One can understand the confusion of a person who discovers holes in his tonsils. In fact, there is indeed cause for alarm - this symptom indicates a serious pathological process in the oral cavity. And if adults have hope of doing without a protective barrier, the role of which is played by the tonsils, then in children, whose body and immunity are not yet fully strengthened, this disease poses a threat to health.
To prevent holes in the tonsils (tonsils) from causing complications, you need to promptly pay attention to alarming symptoms, identify the cause of their formation and receive qualified medical care.
Holes in the tonsils: what are they?
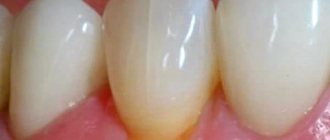
Normally, in a healthy person, the tonsils are structured like a porous sponge and contain approximately 20 depressions (lacunae), which are designed to contain pathogens. During illness, this first line defense mechanism prevents the infection from progressing further.
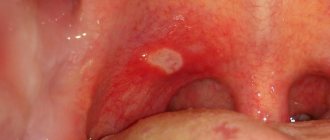
Microbes settle in the gaps - clots of white or yellow pus become noticeable on the tonsils; by the way, these are the only tonsils in the body that you can see for yourself.
This organ has the ability to recover on its own and after treatment, the tonsils take on their previous appearance, becoming whole, dense, covered with pale pink mucous.
Holes in the tonsils: photo
In the case of frequent illnesses, complications, or reduced immunity, this process is disrupted and the lacunae are closed with degenerated lymphatic tissue, which visually looks like holes in the palatine tonsils. These holes become collections for food debris, bacteria, and dead epithelial cells, which form purulent plugs.
When asked what kind of holes are in the tonsils, the doctor diagnoses the patient with chronic tonsillitis.
What are the symptoms?
In addition to visual identification, holes in the tonsils are accompanied by other symptoms that should alert you. These include:
- swelling of the palatine tonsils;
- sensation of a foreign body in the throat;
- discomfort when swallowing, inability to perform a full act of swallowing;
- expectoration of white lumps (caseous plugs);
- foul breath that cannot be masked by anything;
- elevated body temperature (sometimes).
Together, these symptoms indicate the development of an inflammatory process in the throat.
Severe tonsillitis tonsillitis
The most serious pathology caused by the active reproduction of streptococcus or the penetration of viruses of various natures is considered to be sore throat. It is very important to diagnose in time to prevent the development of serious complications.
As a result of normal hypothermia, a person’s immunity weakens, and bacteria and viruses begin to actively colonize new territories. With an advanced cold, tonsillitis develops, the signs of which are:
- Weakness, headache, fever. Body temperature rises to 39 C.
- Sensation of a foreign body in the throat, difficulty swallowing saliva and eating.
- Change in color of the tonsils to red, increase in their size, loosening, whitish coating.
- In places where there were pits, nodules filled with pus can be seen on the tonsils, which are opened as a result of regular rinsing.
- The lymph nodes in the neck enlarge, which the specialist feels upon palpation.
Tonsillitis is not only a consequence of the inflammatory process if there are holes in the tonsils, but in itself actively contributes to the formation of new depressions. It is very important to treat sore throat thoroughly and promptly in order to prevent pathologies such as damage to the heart, kidneys, joint and bone tissues.
Causes of holes in tonsils
Holes in the tonsils cannot just happen. Their appearance means an active increase in lymphocytes (the body's defenders), in tissue cells that begin to divide and grow.
As a result, the tonsils acquire a loose, deformed structure. The reasons why holes remain after traffic jams include:
- bacterial infections. Due to the proliferation of microbes, the lymphatic tissue of the tonsils becomes swollen, which leads to the expansion of natural lacunae;
- rehabilitation period after illness. The tonsils need some time to recover in size after suffering a viral disease;
- frequent hypothermia;
- enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsils (adenoids). This pathology is accompanied by a chronic inflammatory process;
- inflammation of the maxillary sinuses, which is characterized by the accumulation of large amounts of pus;
- dental diseases;
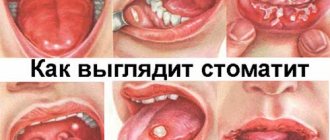
- dental infections of the oral cavity – stomatitis, inflammation of the tongue, gingivitis;
- congenital or acquired deformation of the nasal septum.
