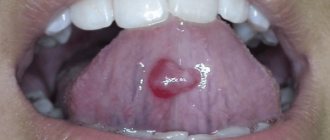
Composition and properties of biological fluid
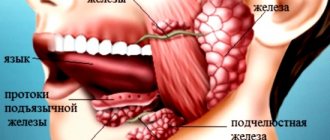
Saliva is a secret that is produced by the glands of the same name almost continuously.
The versatility of this biological fluid is determined by its liquid consistency and component composition. It takes part in speech, chewing and digesting food, protecting the oral cavity from “attacks” of pathogenic microorganisms and traumatic injuries. Saliva is a clear, colorless liquid with a neutral alkaline reaction. 98% of this secretion consists of water. In combination with mucin, the main component of this biological fluid acts as a lubricant.
The following substances are present in saliva:
- antimicrobial components (lysozyme, secretory immunoglobulin A);
- digestive enzymes (ptialin, lingual lipase);
- epidermal growth factor;
- chloride, potassium, sodium and other electrolytes;
- amino acids, glucose, lactic acid, vitamins K, C, B1, H.
By and large, the composition of saliva almost completely reflects the structure of blood plasma. True, passing such a test is much easier.
Saliva is a clear, colorless liquid with an alkaline reaction (pH = 7.4 – 8.0). In addition, saliva is an excellent material for biochemical research. It consists of more than 98% water. Water and mucin act as a solvent and oil. Saliva also contains:
- antimicrobial substances: lysozyme, lactoperoxidase, secretory immunoglobulin A;
- digestive enzymes: tongue lipase and ptyalin (salivary amylase), mucin;
- electrolytes: sodium, potassium, chloride,
- epidermal growth factor;
- buffer system components;
- microelements;
- amino acids;
- lactic acid
- glucose;
- vitamins C, B1, B12, H, K.
In addition, saliva is a dynamic medium and therefore reflects daily changes in the body. Which ones can be easily determined by doing a saliva composition test.
Infections transmitted through saliva
A number of infectious diseases can be transmitted through saliva:
- herpes virus;
- cytomegalovirus;
- papilloma virus;
- Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that causes stomach ulcers.
All these infections are transmitted through saliva, through a kiss.
Also, if you suspect the presence of helminths or Giardia, you can do a saliva test. It will contain toxins, waste products of parasites that poison the body.
There are many infections whose pathogens are present in saliva.
They can be contracted through kissing or oral sex.
Most often, viral infections are transmitted in this way.
It can be:
- herpes viruses type 1 and 2
- Infectious mononucleosis
- cytomegalovirus
- papillomavirus
Having become infected with these infections, a person becomes their carrier for a long time, and sometimes forever.
But this does not mean that it always remains contagious.
During most periods of time there is virtually no viral shedding.
Even if viral DNA is present in saliva, there are not enough viruses to infect a person.
However, during the period of exacerbation, active viral shedding begins.
Therefore, close contacts are highly likely to lead to infection.
To avoid becoming infected, it is important to avoid these contacts if:
- the other person has a rash on their lips or mouth
- there are signs of inflammation (redness of the oropharynx, erosion in the oral cavity, enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes)
Among the listed infections, most are transmitted only by contact.
The exception is cytomegalovirus.
It is more contagious.
Therefore, transmission of the disease is possible through airborne droplets.
Particles of saliva enter the environment.
They are inhaled by humans, resulting in infection.
However, the risk of infection this way is very low.
Only syphilis can be transmitted through a kiss.
However, the likelihood of infection remains low.
Infection is possible only if there is: on the lips or in the mouth:
- chancre
- secondary period rash
Infection with gonorrhea or chlamydia can occur through oral sex.
But it is unlikely: usually very little bacteria is released from the oropharynx.
There are rumors that HIV is transmitted through any body fluids, including saliva.
Many have heard that saliva can even diagnose this infection.
Is this true or fiction?
Both statements are incorrect.
HIV is indeed present in small amounts in saliva.
