A person has experienced an unpleasant sensation at least once in his life - pain in the area of the auricle. The ear and behind it begin to hurt. The question arises: is the facial nerve cold? Pain in the area of the facial nerve indicates serious illness. To make a correct diagnosis, you need to consult a specialist.
Only an otolaryngologist can make the correct diagnosis. After examining the patient, neuritis is diagnosed - a disease when the facial nerve is cold. The diagnosis is made exclusively by the doctor, but even if you are not a professional, the disease is easy to recognize. Such a patient does not control the facial muscles. This occurs in most patients and accounts for 90% of the total number of patients.
If the facial nerve is cold, how to determine the main symptoms? What you should pay attention to?
There are many reasons for the occurrence of the disease. To protect yourself from it you need to know why it occurs and how to treat it.
If a person has a cold on the facial nerve, the main symptoms are:
- the facial nerve is cold, the symptom is the inability to smile. Even such a person’s speech is difficult. Complete absence of facial muscles. In order to understand whether there is a problem with the facial nerve, it is enough to pay attention to the smile. The corners of the patient's lips rise asymmetrically. An attempt to smile ends in failure;
- when the nerve gets cold, the sensitivity of the skin on the face disappears. This condition also affects the jaw. It lacks sensitivity;
- Do you have a cold on your facial nerve? The main symptom will be a disruption in the functioning of the glands that produce saliva and tears.
The most common cause is the appearance of neuralgia. Along with neuralgia, the patient experiences severe pain.
One common sign is the appearance of muscle weakness on the face. Even if you look at the patient with the naked eye, you can see that the muscles on his face do not react to anything.
A cold facial nerve is determined by symptoms of compression of the trigeminal nerve, that is, nerve impulses stop passing through the fibers.
Symptoms of neuritis
The appearance of the disease is associated with many reasons. One of them is neuritis. To confirm the diagnosis, you need to visit a specialist. Most often, the disease occurs under the influence of external factors.
- blown facial nerve? The distinctive symptom will be inflammation, which is associated with infection;
- damage to nerve fibers;
- in the area where the nerve passes, inflammation appears, which is noticeable even with the naked eye;
- factors influencing diabetes mellitus;
- cardiac ischemia.
How to determine whether the facial nerve has a cold and the symptoms of the disease? Most often, in a conversation with specialists dealing with diseases of the jaw and facial nerve, the fact that the disease appears under the same circumstances becomes clear. This is almost always hypothermia. Being in a draft causes swelling of the trigeminal nerve.
Symptoms
As statistics show, neuritis most often manifests itself in patients of the older age group, or more precisely, over 50 years. If such a patient has caught a cold of the trigeminal nerve, treatment cannot be delayed, since the disease in this case will progress quite rapidly. For what reason the nerve was cold, what to do in this case and how to treat it, only a neurologist can determine. Self-medication in the treatment of neuritis is contraindicated.
If a patient of a different age category is admitted with suspicion of neuritis, most likely we are talking about a serious pathology in the body. Symptoms that the facial nerve is cold are manifested in the following factors:
- severe pain in the facial muscles;
- while chewing food, discomfort and painful shootings are felt - trigeminal neuralgia has appeared;
- pain appears only on one side of the face;
- the skin on the face becomes too sensitive, or vice versa – loses sensitivity. In this case, the affected part of the face may become distorted, and the corner of the mouth may go down.
Causes
If the trigeminal nerve on the face is cold, first of all you should understand the causes of the pathology. Most often, they are the most ordinary situations that people encounter almost every day. These include:
- air conditioner on;
- an open window in a vehicle or at home;
- cold wind.
You should know that the inflammatory process in the body can begin a few minutes after contact with a flow of cold air.
Reasons for the development of edema
The causes of swelling of the optic disc (optic disc) are different. Diseases of internal organs and the brain, infections and eye diseases lead to pathology.
Brain diseases
The underlying cause is always an increase in intracranial pressure. It develops due to impaired circulation of fluid inside the skull.
Brain diseases lead to it:
- Tumors of various origins. They compress adjacent tissues, disrupting the outflow of fluid.
- Intracranial bleeding. Blood pours into the cranial cavity, disturbing the balance of fluid inside and creating additional pressure.
- Traumatic brain injury. Various areas of the brain are damaged. Sometimes bone fragments become embedded in the brain tissue. Bleeding begins. Inflammation begins. Moisture circulation is disrupted.
- Suppuration. Pus collects inside the skull. The abscess puts pressure on the adjacent tissues, disrupting the natural circulation process.
- Brain swelling. This condition occurs due to various diseases. Infections and injuries lead to it.
- Hydrocephalus. With this disease, fluid from the spinal cord accumulates inside the skull.
