribed only by a qualified doctor based on test results, taking into account the patient’s medical history, concomitant diseases, etc.
Eradication is essentially ridding the body of an infectious agent. Chlamydia is an intracellular resident, which, in addition to its main form, can exist in the L-variant (vegetative), which is not capable of exiting the cell and reproducing without significantly suppressing the host’s immunity, escaping from the effects of antibacterial agents or physical influences (increased temperature). The best way to treat chlamydia is with drugs from three antibacterial groups: tetracyclines, macrolides and fluoroquinolones.
It is worth noting that before starting therapy, sowing chlamydial cultures to determine sensitivity to antibiotics is not advisable, since studies conducted in 2000 at the Research Institute of Obstetrics and Gynecology named after. D.O. Otta RAMS, St. Petersburg, Research Institute of Physico-Chemical Medicine of the Russian Ministry of Health, Moscow, Institute of Clinical Bacteriology, Uppsala University, Sweden, showed that laboratory-resistant strains retained their sensitivity to antibiotics in patients.
Antimicrobial agents are the main ones in the treatment regimen for chlamydia. And as a rule, for chronic chlamydia, drug treatment consists of using a combination of 2 antibiotics. The duration of the course of treatment and individual dosage are determined by the attending physician depending on the type of disease and the dynamics of the inflammatory process.
When choosing an antibiotic for chlamydia, laboratory data to determine the sensitivity of the pathogenic microorganism to a specific antibacterial drug is indispensable. Therefore, it is advisable to supplement cultural methods of laboratory diagnostics with an antibiogram.
Doxycycline (Unidox Solutab, Dorix, Vibramycin, Vibra-Tabs). The Solutab form increases the bioavailability of the drug (that is, its penetration into tissues) by up to 93%.
Based on materials from zdravotvet.ru
Gonorrhea can only be cured with the appropriate antibiotic. Antibacterial therapy itself is fast and effective, but has its own nuances and characteristics. Gonococcus (the causative agent of gonorrhea) evolves, like all living organisms. Those bacteria that became resistant during the first course of treatment survive, multiply and cause the disease again. And if you skip the time of taking medications or do not pay attention to the recommendations of doctors, then the person in whose body this happened and all his partners will no longer be able to get rid of the infection with the same drugs.
We tell you how doctors treat gonorrhea in a variety of life situations.
Recently, the sensitivity of gonococcus to basic drugs has changed greatly. Studies conducted that examined the most common strains in Russia showed:
Structural formula of Ceftriaxone
- Ceftriaxone, a third-generation cephalosporin drug, has the highest activity against gonorrhea pathogens.
- Spectinomycin has approximately similar activity to it.
- The drug Ciprofloxacin has currently lost its high activity against gonorrhea pathogens. The sensitivity of gonococci to the drug is average. However, it is also a good alternative antibiotic.
- Penicillin drugs, due to their widespread use earlier, as well as tetracyclines now have low antigonococcal activity, and therefore are almost never used.
To reduce the development of resistance (insensitivity) of gonococci to antibiotics, their rational use is important. It involves the division of antibiotics into basic, alternative and reserve drugs.
The main drugs include antibiotics, which are highly active against the causative agent of gonorrhea. These are the number one drugs in treating infection. Treatment with them begins first of all according to the standard regimen immediately after laboratory diagnosis of gonorrhea. These include: Ceftriaxone and Cefixime.
Alternative drugs include a group of antibiotics with high and moderate activity against pathogens. They are used when other antibiotics are ineffective or intolerant. In the latter case, it is recommended to use alternative drugs only after individual sensitivity to them has been determined in the laboratory (bacterial culture).
The following alternative drugs are currently used: Spectinomycin and Ciprofloxacin.
Reserve antibiotics are drugs used only when other antibiotics are ineffective. They have high activity against the pathogen. They are prescribed only by a doctor and only after a course using primary and alternative drugs. If you use reserve antibiotics yourself, there will be a risk of developing a strain that is no longer sensitive to any modern antibiotics. The reserve drug for the treatment of gonorrhea is Ofloxacin.
Standard regimens recommended for treating gonorrhea include both injections and pills. The choice of drug form depends on the form and stage of the disease. For fresh acute uncomplicated gonorrhea, tablets can be used. However, preference should be given to administering the medicine through intramuscular injection: this way, gonorrhea can be cured faster and there will be fewer side effects. For all other forms and stages of gonorrhea, antibiotics are prescribed only in the form of injections.
