What is stomatitis
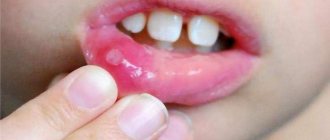
Stomatitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. It is characterized by the formation of bubbles and ulcers, suddenness and rapid flow. When there is a combination of gum damage, they speak of gingivostomatitis.
The most common form of the disease is fungal or herpetic. Before therapy, careful diagnosis and identification of microflora is required. First of all, the cause is eliminated and symptomatic treatment is carried out.
With proper therapy, even at home, stomatitis disappears within 10 days.
Symptoms of stomatitis
The characteristics of the manifestation of stomatitis largely depend on the form of inflammation, the duration of the course and the state of the human immune system. The mucous membrane of the cheeks and lips, gums, tongue, soft and hard palate is affected. Manifestations of the disease in the form of morphological elements or plaque are observed even in the upper respiratory tract.
Main signs of stomatitis:
- hyperemia of the mucous membrane;
- bleeding gums;
- swelling of the tongue;
- plaque of varying consistency;
- pain when eating;
- the presence of various morphological microelements (ulcers, blisters, papules, aphthae, erosions).
Attention! A patient with stomatitis should be isolated in the first days of the disease. Some forms of pathology are extremely contagious at the very beginning.
Causes of stomatitis on the gums
Stomatitis often appears in the mouth, why does this happen? The main reason for the appearance of stomatitis on the gums is a weakening of the body’s immune system.
Factors contributing to damage to the periodontium and the entire oral mucosa are similar. But gum inflammation occurs more often in the following cases:
- poor oral hygiene;
- long-term and frequent treatment with antibacterial drugs;
- multiple caries;
- incorrectly made or old bridges;
- weak general and local immunity;
- smoking and frequent drinking of alcohol;
- diabetes;
- the presence of severe general diseases of the body;
- occupational hazards.
The causes of stomatitis in the mouth in adults also lie in genetic predisposition. The disease can develop in the form of frequent allergic reactions of the gums to many irritants.
Types of stomatitis in the mouth
Manifestations of inflammatory diseases on the oral mucosa and gums are varied. It depends on the forms of the disease. Before prescribing medications for stomatitis, it is necessary to establish what caused the inflammation. It is customary to distinguish the following types of stomatitis:
- Bacterial. The culprits of the pathology are gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The active development of microorganisms leads to inflammation, and then the formation of purulent exudate. If left untreated, the gums and adjacent tissues begin to deteriorate and extensive erosions appear.
- Viral. The cause is often the herpes simplex virus or Epstein-Bar virus. In this case, they talk about herpetic stomatitis. Initially, bubbles appear on the gums, mucous membranes of the lips, cheeks and palate. Then they quickly burst, forming erosions, and in severe cases, ulcers.
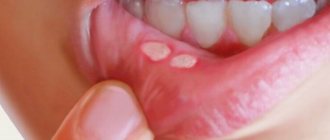
- Aphthous. It is the most common form in adults. It occurs for various reasons. The appearance of specific elements in the form of aphthae is characteristic.
- Traumatic. Appears as a result of acute or chronic injury to the oral mucosa. Injuries are found on the cheeks, gums, and lips. They disappear completely after eliminating the cause. In severe cases, it is necessary to anoint the stomatitis with anti-inflammatory gels for several days.
- Allergic. The disease is associated with the entry into the body or directly into the oral cavity of a strong irritant.
- Fungal. Against the background of a decrease in immunological status, fungi grow and multiply, mainly of the genus Candida. Fungal stomatitis is characterized by a whitish coating on the entire mucous membrane of the oral cavity. There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth, burning and itching.
- Ray. It happens rarely, due to radiation sickness. The initial manifestation is compaction, which turns into erosions and ulcers.
- Chemical. Occurs against the background of acid or alkaline burns. Requires immediate treatment.
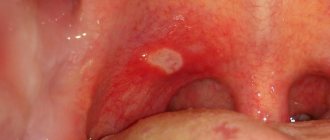
How stomatitis manifests itself on the gum is shown in the photo below.
Aphthous stomatitis
Stages of disease development
In each clinical case, stomatitis can develop differently. The classic stages of development are the following:
- Initial. There is a modification of the mucous membrane, hyperemia and swelling.
- Average. After 1–2 days, plaque and morphological elements are formed. The general condition of the body begins to suffer.
- Heavy. The blisters burst, the ulcers begin to bleed, and the plaque turns gray. Body temperature rises, pain reaction intensifies, especially when eating.
Attention! It is possible to prevent the formation of a severe lesion. The main thing is to choose an effective remedy and eliminate the possible cause that provoked stomatitis.