- Craniosynostosis. This pathology is associated with brain deformation. It occurs at an early age due to the rapid fusion of bone joints.
- Incorrect tissue fusion. Pathology is caused by birth trauma or lifetime damage to the skull.
We recommend further reading: Causes of morning puffiness under the eyes and methods of treating them
Other possible causes of increased intracranial pressure include diseases such as:
- meningitis - inflammation of the membranes of the brain;
- encephalitis – inflammation of the brain;
- stroke - a sudden disruption of the blood supply to the brain;
- renal failure - impaired renal function;
- lymphoma is a disease of lymphatic tissue;
- leukemia is a malignant disease of the circulatory system;
- sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease that leads to the formation of granulomas.
Infections
Infections and viruses that enter the body cause inflammation of the optic nerve. Harmful bacteria penetrate the eye during human life. Sometimes they are associated with cosmetic procedures. Inflammation occurs after eyelash extensions if the cosmetologist did not follow hygiene rules. Often the negative comes down to inflammatory eye diseases. But the infection process sometimes spreads further, affecting internal organs. You should be careful when choosing a cosmetologist. You need to visit only trusted specialists.
The development of swelling of the optic nerve is facilitated by infections that affect not individual organs, but the entire body:
- syphilis;
- flu;
- tuberculosis.
Inflammation with subsequent swelling of the optic disc is the result of complications of the underlying disease.
Diseases of internal organs
Papilledema often develops against the background of pathologies of various internal organs. The human body is a single whole. All organs and systems are closely interconnected.
Problems in one place will lead to problems in another. Papilledema is caused by:
- Respiratory failure. With this pathology, normal blood composition is not maintained. It is poorly saturated with oxygen. This leads to the fact that the life-giving fluid is not able to saturate the tissues. Their starvation begins.
- Muscle hypotension is a pathological process that develops against the background of complex pathologies of the central nervous system. Decreased muscle tone negatively affects the functioning of all organs.
- Hypervitaminosis with excess vitamin A. It threatens lovers of uncontrolled intake of vitamin complexes and dietary supplements.
- Hyperammonymia is a disease associated with elevated levels of ammonia in the blood. It is caused by metabolic disorders and insufficient breakdown of urea enzymes.
- Guillain-Barré syndrome is an acute autoimmune disease caused by elevated protein levels.
- High altitude mountain sickness. State of oxygen starvation.
- Malignant hypertension. A sharp rise in blood pressure. The condition requires emergency medical attention.
All of these diseases lead to nerve pathology. In some cases, their nutrition is disrupted. In others there is compression. Nerve cells are affected by pathogens. Eventually papilledema occurs.
We recommend further reading: Eye swelling due to allergies
Eye diseases
Infectious eye diseases are common. People experience conjunctivitis several times throughout their lives. Other diseases appear less frequently.
Ophthalmology identifies the following infectious eye diseases:
- Blepharitis is not just one disease. This name hides a whole group of infectious lesions that cause inflammation of the eyelids.
- Keratitis is inflammation of the cornea of the eye. It is a complication of influenza and tuberculosis.
- Endophthalmitis is a purulent inflammation of the inner membranes of the eye.
- Trachoma is a chronic infectious disease of the organs of vision caused by chlamydia. Affects the conjunctiva and cornea. Leads to complete blindness.
- Dacryocystitis is inflammation of the lacrimal sac.
Each of the diseases is dangerous in itself. All of them lead to clouding of the retina. But the inflammation spreads, affecting nearby organs. It causes swelling of the optic disc. Infectious eye diseases must be treated promptly. This will help prevent the spread of infection and preserve your vision.
Symptoms of neuropathy
Neuopathy is a disease in which the patient experiences a large amount of discomfort and pain.
Regardless of the reasons that influenced the changes in the nerve process, the disease develops in all cases of solitary. Symptoms occur:
- pain, most often in the area of the back wall of the auricle;
- When eating food, the taste is not felt;
- Difficulty swallowing saliva;
- When trying to close his eyes, the patient feels discomfort and cannot close his eyes completely;
- Facial muscles are asymmetrical;
- An attempt to close your eyebrows or wrinkle your forehead ends in failure.
If these symptoms are present, we can talk about a cold nerve. Advanced cases can only be corrected by surgery, since drug treatment is useless.
Main symptoms
Neuritis of any etiology has a characteristic clinical picture:
- Pain is the first sign of tissue damage.
The pain is shooting, paroxysmal, very strong, lasting up to a couple of minutes. Appears in one half of the face.
IMPORTANT!
A dull aching pain may appear, similar to a toothache due to advanced caries or pulpitis, which leads to the need to visit the dentist.
- Redness of the sclera of the eyes and face.
- Increased salivation.
- Tearing.