Medicine for gonorrhea (gonorrhea) in tablet form:
- Cefixime – orally, one tablet of 400 mg or two tablets of 200 mg. The drug should not be used if you have a history of allergies to other cephalosporins or penicillin antibiotics. Use during pregnancy is possible, but consultation with a doctor is required.
- Ciprofloxacin - used orally, a single dose of 500 mg for acute uncomplicated gonorrhea and cystitis. Used only in case of ineffectiveness/intolerance of cefixime. It is also used for concomitant chlamydia, in this case the course lasts 10 days. Contraindicated during pregnancy.
- Ofloxacin - administered orally, once 400 mg. Used only when previous drugs are ineffective. For mixed infection (gonorrhea, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis) - 800 mg per day for 7-14 days. Contraindicated during pregnancy.
If you decide to treat gonorrhea with tablets, the parallel use of local drugs is highly recommended: antiseptic solutions, suppositories, ointments.
Antibiotic injections for gonorrhea:
Uncomplicated gonorrhea can be cured with one injection. The drugs are injected into the gluteal muscle. Complicated forms are treated intramuscularly and intravenously, in a hospital course.
- Ceftriaxone – 250 mg intramuscularly once. The drug is pre-dissolved in 2 ml of 1% lidocaine solution. Used in cases of gonococcal infection of the genitourinary tract and pharynx (pharyngitis). For gonococcal conjunctivitis, it is administered intramuscularly at a dose of 1000 mg, pre-dissolved in 3.5 ml of lidocaine solution. Approved for use by pregnant women, but prior consultation with a specialist is required. For complicated gonorrhea, 1000 mg is administered intravenously every 24 hours for 14 days.
- Spectinomycin - 2000 mg intramuscularly once. If there are complications, 2000 mg is administered intramuscularly every 12 hours for 14 days. The drug can treat gonorrhea in pregnant women, but only under the supervision of a doctor.
Antibacterial therapy is carried out with all the above drugs, taking into account individual contraindications. However, unlike men, in women, after a course of antibiotics, the normal microflora of the vagina is disrupted, which leads to fungal and bacterial vaginitis. Therefore, it is recommended to carry out local therapy with antifungal drugs and probiotics in parallel with antibiotics. The main topical preparations for women are sold in the form of vaginal suppositories:
- Suppositories containing lactobacilli : Acylact, Ecofemin, Lactobacterin, Laktonorm. The course is 10 days, 1 suppository at night.
- Antifungal vaginal suppositories : Isoconazole (Gyno-travogen ovulum) 600 mg, Clotrimazole 200 mg (Candide, Kanison, Candibene). The suppositories are inserted deep into the vagina using fingertips, immediately before bedtime.
Topical antiseptics (suppositories, ointments, creams) are used as an additional aid in antibiotic therapy, as well as to cure gonorrhea in pregnant women - as an alternative method if it is impossible to take the drug orally. Depending on the various manifestations of the disease, the following types of local therapy are used:
- for inflammation of the external genitalia : in the acute stage - warm sitz baths with a 0.01% solution of potassium permanganate or chamomile infusion (1 tablespoon per 2 cups of boiling water) - 10-15 minutes 1-2 times a day. In the subacute stage - lubrication with a 10% solution of protargol in glycerin.
- For urethritis (inflammation of the urethra): in the acute stage - deep rinsing and instillation of a 1-2% solution of protargol or collargol. In subacute - instillation of 3-5% protargol solution
- For vaginitis : vaginal suppositories with antiseptics (Hexicon, Betadine).
The use of any suppositories is contraindicated during menstruation. In this case, women are recommended to begin the course of treatment from the second day after the end of menstruation.
Many private clinics and pharmacies. companies offer special medications designed specifically for men. But all this is a deceptive marketing ploy. To treat gonorrhea, the same medications are used for both men and women. They include antibiotics of various groups, used according to standard regimens. The difference in treatment may only lie in the use of additional local therapy.
Men are recommended to wash the urethra daily with antiseptic solutions: 0.05% aqueous solution of chlorhexidine or 0.02% potassium permanganate.