Features of the flow
The inflammatory process may be mild, localized in one area. It appears in the form of single lesions. Or maybe it’s heavy. In this case, ulcerative formations spread everywhere in the mouth, forming on the tongue, gums, and the inner surface of the cheeks. The more of these formations, the more severe the disease is.
Typically, in adults, the disease does not cause general distress; the patient’s main complaints are discomfort and pain. The doctor and the patient should be alarmed by conditions that indicate a severe course of the disease:
- fever, increased temperature;
- inflammatory processes in the eye area;
- the appearance on the skin of fluid-filled blisters with a diameter of more than 10 mm - skin bullae.
In these cases, we can talk about the pathological spread of infection.
Treatment of stomatitis at home in adults
Therapy for inflammatory lesions of the oral cavity is individual in each clinical case. Below we will look at how to treat stomatitis in an adult’s mouth, and which medications are best to choose. First of all, the form of the disease is taken into account depending on the cause of its occurrence.
Candidal stomatitis
- You will need antifungal drugs, such as Nystatin ointment, Pimafucin, Levorin. The drugs are prescribed depending on the patient’s age and body weight.
- To strengthen local immunity, Imudon is used, 6 tablets per day for a week.
- Miconazole is required for disinfection and bactericidal effects.
- When cracks and ulcers appear, they are treated with Fukortsin.
- For minor plaque on the tongue, lips or gums, the affected areas are irrigated with a solution of borax in glycerin.
Viral stomatitis
- For treatment, agents are selected that have a pronounced antiviral effect. A drug such as Viferon helps with stomatitis. It not only has an antiviral effect, but is also able to activate the immune system.
- It is recommended to treat the affected areas with Oxolinic ointment 0.25% 4 times a day.
- In adults, Acyclovir is suitable, which directly destroys the DNA of microorganisms. It is used in the form of ointments and tablets.
Bacterial stomatitis
- Antibiotics are required to treat this form. Microflora can be suppressed using Lincomycin, which destroys gram-positive organisms. The drug is prescribed orally in the form of capsules up to 4 times a day.
- When ulcers appear, Metronidazole or Biseptol tablets are required for a course of up to 5 days.
- In severe cases of inflammation, strong antibacterial drugs are needed, for example Amoxicillin.
- If stomatitis is localized on the gum, then the area of inflammation is treated with Miramistin in the form of a spray, or an application is made with Chlorhexidine.
Allergic stomatitis
- After eliminating the allergen, antihistamines are needed. Loratadine is suitable for relieving swelling and itching.
- Suprastin is a highly effective and safe remedy.
- In case of a severe allergic reaction, Cetirizine tablets for stomatitis in the mouth are prescribed.
- After examination, the doctor prescribes drugs such as Tavegil, Diphenhydramine and Ketotifen.
- In addition, it is necessary to take vitamins B, C, A and E.
Traumatic stomatitis
- If there is any wound, every effort should be made for speedy regeneration. Bioparox is applied to the affected area in the form of inhalation, and irrigation is done with Chlorophyllipt, propolis or Ingalipt aerosol.
- Solcoseryl is used as an ointment for stomatitis in the mouth at the regeneration stage.
- The gums, mucous membranes of the lips and cheeks are lubricated with methylene blue. The drug is absolutely safe and can be used even during pregnancy.
Aphthous stomatitis
- This severe form of the disease requires the use of potent drugs. The glucocorticoid drug Dexamethasone is often prescribed as a rinse. It effectively relieves inflammation and allergic reactions.
- It is recommended to apply a thin layer of Clobetasol ointment directly to the aphthae, since it is a hormonal agent.
- To stop bleeding of the gums and mucous membranes, the oral cavity is treated with Rotokan solution.
- To make regeneration faster. The affected area is covered with Vinilin bactericidal ointment.
- For antiseptic treatment, a solution of Furacilin, Streptocide and Lugol spray is suitable.
The question often arises: is it possible to smear brilliant green on stomatitis in the mouth? Yes, this is allowed in adults too. Brilliant green tincture will cause serious discomfort after processing. Today there are more gentle methods and means of influence, with a pronounced antiseptic effect.
An unpleasant disease: how stomatitis appears
Everyone had stomatitis. In itself, it is not dangerous. White sores only 0.3-1 mm wide appear in the mouth. If there are several of them, more than 10, then you should seriously think about your health and pay attention to:
- Diet
Be sure to eat more fruits and vegetables, especially in winter. Take vitamins, brew herbal teas;
- Hygiene
You should always wash vegetables and fruits. Even if they are from a summer cottage and grew up in an ecologically clean area. Very often in children, stomatitis appears from dirt - they ate something unwashed, and the mucous membrane was immediately damaged;
- The water you drink
Just because your city has good water does not mean you can drink it straight from the tap. Chlorine and other substances are added to it. They can harm the gums, mucous membranes, teeth, and esophagus. These rules are simple and understandable to everyone, but sometimes we forget about them. The result is irritation of the mucous membrane, the appearance of ulcers.