When the throat hurts very badly and holes in the tonsils, which are filled with pus, appear as a result of lacunar tonsillitis.
All these factors significantly reduce the body’s defenses, as a result of which the tonsils, being the center of attack of pathogenic bacteria, become deformed.
Treatment
You can get rid of holes in the tonsils only by eliminating the inflammatory process in them. It is unlikely that you will be able to cope with the problem on your own, but the doctor will help you do everything correctly and in the shortest possible time. Bacterial tonsillitis and exacerbation of tonsillitis cannot be avoided without the prescription of antibiotics, taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen (for a period of at least 10 days).
In the chronicization stage, a special place is occupied by washing lacunae with antiseptic solutions (for example, furacillin). In these cases, you can use the vacuum method, which is more effective than introducing liquid from a syringe. Complex treatment also includes physiotherapy: UHF, electro- and phonophoresis, laser therapy, microwave exposure. To increase the overall reactivity of the body, immunostimulants and vitamins are indicated. If conservative methods fail to remove inflammation and purulent plugs in the lacunae, then the tonsils are removed (tonsillectomy).
People with inflamed tonsils can find holes in their tonsils. And this state of affairs is unpleasant. And in order to protect yourself from complications and eliminate the problem in a timely manner, you need to seek qualified medical help. The doctor will assess all risk factors, conduct a diagnosis and be sure to prescribe effective treatment.
Do I need to see a doctor?
If, with the help of a mirror, a hole was discovered in the tonsil, and there is pus inside, this is a serious reason to consult a doctor, since in this way only a small part of the inflammatory process can be seen.
Moreover, it is categorically impossible to remove these accumulations of pus on your own - even the slightest damage to the lymphoid tissue can provoke the spread of infection throughout the body, including blood poisoning.
Cases where there are holes in the tonsils, but they are without pus, should not be ignored by doctors either. The presence of such a deformation indicates the absence of a natural barrier to infections and is a favorable environment for the free proliferation of pathogenic microbes.
First, you can seek help from a general practitioner, who, if necessary, will refer the patient to specialized specialists - an otolaryngologist or an ENT surgeon.
General information
The palatine tonsils, or simply called tonsils, are the central lymphoid formation of the pharyngeal ring. They are the first barrier to infectious agents, and therefore play an extremely important role for the human body. In the tonsils, the maturation of lymphocytes occurs - the main elements of the immune system, which participate in cellular and humoral (due to the antibodies produced) protection. In addition, they participate in local digestion processes, producing enzymes: amylase, lipase, phosphatase.
The tonsils have certain morphological characteristics that allow them to occupy a special place in the physiology and pathology of the pharyngeal ring:
- The lacunae turn into deep crypts that penetrate the entire thickness of the tonsil.
- The epithelium is in contact with lymphoid tissue over a large area; it is easily permeable to cells and antibodies.
- On the side, the tonsils are covered with a dense capsule.
- They have a rich blood supply; quite large vessels pass nearby.
After 14 years, the lymphoid tissue of the pharynx undergoes reverse development (involution). The follicles are gradually replaced by connective and adipose tissue. This process continues throughout life - until old age. The surface of the tonsils, accessible to direct inspection, is smooth, smooth or lumpy, pink. The size of the organ is very variable: in some people the tonsils are hidden behind the anterior palatine arches, while in others they protrude quite far beyond their edges.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
At the appointment, the doctor examines the tonsils using a laryngeal mirror, a magnifying glass and a light source, collects anamnesis, and states the general condition.
Additionally, he examines the nasal cavity and auditory canals. To make a diagnosis and identify concomitant diseases, the doctor gives directions for laboratory and diagnostic tests:
- General and biochemical blood test. Indicators of the levels of red blood cells, leukocytes and platelets will help determine the presence of an inflammatory process or any neoplasms;
- general urine analysis. Necessary for detecting pathological processes in the body that reduce immunity and worsen the patient’s condition;
- smear for bacterial culture. Epithelial cells of the pharynx will help determine the type of pathogenic organisms, which will help in choosing the right therapeutic tactics.