It is also possible to wash the urethra with a 0.25-0.5% solution of silver nitrate, a 2% solution of protargol or 1% collargol, but these antiseptics are used only when urethritis is complicated (the appearance of a mild infiltrate) and are prescribed only by a doctor.
If the skin is affected, use warm baths with a 0.01% solution of potassium permanganate, 0.02% solution of furatsilin.
In most cases, gonorrhea is transmitted in combination with other sexually transmitted infections. If concomitant infections are added to anti-gonorrhea drugs, additional antibacterial therapy is prescribed, or a drug from the fluoroquinolone group (Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin) is prescribed with an extended course of treatment.
- Ciprofloxacin – orally, once 500 mg for 10 days, or
- Ofloxacin - orally, 800 mg per day for 7-14 days, or
- Doxycycline (in addition to Cephalosporins, Spectinomycin) : orally, 100 mg 2 times a day for 7 days, or
- Erythromycin (in addition to the main treatment) – 0.5 g orally every 6 hours for 10 days
For the treatment of concomitant trichomoniasis:
- Metronidazole (in addition to the main treatment) 500 mg 3 times a day for 7 days, or
- Tinidazole 2g orally once a day for 3 days
For the treatment of concomitant syphilis:
For 6 weeks after infection, syphilis may not show up in laboratory tests. When co-infected with other sexually transmitted infections, this period is extended. Therefore, preventive (preliminary) treatment of syphilis is recommended simultaneously with treatment of gonorrhea.
If tests for syphilis are negative:
- Bicillin 5 – intramuscularly, 1.5 million units, just two injections per week, or
- benzylpenicillin novocaine salt – intramuscularly, 600 thousand units 2 times a day, course – 7 days
If tests are positive for syphilis:
- Bicillin 1 – intramuscularly, 2.4 million units – once every 5 days, for 12 days, or
- Benzylpenicillin (novocaine salt) – intramuscularly, 600 thousand units – 2 times a day, course of treatment – 20 days
Based on materials from polovye-infekcii.ru
"Tsiprolet": the main advantages of the drug
The drug "Ciprolet" is a fluoroquinolone of the latest generation. The name of the active substance is ciprofloxacin hydrochloride. Its range of therapeutic effects is wide. The priority over other antibiotics is as follows:
- influence on different groups of microbes;
- duration of emergence of resistance to it;
- accumulates in the affected area after a few hours;
- penetrates well into the bladder tissue;
- quickly affects the pathogen;
- lasts a long time in the hearth;
- it is convenient to take;
- does not harm the body’s own flora;
- does not irritate the intestinal tract.
It is recommended to immediately treat inflammation of the bladder with an antimicrobial agent that is sensitive to the agents that caused the process. If the infection is only slightly “muffled”, in the future this will lead to chronicity of the disease. Therapy will then be long and complex.
Application
Quite often, doctors prescribe Metronidazole along with Tsiprolet. This is due to the fact that compatibility enhances the antimicrobial activity of drugs.
The following indications exist for the use of drugs in combination:
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the gynecological area;
- severe infections caused by anaerobic microorganisms;
- infectious and inflammatory lesions of the peritoneum, severe, complicated by peritonitis.
- infection with protozoa causing mixed abdominal infections.
Use for cystitis
The drug is produced in the form of tablets with a dosage of 250 and 500 mg, there are infusions of 100 ml. Eye drops are also used in medical practice, but they are not used often. An aqueous solution for intravenous administration is prescribed for complicated courses.
It is recommended to take “Tsiprolet” for cystitis in tablet form. Only in severe cases is it administered into the bloodstream in a hospital setting. In this case, the drug is prescribed first by infusion and then orally. This way, the maximum therapeutic effect is immediately achieved, then maintenance treatment is necessary.
According to the instructions, acute uncomplicated cystitis requires taking 1 tablet of 500 mg or 2 tablets of 250 mg twice a day for three to five days. If there is no improvement in the condition, the drug is discontinued and another one is prescribed. When symptoms alleviate, the dose is reduced (250 mg every 12 hours) and administration is extended to 7 days. Usually the course lasts no more than 10 days.
If an exacerbation of a chronic process occurs, the treatment regimen will be as follows: 500 mg per day for a total duration of one week.
It is recommended to take the tablets before meals, preferably on an empty stomach. You need to take the drug with plain water.