It can be determined there by laboratory methods, for example using PCR.
But world history does not yet know of a single case when another person was infected through saliva.
HIV is generally a low-contagious infection.
It is very difficult to become infected with it.
You can live with an HIV-infected person in the same apartment for decades and not contract this disease from him.
Infection does not occur through kissing or skin-to-skin contact.
Even with vaginal intercourse, the risk of infection is minimal.
For infection to occur, the infection must enter directly into the blood.
And a biological fluid containing many viral particles must get there.
Saliva is not one of these.
It is impossible to become infected through it, even if saliva gets on a damaged skin wound.
As for HIV tests, some of them are actually based on the use of biomaterial from the oral cavity.
Therefore, in everyday life it is generally accepted that these are rapid tests for HIV using saliva.
And if you ask for such a test at a pharmacy, no one will be surprised.
However, in reality, they do not use saliva for testing, but transudate from the oral mucosa.
This is a liquid contained on the surface of the gums and covering some other areas of the mucous membrane.
For testing, this fluid is collected with a special swab.
Some bacteria, viruses and fungi can be identified in saliva.
Therefore, it is sometimes used as a biomaterial.
Streptococcus
Some laboratories test streptococcal DNA in saliva.
They perform saliva PCR for infection.
It is taken into account that streptococci can be present in the oral cavity normally.
Therefore, small amounts are allowed and are not considered a sign of pathology.
The threshold value is considered to be 10 to the 4th power of DNA copies per ml of saliva.
If there are fewer bacteria, the result will be considered negative.
Streptococci are the causative agents of many infections.
They cause pharyngitis, bronchitis, tonsillitis (sore throat), and pneumonia.
Often affects the skin and urinary system.
Saliva analysis is usually taken from patients with:
- prolonged cough against the background of low-grade (slightly elevated) or normal body temperature
- diseases of the bronchopulmonary system with blurred clinical symptoms in people with immunodeficiencies
- clinical signs of inflammation of the oral cavity and oropharynx
We invite you to read: Why does anesthesia not work during dental treatment?
Determining the streptococcal etiology of the disease is important in terms of choosing therapeutic tactics.
Unlike viral infections, bacterial ones are treated with antibiotics.
Streptococci over a long period of time can lead to serious complications: rheumatism, glomerulonephritis, damage to the heart valves.
Candidiasis
PCR for candidiasis is carried out to identify fungi of the genus Candida.
The objectives of the study are as follows:
- confirm the presence of candida in the mouth
- distinguish colonization of the oropharyngeal mucosa by fungi from candidiasis (a pathological process of fungal etiology)
- assess the severity of the infectious process
- establish the type of Candida, which is important for choosing therapy (5-8 fungi of the genus Candida can cause inflammatory processes in the oral cavity)
Superficial oral candidiasis is not uncommon.
They can occur in many clinically healthy people, are easily tolerated and resolve without treatment.
Candida is present in the mouths of 30-50% of clinically healthy individuals.
Severe fungal infections are typical for people with immunodeficiency conditions.
Indications for testing:
- stomatitis of unknown etiology
- suspected fungal infection of the mouth
- inflammation of the oral mucosa due to immunodeficiency
- the appearance of symptoms of candidiasis during long-term therapy with antibiotics, cytostatics, glucocorticoids or immunosuppressants
Analyzes are issued qualitative or quantitative (indicating the concentration of Candida DNA in 1 ml of saliva).
Quantitative analyzes are preferred.
They allow you to distinguish candidiasis from manifest candidiasis.
Cytomegalovirus
It is a common virus of the herpes family that:
- present in the body of most people
- dangerous for pregnant women
- Causes symptoms mainly in children or immunocompromised individuals
Indications for donating saliva for cytomegalovirus:
- pregnancy planning
- signs of intrauterine infection
- immunosuppression or HIV
- clinical signs of infectious mononucleosis with a negative saliva test for Epstein-Barr virus
- some symptoms that have existed for a long time, the cause of which is unknown: enlarged liver, spleen, slightly elevated body temperature, increased levels of liver enzymes in the blood
- atypical course of pneumonia
Cytomegalovirus infection occurs with periods of remission and exacerbations.