Bacterial studies are carried out with a button probe, which is inserted to determine the presence of adhesions characteristic of chronic tonsillitis.
If a malignant neoplasm is suspected, a biopsy of the lymphoid tissue of the throat is performed.
Additional diagnostics
To establish the nature of changes in the tonsils, the doctor requires the results of additional diagnostics. Therefore, after a clinical examination, he will refer the patient for laboratory tests:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Blood biochemistry (acute phase indicators).
- Throat smear (cytology, culture).
And with the help of instrumental methods it is possible to identify functional and organic disorders in the internal organs that may accompany chronic tonsillitis (ECG, ultrasound of the kidneys).
Treatment methods
You can get rid of holes in the tonsils filled with pus only by eliminating the true cause of the inflammatory process. Self-medication in such cases is contraindicated, since only an experienced doctor will be able to provide complex therapy, minimizing serious complications.
Taking antibiotics
When pus accumulates in the lacunae, broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are used, which not only inhibit the proliferation of bacteria, but also completely destroy them. Depending on the type of pathogenic pathogens, drugs such as Azithromycin, Tsiprolet, Amoxicillin are prescribed.
Washing tonsils in the ENT office
To clean them of purulent plugs, a syringe with a special attachment is used, which directs the disinfectant composition directly into the lacunae. A jet under pressure knocks out the plugs, and the tonsils are cleared. For full results, at least 15 sessions are required.
Vacuum lavage of the tonsils is carried out under local anesthesia using a device. A special nozzle is attached to the tonsil, and the purulent contents are sucked out through it. The tonsils are then treated with an antiseptic to prevent relapse.
Another device, Tonsilor, is actively used by doctors to treat purulent tonsils. The impact on the tonsils is carried out using ultrasound and vibrations transmitted by a special attachment. When the purulent plug becomes pliable, it is washed out with a medicinal solution, which is delivered in a strong stream.
Physiotherapy
The most popular and effective procedures are using:
- ultraviolet rays, which have a powerful antibacterial effect;
- laser, which activates blood and lymph flow in the tonsils, relieves inflammation;
- ultrasound, with the help of which medications penetrate deep into the tissue of the tonsils.
Also, throughout the entire treatment, the doctor prescribes rinsing the mouth and throat with antiseptic solutions (Furacilin, Miramistin), taking immunostimulating drugs, and vitamin complexes.
Operation methods
Classic loop removal
The correct medical name for this operation is extracapsular tonsillectomy, which is performed using a special loop. The method is traumatic and is currently rarely used. Typically used when the patient has a peritonsillar abscess.
Application of an ultrasonic scalpel
The ultrasonic scalpel vibrates with enormous frequency and raises the temperature in the tissues of the operated area up to 80 degrees. This makes it possible to minimize the likelihood of bleeding. However, it may cause burns. Therefore, the art of the surgeon is of great importance - only in skillful hands is an ultrasonic scalpel completely safe and allows you to avoid postoperative complications.
Radiofrequency ablation
With this approach, radio waves are converted into thermal energy, which enters the tissue of the tonsils through a special probe.
The main advantage of this approach is an easy postoperative period, which makes it possible to almost immediately return to your usual routine of life at work or school.
The disadvantage of this method is that it is impossible to completely remove the tonsil the first time. Therefore, in cases where complete tonsillectomy is required, radiofrequency ablation is not used. But it is actively used for tonsil hypotrophy, when only part of them needs to be removed.
Electrocoagulation
Removal is carried out with high frequency electric current.
The method is traumatic, as it involves heating the tissues of the tonsils to 400 degrees and charring them. The likelihood of bleeding with this approach is minimal. But the postoperative period is long and painful, as severe tissue burns occur.
Moreover, despite the severe burn, the tonsils cannot be completely removed at one time. And if a complete tonsillectomy is indicated, the procedure is repeated more than once.