All substances containing calcium reduce the ability of Tsiprolet to be absorbed, so the amount of dairy products is limited during the period of administration.
Contraindications and side effects
Like every medicinal drug, Tsiprolet causes negative reactions and consequences during use. Contraindications include severe individual sensitivity to the substance. The medicine is also not prescribed to teenagers and children: it can have a bad effect on bone formation. If there are problems with the intestines, the drug may increase their manifestations.
The periods of gestation and breastfeeding are a special time when women are very cautiously recommended to take any medications. Patients with confirmed atherosclerosis require special attention. The doctor also takes into account all possible complications when treating cystitis.
Negative consequences of taking the drug include:
- problems in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels;
- changes in the condition of central and peripheral nerves;
- disruptions of the gastrointestinal tract;
- deterioration in the formation of blood cells;
- allergies;
- increased sensitivity to light.
The drug is well tolerated, negative reactions and consequences are quite rare. The condition may worsen in the form of changes in heart rate and shortness of breath. This sometimes happens after taking a loading dose in patients with a history of vascular and cardiac problems. When the drug is discontinued, all the negativity goes away.
Possibility of use in complex therapy
The inflammatory process of the bladder in women is often accompanied by problems of the ovaries, uterus and uterine appendages. This complex is usually caused by an association of microorganisms. This means that several drugs with different effects are used for treatment. They combine antibacterial drugs of different spectrums. "Tsiprolet" for cystitis in women is prescribed with anti-inflammatory substances, painkillers, nitrofuran group drugs and sulfonamides.
Men get cystitis less often. This disease is provoked by the following reasons:
- prostate problems;
- foci of chronic infection;
- infection through sexual contact.
Congestion and inflammation of the prostate contribute to the spread of the process to the bladder. When the first symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor. The doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment. Since there may be several reasons, comprehensive therapy is recommended. They use not only anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulatory drugs, but also antimicrobial drugs of different spectrum.
Among the fluoroquinolones used:
- "Tsiprolet";
- "Nolitsin";
- "Tsifran".
Prostatitis requires strict adherence to the duration of treatment and dosages of drugs. Medical consultation and laboratory diagnostics are required. The doctor takes into account the characteristics of the course, sources of infection, and the presence of chronic foci.
“Tsiprolet” is not recommended to be combined with magnesium, zinc, iron, and aluminum. These elements need to be taken into account in medicines and foods. The interval between the use of such incompatible substances is about three hours.
The rate of absorption of the drug is slowed down by antacids. They are taken 4-5 hours before using the described medication. This recommendation can be applied, for example, to Didanosine.
The combination of large doses of ciprofloxacin with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can provoke seizures. The exception is acetylsalicylic acid. If it is necessary to take the drug simultaneously with Cyclosporine, the negative effect on the kidneys should be taken into account. When using Theophylline in parallel, its content in the blood is monitored. The dose is adjusted according to the indicators to avoid complications.
Actions in case of overdose
In order to avoid unwanted reactions, the drug should be prescribed by a doctor. He also controls the duration, effectiveness and dosage of treatment. The drug is well tolerated and rarely causes adverse reactions. Overdoses occur occasionally. Their danger is that the antidote for ciprofloxacin is not known to medicine.
If severe diarrhea and other symptoms of poisoning appear while taking the drug, stop taking the drug immediately. Emergency measures include gastric lavage with special substances, while giving plenty of fluids and monitoring the patient. If the measures do not have the desired effect, hemo- or peritoneal dialysis is performed.
Nystatin
Nystatin is a medicinal antifungal drug that has a fungistatic effect. Available in the form of tablets (250,000 and 500,000 units), vaginal and rectal suppositories, and ointments.
Pharmacological action of Nystatin
According to the instructions, the active ingredient of the drug is nystatin.
Excipients of the tablets are emulsion KE-10, pigment titanium dioxide, vanillin, Tween 80, methylcellulose, stearin, medical talc, stearic acid, milk sugar, potato starch.
An auxiliary component of Nystatin suppositories is a fat base. The ointment contains excipients such as medical petroleum jelly and anhydrous lanolin.
According to the instructions, Nystatin is a polyene group antibiotic produced by the actinomycete Streptomyces noursei.
The components of the drug bind to stearins in the cell membranes of fungi, which leads to their inability to function as a selective barrier, and this causes the loss of their main cellular components.