In immunocompetent individuals, symptoms usually occur only during the acute period, immediately after infection.
But then the virus goes into latent form and remains in this state throughout life.
At the same time, its concentration in DNA in saliva decreases to an undetectable level.
Detection of DNA during the PCR reaction indicates that viral shedding has begun.
This indicates an exacerbation of cytomegalovirus infection.
Epstein-Barr virus
This is another virus of the herpes family.
It is the causative agent of infectious mononucleosis.
When infected, it most often primarily affects the oropharynx and salivary glands.
Its DNA can be detected in clinically healthy individuals.
Therefore, the results are interpreted in conjunction with other tests and the clinical picture.
Almost all people are infected with the Epstein-Barr virus.
Antibodies in the blood can be detected in anyone, and this suggests that the immune system is already familiar with this pathogen.
Saliva is the main biomaterial for testing for Epstein-Barr virus.
It is through it that this pathogen is most often transmitted.
It is slightly contagious and almost does not spread by airborne droplets.
The infection caused by this virus is usually called the “kissing disease”, since it is through kissing that it is most often transmitted from person to person.
Herpes type 6
Herpes virus type 6 comes in two subtypes: A and B.
Virus 6A is associated with several diseases of the central nervous system, including multiple sclerosis.
Virus 6B is the causative agent of sudden exanthema (roseola).
This is a childhood infection that manifests itself as a skin rash.
The virus poses a significant threat only to patients with immunodeficiencies.
In them it can cause encephalitis, pneumonia, affects the bone marrow and inhibits hematopoietic function.
Viral DNA can be detected in saliva.
PCR is used to detect it.
Biomaterial is collected before antibiotic therapy begins.
6 hours before collecting saliva, you should not dissolve any medications or irrigate the oropharynx.
You can't chew gum.
Immediately before taking saliva for analysis, you need to rinse your mouth with clean water.
Some laboratories will ask you to do this 2-3 times.
Saliva is collected in a special sterile tube of small capacity (usually 2 ml).
The volume of collected biomaterial must be at least 1 ml.
In children, saliva is sucked out with a syringe for analysis.
After placing the biomaterial inside the test tube, it is hermetically sealed and sent to the laboratory.
The transport medium is not used.
Before shipment, the biomaterial is kept in the refrigerator.
It cannot be stored for more than 12 hours.
To take a saliva test for infections, contact the author of this article, a venereologist in Moscow with many years of experience.
Similar chapters from other books
Clinical study
Clinical study Patient with digestive system disorders One should not think that everything is nervous in the Ignace type. The subject can detect such objective manifestations as should be well known in order to avoid sources of possible errors. So,
Clinical study
Clinical study: A patient with damage to the digestive tract. Most often (in this type) there is a patient with damage to the digestive organs. Here we have to study two groups of symptoms: gastric and intestinal. Stomach disorders. How does it seem
Clinical study
Clinical study Now let's engage in a clinical study of patients with the Cantharis type. A patient with damage to the digestive tract. The digestive system with the Cantharis type reveals two localizations of the lesion: in the pharynx and in the small intestine. Localization
Clinical study
Clinical study Otitis What are the manifestations of the type of otitis that is affected by Capsicum? The patient experiences a rise in temperature - quite suddenly, there is thirst during chills, a feeling of coldness in the back, forcing the patient to ask for a poultice or
Clinical study
Clinical study Patient with damage to the digestive organs This is the most common patient of the Colocynth type, the most common one. How does he show himself? In a very difficult state: lies in a pointer dog position, bent double and pressing hard with hands on the area where
Clinical study
Clinical study: A patient with damage to the digestive tract in the oral cavity. This is exactly the condition of the teeth discussed above. And Creosote turns out to be the best remedy for a child, indicated for rapidly developing dental caries that turn black with
Examination of sperm, saliva, urine, hair. Issues resolved by forensic medical examination
54. Study of sperm, saliva, urine, hair. Issues resolved by forensic medical examination. Examination of sperm. When investigating sexual crimes, the object of forensic biological examination is stains of sperm (male seminal fluid). Items on
What is the purpose of saliva?