Cryodestruction
In everyday life, this method is called “cauterization with liquid nitrogen.” Exposure to low temperatures (-190 degrees) kills tonsil tissue.
The death of frozen tissue of the tonsils occurs gradually. Complete healing occurs in at least a week. Often two. During this time, the patient is forced to constantly gargle to wash out dead pieces of tangerine.
The method is shown for partial removal while preserving the deep layers. It is often possible to preserve the lacunae of the tonsils by simply making them less deep.
Pros of this approach:
- bloodlessness;
- low pain during the operation itself, allowing the patient to be given lighter anesthesia;
- speed of manipulation (2 minutes is enough for each tonsil);
- good tolerance of the procedure by children.
Laser exposure
There are several types of tonsil surgery performed with a laser. Each type of surgical intervention requires the use of a certain type of laser.
- Fiber optic is used for complete tonsillectomy, indicated for severe inflammation.
- Holmium is used to eliminate local foci of infection inside the tonsils, without completely removing them.
- Infrared is used when it is necessary not only to remove part of the tonsils, but also to sew together their remaining fragments.
- Carbon allows you to evaporate part of the lymphoid tissue. Indicated for hypertrophy.
Any type of laser surgery is characterized by the absence of bleeding, the speed of manipulation, and a low likelihood of infectious complications.
Microdebrider
The method involves the use of a device that, rotating at high speed, cuts off part of the lymphoid tissue. This approach is considered low-traumatic, as it has a short recovery period after surgery. Used only to remove part of the tonsils during hypertrophy. Not suitable for complete tonsillectomy.
Coblation, or coblation
Or bipolar radiofrequency ablation. The most advanced method for removing tonsils.
The colbator device generates a stream of ions that passes through the tonsils, destroying them. Unlike other modern methods associated with strong tissue heating, this approach heats the lymphoid tissue only to 60 degrees.
Pros:
- the ability to accurately control the amount of lymphoid tissue removed, including in hard-to-reach places;
- low pain of the operation;
- no bleeding;
- rapid recovery after intervention;
- low risk of complications;
- Possibility of use in weakened patients of any age.
Anesthesia methods
Traditionally, tonsils were removed under local anesthesia. To do this, a solution of lipocaine or another anesthetic mixed with adrenaline (to reduce bleeding) was applied around the surgical field.
This anesthesia is called infiltration anesthesia. These days it is still used in most cases.
However, recently, tonsillectomy is often performed under general anesthesia. This is due to the fact that new drugs have appeared that make general anesthesia no longer such a difficult test for the body as it was before. And since many patients have a difficult time undergoing the operation purely mentally, in good clinics they are offered to resort to general anesthesia.
How to treat at home?
Trying to remove purulent plugs at home is not worth it because of the huge risk of complications. However, for disinfection and strengthening local immunity, traditional medicine recipes can be useful. Suitable for rinsing:
- decoction of onion peels. It must be washed, poured with a small amount of water, brought to a boil and simmered over low heat for 5-7 minutes. Then let the broth brew for at least 3 hours. Use warm;
- beet juice. The root vegetable, crushed in a blender, is sprinkled with table vinegar and left on the table for several hours. Then the juice is squeezed out of the grounds and gargled with it;
- herbal infusion. Pour dry raw materials of chamomile, calendula and plantain into a thermos, pour boiling water over everything and leave to steep for several hours. Gargle after every meal;
- soda-salt solution. Dissolve a teaspoon of salt and soda in a glass of water, mix and use several times a day. The solution has a powerful antiseptic effect.
Rinsing should be done with your head thrown back so that the medicinal composition affects the tonsils as far as possible. The duration of each rinse should be at least 20 seconds.
Do they grow on their own?
If after a sore throat there are holes in the tonsils, the likelihood that they will completely heal is minimal, these holes will remain forever. You must be prepared for the fact that a caseous plug will form again at the mouth of the lacuna, do not start this process, and undergo treatment on time.
How to treat white plaque on the tonsils?