The action of Nystatin is aimed at defeating pathogens of mold mycoses, sporotrichosis, chromomycosis, blastomycosis (deep and visceral), and dermatomycosis. The drug is effective against some pathogenic protozoa.
When used, Nystatin affects the yeast-like fungi Candida and Aspergillus. The medicine blunts the development of vegetative forms of dysenteric amoebae in the intestines.
Nystatin has been noted to be highly effective for thrush.
In accordance with the instructions, Nystatin in all forms of release is not active against viruses, actinomycetes and bacteria.
When applied locally and externally, the drug is not absorbed through the mucous membranes and skin. When administered internally, Nystatin is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. It is excreted unchanged from the body along with feces.
Indications for use of Nystatin
Nystatin is prescribed for the prevention and treatment of fungal diseases of internal organs, mucous membranes, skin, and gastrointestinal tract, which are caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. These include candidiasis of the skin, mucous membranes and internal organs, candidiasis of the oral cavity and vagina.
Nystatin is prescribed for thrush, as well as for the purpose of preventing the development of candidiasis while taking high doses of antibiotics (especially tetracyclines) to young children, debilitated patients and the elderly.
Methods of using Nystatin and dosage
Adults should take Nystatin tablets 500,000 units 3-4 times a day or 250,000 6-8 times a day; for the treatment of severe candidiasis of internal organs and candidosepsis - 500,000 units 6-8 times a day. For children, the dosage of Nystatin tablets depends on the age of the child: up to 1 year, ¼ tablet of 250,000 units is prescribed, 1-3 years - 1 tablet. 250,000 units, from 3 years – 250,000-400,000 units. The frequency of taking tablets for children is 3 times a day.
Nystatin ointment for mycoses of the mucous membranes, skin dermatitis and fungal complications that arise when taking antibiotics is applied to the affected surfaces 2 times a day until the symptoms of the disease completely disappear.
For thrush, Nystatin is prescribed in the form of suppositories. Nystatin suppositories are also recommended for the treatment of candidiasis of the lower intestines, vulvovaginitis and colpitis. Rectally, 1 suppository is injected deep into the rectum 1-2 times a day. Use 1 Nystatin suppository intravaginally 2 times a day.
The duration of the course of use of Nystatin is 10-14 days.
In case of relapses, it is recommended to carry out repeated courses of treatment with the drug at intervals of 2-3 weeks.
A combination of local treatment with oral Nystatin is effective.
Side effects of Nystatin
Nystatin in all forms of release can cause the development of adverse reactions in the form of allergies, accompanied by rashes, skin itching, skin hyperemia, and urticaria.
When using Nystatin suppositories, vaginal irritation is possible; when taking Nystatin tablets, a bitter taste in the mouth, nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea may occur.
Contraindications to the use of Nystatin
The medicine is not prescribed to patients with hypersensitivity to its components, liver dysfunction, peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, or pancreatitis.
According to the instructions for Nystatin, the drug can be used during pregnancy and lactation.
Overdose
According to reviews, overdose may increase side effects.
Additional Information
During Nystatin therapy for thrush, you should abstain from sexual intercourse. Joint treatment of both sexual partners is also recommended.
In accordance with the instructions, Nystatin should be stored in a cool, dark place out of reach of children.
Nystatin is available from pharmacies with a doctor's prescription.
Shelf life – 24 months.
zdorovi.net
Drug substitutes for the treatment of cystitis
In case of inflammation of the bladder, preference is given to remedies that quickly help. In addition, the minimum number of side effects, ease of administration, and low price are important. Prescribed for cystitis, “Tsiprolet”, according to patient reviews, is such a drug. If therapy was started on time, the drug will overcome the disease easily and without negative reactions.
About 40 drugs with similar effects are registered. The main one is “Medociprin.” The most common are “Tsifran”, “Tsipromed”, “Tsiprinol”, “Ciloxan”, “Ecotsifol”. The active ingredient is ciprofloxacin.
The attending physician should select similar medications. It is not recommended to do this on your own. The wrong choice may not only not give the desired result, but also worsen the situation.
Patients and specialists about the medicine
The opinions of patients suffering from cystitis are almost all positive. It is noted that the therapeutic effect occurs on the second or third day of administration. Symptoms go away quickly and easily. It is convenient to take the drug, the price is pleasantly surprising.