Chapter 3 Study of saliva, stomach and duodenal contents
Chapter 3 Study of saliva, stomach and duodenal contents Study of saliva Study of saliva is recommended to identify:• gingivitis,• dental caries,• comprehensive gastroenterological assessment of the digestive system.
Saliva examination
Saliva examination Saliva examination is recommended to identify:• gingivitis,• dental caries,• comprehensive gastroenterological assessment of the digestive system,• stomatitis,• chronic periodontitis. The main object of the study is
3.2.3. Functions of saliva
3.2.3. Functions of saliva Saliva plays a huge role in maintaining the normal condition of the organs and tissues of the oral cavity. It is known that with hyposalivation, and especially xerostomia (lack of saliva), inflammation of the oral mucosa quickly develops, and after 3–6 months it occurs
saliva pH
Saliva pH The acidity of saliva depends on the rate of salivation. Typically, the acidity of mixed human saliva is 6.8–7.4 pH, but with high salivation rates it reaches 7.8 pH. The acidity of the saliva of the parotid glands is 5.81 pH, and that of the submandibular glands is 6.39 pH. On average, children
Chapter 3 Study of saliva, stomach and duodenal contents
Chapter 3 Study of saliva, stomach and duodenal contents Study of saliva Study of saliva is recommended to identify:• gingivitis,• dental caries,• comprehensive gastroenterological assessment of the digestive system.
Composition and properties of saliva
Composition and properties of saliva Saliva found in the oral cavity is mixed. Its pH is 6.8–7.4. An adult produces 0.5–2 liters of saliva per day. It consists of 99% water and 1% solids. The dry residue is represented by organic and inorganic substances.
Functions of saliva
Functions of Saliva Saliva has the following functions. Digestive function - it was mentioned above. Excretory function. Saliva may contain some metabolic products, such as urea, uric acid, drugs (quinine, strychnine), and
Types of research
Saliva analysis is a modern diagnostic technique, the purpose of which is to identify various infections in the body. This test is carried out in a laboratory, but it is quite possible to purchase a kit for home testing. A sample for subsequent research is taken from the inside of the cheek with a cotton swab.
Biochemical analysis of saliva makes it easy to identify dysbiosis of the oral cavity, which, in turn, indicates various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The test is also carried out for infections and viruses. It is widely used in dentistry to determine the causes of caries, gingivitis and other “local” pathologies.
By taking a saliva sample, you can also do a paternity test (DNA). Such studies are carried out exclusively in specialized LHC laboratories. To make the result as reliable as possible, you will need three samples for comparison. A scraping of the epithelium is taken with a cotton swab from the inside of the cheek, the smear is dried in a dark place at room temperature, after which it is transferred for further study.
Why take a saliva sample for weight loss: such a test allows you to determine which factor (or several) is preventing the human body from effectively coping with fat burning. Analysis of this biological fluid helps to identify malfunctions in the functioning of organs and systems (primarily the digestive tract, excretory, hormonal systems).
Based on the findings obtained from the study, the patient is selected a diet, type of physical activity, vitamins, nutritional supplements and other “auxiliary” procedures that contribute to a healthy fight against excess weight.
Saliva PCR (polymerase chain reaction analysis) is essentially a genetic test (DNA). Usually, PCR of saliva determines the presence of sexually transmitted infections (scraping of the epithelium from the inside of the cheek is taken). In addition to this biological fluid, blood, urine, etc. are used to carry out the PCR test.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with 6 important facts you need to know about exposure of the neck of a tooth.
One of the most dangerous pathologies that a saliva DNA test can detect is the Epstein-Barr virus (herpes). Testing for EBV can help prevent lymphoma, infectious mononucleosis, nasopharyngeal carcinoma and other diseases in a timely manner, the development of which is caused by this virus.