Fluconazole is effective if the cause of plaque on the tonsils is a fungus
It is not the plaque on the tonsils that needs to be treated, but the disease that caused its appearance. Pharyngitis and tonsillitis are treated with the following means:
- antiseptic solutions for gargling,
- lollipops containing antiseptic,
- throat sprays,
- antibiotics (strictly as prescribed by the doctor),
- immunostimulants,
- antipyretics (at high temperatures).
As a first aid, you can try gargling with a solution of soda or sea salt (one teaspoon per glass of water), iodine (5 drops per 250 ml of water), chamomile or calendula decoction. Among the lozenges for sore throat, we recommend Strepsils, Septefril, Hexoral. This will relieve pain and discomfort, but will not replace complex therapy, so you will still have to see a doctor.
Stomatitis is treated with local remedies - sprays and antiseptic solutions. In case of a bacterial infection, you can gargle with Furacilin solution, for the preparation of which you need to grind one tablet into powder and dissolve in a glass of water. Rinsing is carried out 3-4 times a day.
Oral candidiasis is treated with the following remedies:
- antifungal drugs in tablets (Fluconazole, Nystatin),
- ointments for treating the oral cavity (Candide, Clotrimazole),
- antiseptic mouth rinses,
- drugs to enhance immunity.
Treatment is selected by the doctor individually for each patient. As first aid for candidiasis, you can use a soda solution for mouth rinsing - a teaspoon of soda in a glass of water. This remedy will reduce discomfort and eliminate plaque on the tonsils due to thrush, although not for long.
What can be dangerous: possible complications
If tonsils with holes are ignored, the consequences can be very serious and even life-threatening. It's all about the high risk of infection getting from purulent lacunae into the blood. This can cause the following complications:
- cystitis;
- inflammatory process in the kidneys;
- persistent sore throat;
- toothache;
- pathological processes in the nasopharynx;
- inflammation of the respiratory tract;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- meningitis.
Purulent tonsils, as a constant source of infection, are very dangerous due to their close connection with the digestive, respiratory and circulatory systems.
Untimely and incorrect treatment can lead to an increase in the number of holes in the tonsils and an increase in the inflammatory process.
Features of the postoperative period
- Within 2-3 days after the operation, white spots are clearly visible on the back of the throat, which gradually become paler and paler. These are scabs formed in place of lymphoid tissue, which are a normal consequence of the removal of the tonsils and disappear after 2 weeks.
- Many patients complain of nasal congestion caused by swelling in the nasopharynx. Swelling can persist for quite a long time - up to several months.
- Snoring is a common consequence of the operation. Moreover, it occurs even in young children. It usually goes away within a few weeks.
- The timbre of the voice may change.
- Sometimes bad breath occurs.
- In the first days after surgery, there is an increase in body temperature, usually to subfebrile levels.
- Of course, after tonsillectomy, as after any other surgical intervention, pain occurs. The pain is most severe the day after surgery. It often radiates to the ears and cervical lymph nodes. Vividly intensifies when swallowing.
Complete epithelization of the wound formed at the site of the tonsils is completed three weeks after the intervention. By this point, most of the unpleasant symptoms have passed.
When is surgery needed? Surgical removal
Removal surgery is needed only if their tissues are irreversibly atrophied, and constant sore throats seriously undermine the body. The surgical procedure is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia and gets rid of caseous plugs forever. Rehabilitation takes place in a hospital under the supervision of a doctor and takes up to 6 days.
Another method of removing tonsils is cryodestruction. When exposed to low temperatures with the help of liquid nitrogen, the tonsils are completely destroyed. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and takes only a few minutes. Hospitalization after manipulation is not required.
Peritonsillitis
This name is given to the inflammatory process that develops in the fatty tissue surrounding the tonsil. Peritonsillitis develops as a result of insufficiently effective or incomplete treatment of ordinary bacterial tonsillitis, general weakness of the patient (state of immunodeficiency, systemic metabolic disorders, alcohol abuse, smoking, repeated hypothermia).
As a rule, its clinical signs appear 1-2 days after the onset of normal inflammation of the tonsils. Bilateral paratonsillitis is observed extremely rarely; unilateral paratonsillitis is more often diagnosed. In the worst case, a peritonsillar abscess is formed from the inflamed area of tissue.