"Tsiprolet", used for prostatitis, according to men's reviews, works without causing side effects. I really like that you can take it once a day. The only thing I don’t like is that you can’t combine it with dairy products and alcoholic drinks.
Doctors note the rapid onset of positive dynamics. It can be prescribed from the first hours of the disease, without waiting for sensitivity tests. It does not affect the body’s own flora and does not require subsequent corrective treatment. Therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis and does not require constant monitoring.
Is it possible to drink alcohol while being treated with Trichopolum?
The simultaneous use of medications and alcoholic beverages is not recommended in most cases. Trichopolum and alcohol are also incompatible. The active substance of the drug interacts with ethyl alcohol and forms compounds dangerous to the human body.
Trichopolum is utilized by the body for a very long time, and in case of alcohol poisoning of the liver, elimination is even slower. The compatibility of the drug with alcoholic beverages is absolutely excluded due to the sharp depression of the central nervous system.
Drug interaction with alcohol
The drug is 100% incompatible with any alcoholic beverages. Alcohol disrupts the metabolic processes of the liver, which causes serious harm to the body. The nervous system, as well as the gastrointestinal tract of the drinker, is especially affected.
A patient taking alcohol simultaneously with Trichopolum may experience the following negative reactions:
- abdominal pain will appear;
- your head will feel dizzy;
- nausea and vomiting will occur;
- the skin will turn red;
- blood pressure will decrease;
- cold sweat will appear.
The consequences of the combination will continue both during the treatment period and for some time after its completion. The severity of side effects is directly related to the strength of the drinks and the volume of alcohol consumed. An allergic reaction can be expressed in the appearance of anaphylactic shock and edema:
- pharynx;
- nose;
- faces;
- Quincke.
You should not drink Trichopolum or alcohol in large doses. Serious consequences can occur: fainting, convulsions and loss of consciousness. Death is also possible.
All clinical symptoms appear within a short time after drinking an alcoholic drink and may remain until detoxification measures are carried out.
Treatment methods for poisoning
With mild poisoning, the symptoms are erased. They can be easily eliminated using activated carbon or any sorbent (Enterosgel, Smecta). The compatibility of Trichopolum with these drugs is beyond doubt.
When treating with Trichopolum, avoid taking medications that contain ethyl alcohol. These include syrups, balms and alcohol tinctures.
It is undesirable to use preparations for external use containing alcohol. It can provoke an allergic reaction. This applies to all perfumes and cosmetics. They also contain ethanol.
The period of elimination of the drug by the kidneys is quite long, so you can drink alcohol only 2 days after the complete end of therapy.
Trichopolum is used to treat patients who suffer from chronic alcoholism. When combining alcohol and Trichopolum, a disulfiram-like reaction is caused. The person experiences a very uncomfortable state. At the same time, there is complete disgust for alcoholic beverages. The patient stops drinking alcohol. This compatibility is used by doctors to treat chronic alcoholics.
Alcohol in the body always very quickly decomposes into metabolites (non-toxic breakdown components). When Trichopolum is consumed with alcohol, this property of the substance is disrupted. Decay products accumulate, causing characteristic symptoms. A person endures this condition very painfully.
If the patient has suffered a disulfiram-like reaction even once, a persistent aversion to alcoholic beverages will be formed. The condition manifests itself as:
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Our readers successfully use Intoxic to get rid of parasites. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention.
- hypotension;
- redness of the face and body;
- heart rate increases;
- noise in the head;
- difficulty breathing;
- feelings of fear of death;
- vomiting and nausea.
The duration of such a reaction and its treatment are proportional to the dose of the drug and the volume of alcohol. Blood pressure may drop quickly and the person may lose consciousness.
Treatment of chronic alcoholism with medications is prescribed in courses. This allows you to prevent exacerbation of the disease (drinking alcohol again).
People with chronic alcohol dependence cope with the desire to drink again under various stresses, which previously led to a new binge.
Therapy is carried out 2 times a year in courses of 2 weeks. The treatment regimen is selected by the doctor.
But Trichopolum cannot be prescribed independently; it should only be part of a complex treatment.
It is strictly forbidden to combine the drug Trichopolum and alcohol with the consumption of alcoholic beverages!