The biochemistry of saliva is aimed at identifying enzymes that are indicators of the “proper functioning” of internal organs (this analysis helps to promptly detect diseases of the kidneys, liver, gall bladder, etc.). It is the biochemical study that detects dysbiosis in the early stages and allows us to establish the causes of the imbalance.
Saliva analysis for tuberculosis and other infections is necessary to identify pathogenic microflora in the body and select the optimal treatment. So, to confirm the diagnosis of tuberculosis, in addition to saliva testing, a blood test for ELISA and PCR is prescribed.
The essence of the test: a special reagent is dripped onto the taken saliva sample, which demonstrates the appropriate reaction. If the smear changes color, tuberculosis is suspected; when the color of the sample remains the same, the person is most likely healthy.
Cortisol is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal glands, takes part in the metabolism of glucose, supports blood vessels, helps them stay in good shape, and affects the body’s protective function. It is cortisol that helps the body “take the hit” in stressful situations. Determining the content of this hormone in saliva is more informative than a similar study of urine.
The list of these includes: obesity, osteoporosis, hypertension. In addition, the content of cortisol in saliva makes it possible to determine the causes of unreasonable weight gain and developmental delays in children.
So, from a saliva sample you can determine:
- predict the risk (establish the causes) of caries;
- determine paternity (DNA test);
- detect dysbacteriosis of the oral cavity (may indicate gingivitis, stomatitis, malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract);
- check a person for drug use (a home test system is not equipped with such a function).
In theory, saliva can reveal the presence of parasites (helminths) in a child’s body. Flatworms and roundworms produce specific toxins that are detected in a sample of this biological fluid. According to not fully confirmed data, a saliva test allows you to determine which foods are not suitable for the body, set the date of ovulation, identify developing cancer, HIV, and even find out the gender of the unborn child.
Most often, such an analysis is prescribed by a dentist or gastroenterologist if dysbiosis of the oral cavity and diseases accompanying this anomaly are suspected. An effective diagnostic method is the examination of saliva for gastrointestinal disorders and problems with other internal organs. The biochemistry of saliva is aimed at identifying those enzymes that ensure the “healthy” functioning of the liver, kidneys, pancreas, gall bladder and other organs.
A comprehensive laboratory study of the composition of salivary fluid allows us to identify a variety of infections, pathogenic bacteria, and microorganisms. A saliva test is done for Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus (EBV and CMV) and other serious pathologies.
The reason for such a test is obvious. It remains to figure out how to properly prepare and conduct the appropriate research (provided that you have to work with a home test system). The saliva sample is taken exclusively under sterile conditions.
The composition of biological saliva depends on many factors: the characteristics of the daily biorhythm of a particular person, the structure of the diet, gender, age, and the nature of regulation. That is why it is still better to entrust the analysis to a professional laboratory assistant.
Scientists suggest that the study of saliva in diagnosing various pathologies (due to its greater information content) will soon replace the more familiar blood test. How to take a sample correctly: saliva must be collected in the morning on an empty stomach (to maximally exclude those factors that could affect its secretion).
To determine the volume and composition of the biological fluid that is produced by the minor salivary glands, strips of filtered paper are taken (their mass is measured before and after the study). Before taking the test, you are prohibited from eating, brushing your teeth, chewing gum, smoking, or using mouth rinses.
So, a study of the composition of saliva is an informative diagnostic measure that allows not only to determine the state of the microflora of the oral cavity, but also to detect infections, viruses, and other pathogenic microorganisms. This test is used, among other things, to establish paternity and even select a diet for weight loss.
How much such an analysis costs depends on the purpose of its implementation and the conditions of a particular laboratory. It is noteworthy that in almost any modern pharmacy you can purchase a special system for home testing of the composition of this biological fluid, however, experts question the informativeness of such a test.
Human saliva is a reliable source that reflects all processes occurring in the body. By analyzing this material, you can do a DNA test, find out what infections a person has, get complete information on how to lose weight, and much more.