The following symptoms are characteristic of paratonsillitis.
- Deterioration of general condition (very high temperature with tremendous chills).
- Significant sore throat that radiates to the neck and ear, worsens when opening the mouth and swallowing.
- With severe swelling, there is a deviation of the head in the direction of the lesion and the inability to open the mouth (trismus), increased salivation.
- Painful enlargement of the lymph nodes on the affected side.
- An unpleasant (putrid) odor may emanate from the patient's mouth.
Upon examination, there is a significant enlargement of the tonsil on one side, a peculiar overhang of the velum (soft palate) on the affected side, bright hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane.
Depending on the stage of the inflammatory process, several variants of paratonsillitis are distinguished.
- Edema is rare and is characterized only by swelling of the tissues and a significant enlargement of the tonsil and palate.
- Infiltrative – the most typical, characterized by a typical mixing of organs in the healthy direction.
- Peritonsillar abscess is the extreme and worst stage of the process, in which an abscess of various sizes forms near the tonsil.
Diagnosis of paratonsillitis usually does not cause significant difficulties for a specialist. It is somewhat more difficult to determine the stage of the process, which is of great importance for subsequent therapy.
Treatment for paratonsillitis only (without an abscess) includes:
- antibacterial therapy with a drug with a wide spectrum of effects;
- rinsing with an antiseptic to reduce swelling;
- systemic antipyretics (if necessary);
- multivitamins and desensitizing agents.
In the event that a peritonsillar abscess has already formed, only surgical intervention is required - opening the abscess. After this, the tissues are washed to prevent recurrent abscess formation.
Prevention
To avoid serious health problems, it is important to follow preventive measures, which include:
- Oral hygiene – regular brushing of teeth, use of medical or home remedies for rinsing after each meal;
- quitting smoking, as the toxic substances of tobacco smoke have a negative effect on the mucous membranes;
- compliance with the temperature regime - hypothermia should not be allowed.
Proper nutrition and an active healthy lifestyle will strengthen the body and enhance its protective reactions.
If you pay attention to the disease in a timely manner, the treatment will be easy and painless. In contrast to advanced cases, when the body has already been subjected to an infectious attack.
Holes of the palatine tonsils - treatment
Although your doctor will not treat tonsil holes, it may be necessary to address the underlying cause of any symptoms. Treatment will depend on the underlying problem.
A person with tonsillitis does not necessarily need treatment, as the body can fight the infection on its own. Your doctor may recommend drinking plenty of fluids, keeping you quiet, and taking pain relievers. If symptoms persist for 3-4 days or become severe, the person should see a doctor. Your doctor can test for streptococcus and prescribe antibiotics or other medications if needed.
If a person suspects that they have a sore throat caused by a streptococcal infection, they should consult a doctor. Your doctor will examine your throat and take a swab to check for the presence of group A streptococcus bacteria. A sore throat may require treatment with antibiotics. Antibiotics help reduce symptoms and prevent the infection from spreading. Treatment for mononucleosis may depend on its severity.
A person with mononucleosis should:
- drink plenty of water and other liquids;
- take medications to reduce high fever.
Doctors do not recommend treating mononucleosis with antibiotics such as ampicillin or amoxicillin.
If the spleen is enlarged, intense physical activity should be avoided, which can cause the spleen to rupture.
You should maintain oral hygiene:
- brush your teeth for 2 minutes at least twice a day;
- to drink a lot of water;
- use an antibacterial mouthwash;
- quit smoking.
Treatment for tonsil stones will depend on how large the stones are and whether they cause any symptoms.
Small stones can often be removed by rinsing with salt water. If this doesn't help, your doctor may use lasers or sound waves to remove the stones. Your doctor may also suggest a simple surgical procedure if the stones are large and difficult to remove.
Antibiotics are sometimes used to treat tonsil stones and their side effects, especially if they cause an infection.
Treatment for oral and tonsil cancer will depend on the type of cancer, its stage, and how far it has spread. Treatment may include surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.