Low immunity
If stomatitis appears frequently, is long-lasting and painful, then you should consult a doctor. This may be a symptom of a weakened immune system or an autoimmune disease. In this case, you need to start treatment. You can combine drug treatment with healing spells - this will speed up recovery and help you get into good shape faster. In any case, pay attention to this symptom. Stomatitis can spread further down the esophagus. In this case, you will need a very strict diet:
- exclude salty, spicy foods;
- you cannot eat solid foods, raw vegetables and fruits;
- alcohol and cigarettes are contraindicated;
- forget about hot drinks, coffee.
It is better to treat the disease before it becomes chronic.
Traditional methods of treatment
Alternative medicine has a large number of recipes for treating the oral cavity and gums in particular. Any folk remedy for stomatitis in the mouth can be used with the main therapy.
Attention! It is prohibited to treat stomatitis with pure honey. Glucose and fructose contained in the product provide a breeding ground for many bacteria. As a result of such therapy, progression of the disease is possible.
If stomatitis appears on the gums, tongue, lips and buccal mucosa, you can use the following recipes:
- Salt solution. The product is used for rinsing. Add 1 tsp per glass of water. salt. Rinse for a minute.
- Aloe and soda. Add a small spoon of soda to freshly squeezed aloe juice and thoroughly dissolve it. The gums are covered with gauze soaked in this mixture. The juice is also used for rinsing.
- Propolis and honey. Beekeeping products will quickly help cure stomatitis in the mouth. Propolis is used only on a water basis. Dissolve a teaspoon of honey in the tincture. Rinse 3-4 times a day until obvious symptoms on the mucous membrane and gums disappear.
- Garlic for lotions. 2-3 cloves of spice, peeled, finely chopped and mixed with 2 tbsp. l. sour cream. Stomatitis should be cauterized 2–4 times a day. If there is severe burning of the gums or mucous membranes, the amount of sour cream should be increased to 4 tablespoons.
- Vegetable juices. Fresh ingredients make a natural mouthwash. The juice of cabbage, carrots and beets has a healing effect.
- Pomegranate. Fresh peel is used to prepare a decoction. 2 tbsp. l. Boil the product in 250 ml of water for 20 minutes. Use as a rinse.
- Kalonchoe. Treatment in adults is carried out with freshly squeezed juice. Use cut leaves as compresses for gums.
Attention! Do not rub soda or salt into the wound surface of the gums and mucous membranes. This will cause additional damage.
Soda and salt solution
Propolis tincture
Rinsing a decoction of medicinal herbs provides a therapeutic effect. These products eliminate inflammation in the gums, plaque, and provide reliable antiseptic treatment and tissue regeneration. The following medicinal herbs are often prescribed to adults:
- pharmaceutical camomile;
- marsh calamus;
- sage;
- calendula;
- St. John's wort.
If your gums are bleeding, oak bark will be a reliable hemostatic agent for stomatitis. Decoctions of raspberry, blackberry and sea buckthorn leaves will help strengthen local immunity.
Nutrition for stomatitis in the mouth
When the oral mucosa and gums are inflamed, eating any food is difficult due to pain. To avoid irritation, a number of rules must be followed:
- consume food in small portions;
- exclude spicy, salty and sour foods;
- It is good to chop any food;
- the temperature of the products should be 37–40 degrees;
- Consume vegetables and berries in the form of puree.
Before eating, treat the mouth and gums with an antiseptic and lubricate the affected areas with Cholisal gel. This will help partially get rid of the discomfort. After eating, rinse your mouth with water or any disinfecting weakly concentrated solution.
Don't self-medicate
To quickly get rid of stomatitis, you need to contact a dentist or therapist when the first signs of the disease appear.
We described what can be expected from the development of the disease in the article “Stomatitis in adults: symptoms and treatment.” The appearance of inflammation of the oral mucosa in adults can be influenced by many causes and pathogens. Therefore, it is impossible to independently diagnose the type of disease. Only a specialist can find out where stomatitis comes from and choose an effective method of getting rid of it.
Treating stomatitis on your own can lead to negative consequences:
- intoxication of the body;
- development of a chronic form of pathology;
- weakened immunity;
- the appearance of foci of inflammation in the throat, sinuses, lungs;
- infection of the circulatory system by pathogenic microorganisms or viruses, and as a result – the development of sepsis.
Bubble formations in the sky