What is a saliva test? Now let's look at this issue. The first thing this phrase is associated with is a DNA test. In detective and crime dramas, the main villain spits into a test tube or a swab is taken from the inside of his cheek with a cotton swab and given for research. After which justice triumphs.
However, this is not all that this test can show. Using a saliva test you can:
- find out nationality,
- establish paternity,
- identify a number of diseases,
- determine a way to lose weight quickly.
Currently, such testing is increasingly gaining popularity; doctors are increasingly making a diagnosis based on the content of saliva.
In addition to such knowledge, a person can find out a genetic predisposition to any diseases by analyzing saliva. In California, researchers at a laboratory have developed a saliva DNA test that can detect genetic mutations and detect more than 100 hereditary diseases. This analysis will help future parents take measures to ensure that the child is born healthy.
This saliva test is done to identify a disease such as dysbiosis. Human saliva contains microorganisms that reflect the state of the gastrointestinal tract. This analysis reflects the condition of a person’s oral cavity and allows one to determine the causes of the disease. Oral dysbiosis is a symptom of:
- caries;
- stomatitis;
- gingivitis;
- various gastrointestinal diseases;
- changes in hormonal levels in the body.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with the inflamed lymph node under the jaw, causes and treatment of the disease
Saliva almost completely copies the composition of blood. But doing a saliva test is much easier. In the future, it is planned that instead of blood, people will donate this material for research.
Currently, there are a huge number of techniques that make it possible to identify many diseases at an early stage and in a very short time. According to scientists, it is possible that in the future, instead of blood, saliva will be taken from a person for diagnostics. Experts believe that a blood test is more accurate, but a saliva test is more convenient for express diagnostics.
First of all, a biochemical analysis of saliva will help identify oral dysbiosis in a person, which is a symptom of diseases such as caries, stomatitis, gingivitis or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Also, a saliva test can detect whether a person has diseases such as HIV or hepatitis, or lung diseases.
Preparing for genetic research
In addition to such knowledge, a person can find out a genetic predisposition to any diseases by analyzing saliva. In California, researchers at a laboratory have developed a saliva DNA test that can detect genetic mutations and detect more than 100 hereditary diseases. This analysis will help future parents take measures to ensure that the child is born healthy.
The biomaterial for research is a sample from the inside of the cheek. Scraping is done with special cotton swabs. One and a half hours before collecting samples, do not eat or smoke. Immediately before taking samples, rinse your mouth with warm water. When collecting a sample from an infant, you must wait at least half an hour after the last feeding. Immediately before collecting the sample, give the infant a drink of warm water from a feeding bottle.
Share
How informative is a saliva HIV test?
So, we found out: rumors that HIV infection is transmitted through saliva are fiction.
But material from the mouth is used to diagnose the disease.
People can do such tests in our clinic.
They can also be purchased and carried out at home.
It should be noted that such test systems are not reliable.
No diagnoses are made on their basis.
They can give both false positive and false negative results.
False positives are more common.
Approximately 10% of people who take the test will receive a positive result.
Despite the fact that in reality there is no HIV infection in their body.
Therefore, after receiving a positive reaction, you should definitely do another test.
For example, donate blood for antibodies.
In this case, the diagnosis can be confirmed.
If the blood test is positive, HIV infection will be determined.
But if it is negative, the disease cannot be ruled out.
Because a blood test for antibodies can only become positive several months after infection.
Further diagnostic tactics depend on how serious the reasons are to suspect a person has HIV infection.
If they exist, then the estimated timing of infection is taken into account.
In case of recent potential infection, it makes sense to carry out PCR: this method gives positive results earlier (even in the acute period of HIV).
Another option to verify the presence or absence of infection is to wait 2-3 months and donate blood for antibodies again.
Modern methods of saliva analysis
The most popular methods currently:
- biochemical;
- DNA analysis;
- PCR analysis;
- for tuberculosis;
- for the content of various infections, HIV.
What is a saliva test called? In medicine, it does not have a special name; it refers to genetic research. The names of saliva tests are the names of what needs to be studied: DNA, infections, genetic abnormalities, to identify a particular disease. Now about each in more detail.
Information obtained during testing
The high accuracy and reliability of genetic DNA research makes it possible to use their results not only in scientific activities, but also to determine the truth in such controversial issues as:
- The presence of genetic pathologies, including a tendency to diseases (hepatitis, diabetes mellitus).
- Establishing relationship with 99.99% accuracy. A saliva DNA test can establish both paternity and maternity.
- Establishing a close relationship when surnames match.
- Definition of ethnic group and genealogical origin.
- Diagnosis of the patient’s tendency to addictions, establishing intolerance to certain foods and medications.
- Personal identification, which is widely used in forensics.
Despite the fact that DNA profiling does not allow a complete study of the genome, it can provide a large amount of information for research.
What STDs don't test for saliva?
There are sexually transmitted infections that affect the oral cavity, but saliva is usually not used to identify them.
These include:
- chlamydia;
- herpes types 1 and 2;
- gonorrhea
- papillomavirus;
- syphilis.
With all of these diseases, either a rash or signs of inflammation in the mouth usually appear.
Scrapings are taken from problem areas.
It is easier to detect bacterial or viral DNA in them.
If these problem areas are not present, there is a high probability that there is no infection in the mouth.
In such a situation, taking saliva for analysis makes no practical sense.
Test for tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is a disease caused by a bacterium that mainly affects the lungs. Anyone can get sick, regardless of age. Treatment will be more successful if the disease is diagnosed early. It is now possible to do a saliva test for tuberculosis. For examination, a swab is taken from the oral cavity.
What does a saliva test for tuberculosis show? The causative agent of this disease is mycobacterium, otherwise known as Koch's bacillus. In saliva, as well as in blood, the presence of the tuberculosis pathogen can be detected. Saliva tests are simpler to perform and do not require complex equipment.
What else does the analysis show?
The saliva test is very common in forensics. Using this analysis, it is possible to determine the DNA of the criminal and detect the presence of drugs in the human body.
Having done a saliva test, a person can receive detailed advice from a specialist on how to eat properly in order to lose excess weight. A diet based on the data obtained will be the most effective.
Canadian scientists, for example, examining human saliva, found that it can be used to determine how tired a person is, and whether he is on the verge of a breakdown. That is, the test will tell you that your strength is running out and you should rest. An indicator for this is the hormone cortisone. Its high or too low content in the body is reflected in saliva. Such an analysis will help you avoid stressful situations and prevent other diseases that arise due to stress.
A person can independently determine by the quality and quantity of saliva that there are health problems. The changes can be quite significant. For example, with gastrointestinal diseases, saliva may change color. With hormonal imbalances, its amount decreases, you feel dry mouth and thirst. Bitterness in the mouth is a sign that the functioning of the liver and gallbladder is impaired. Excessive salivation can occur with:
- diseases of the oral cavity;
- disruption of the nervous system;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- metabolic disorders.
If you discover such signs, you should immediately consult a doctor in order to diagnose the disease in a timely manner.
Sputum. Anaerobes and antibiotic sensitivity
Attention Sputum is collected on an empty stomach.
First brush your teeth, gums and tongue with a toothbrush and rinse your mouth with boiled water at room temperature.
Collection procedure
- Take two deep breaths, holding your breath for a few seconds, and after each deep breath exhale slowly. Then inhale a third time and forcefully exhale (push) the air out. Inhale again and clear your throat well.
- Hold the container as close to your mouth as possible and carefully spit the mucus into it after coughing. Be careful not to get any sputum on the edge of the container. Do not touch the inside of the lid or the sides of the sterile container with your fingers. Close the container tightly with the lid.
- Wash your hands with soap.
- Deliver the morning sputum collected for examination to the laboratory.
Attention! You should not collect sputum released during expectoration, only when coughing. Saliva entering the sample can significantly affect the test result.