- Runny nose.
- Tremor (twitching) of the facial muscles, similar to a nervous tic. This is due to overexcitation of motor fibers.
- Narrowing of the eyes on the affected side—spasm of the eyelids.
- Parasthesia (sensitivity disorder). On the affected half there is a feeling of goosebumps, tingling or, conversely, the skin does not respond to irritants.
- Mental disorders: irritability, anxiety, apathy, silence, depression, feelings of fear, psychosis. They arise due to excruciating, debilitating attacks of pain.
- Facial asymmetry, peeling of the skin, loss of eyebrows, eyelashes, hair or teeth, weakness of the chewing muscles are signs of trophic failure. They appear several years after the onset of the disease due to blood and lymph circulation disorders.
The lesion of the nervus trigeminus affects one facial part (usually the right). It extends to the second side only in severe brain pathologies.
When the trigeminal nerve is cold, the symptoms are varied, but treatment cannot be delayed!
Complications and prognosis
Late seeking medical help or failure to comply with the recommendations of the attending physician entails the formation of complications of facial neuritis:
- paralysis of the facial muscles of varying severity - from mild asymmetry to the development of a pathological “mask”;
- complete weakening of the muscles of the facial part of the skull - a kind of “sliding” of muscle structures downward, drooping of the corner of the mouth, eyelid, eyebrows;
- distortion of taste perception – when part of the tongue is involved in the pathological process;
- sharp deterioration/weakening of auditory and visual activity;
- hemispasms - involuntary twitching of muscle groups.
However, in most cases, the prognosis of the condition, if the nerve has been frozen, is favorable - the disease can be successfully treated with complex treatment. The above complications occur rarely - only in people who are not committed to drug therapy prescribed by the doctor.
Distinctive features and varieties
Where the facial nerve passes, there is a canal of a certain size. If it does not correspond to the norm, then the patient is more often susceptible to the disease. Such patients should not even be overcooled, since a decrease in temperature leads to illness.
In total, there are several types of neuritis in medicine:
- Viral flora that develops in the body can lead to inflammation. The salivary glands will become inflamed, leading to neuropathy;
- Otitis is an inflammatory ear disease and if you do not treat it, it will spread to the trigeminal nerve;
- During the disease, a rash develops, along with this the salivary gland becomes inflamed, and then compression of the nerve occurs;
- Heredity – Merkensol-Rosenthal syndrome. It is rare, but if left untreated, nerve atrophy will occur.
Please note: if the trigeminal nerve is still cold, then you should first consult a specialist. It is he who will help get rid of the disease. Self-medication is excluded.
When treating a disease, several stages occur:
- Relieving tissue swelling. It is carried out when special medications are prescribed that allow fluid to be removed from swollen areas;
- Getting rid of excess fluid in the body occurs naturally;
- Restoring blood circulation is the key to quality treatment;
- Elimination of pain is an important point, after which the patient does not feel the same discomfort.
The doctor does not prescribe treatment at the first appointment or when examining the patient. Prescription of medications or surgical treatment occurs after a complete examination. The main diagnostic methods are magnetic resonance imaging. A serological examination method is mandatory. After undergoing examinations and receiving the results of the examination, drug treatment is prescribed. But it is not always effective.
How to treat a cold trigeminal nerve?
It’s easy to catch a cold, but getting rid of the disease is difficult and takes a long time. A set of measures is required: medications, physiotherapy and rehabilitation.
Although pain due to neuritis may be similar to dental pain, it is diagnosed and treated by a neurologist, not a dentist!
Therapy depends on the etiology of the disease:
- In case of infection, bacteria and viruses are destroyed (antibiotics, sulfonamides, interferon, serums, gamma globulin).
- In case of injury, tissue integrity is surgically restored.
- When pinched, the nerve is released. For ischemia, a vasoactive (vasodilator) agent (aminophylline) is used.
- If you suffer from hypothermia, you should avoid situations and places where you may be exposed to air.
- If you have a weak immune system, you need to take courses of vitamins. After consulting a doctor!
- In case of intoxication, medications (reopolyglucin, sodium thiosulfate, antidotes) and medical equipment accelerate the removal of toxic substances from the body.
- In case of allergies, contact of the allergen with tissues is eliminated.
- For multiple sclerosis, neurologists use an individual approach. The main goal is to put the disease into remission and alleviate its course.
- For neuritis caused by incorrect dental prosthetics, treatment is carried out orthopedically.
IMPORTANT! Careless manipulation of instruments by a dentist can injure neurons and lead to more serious consequences.
Medicines
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating pain and the root cause of the disease:
- Antiepileptic (anticonvulsant) drugs: carbamazepine, lamotrigine, phenytoin, gabapentin, clonazepam, sodium valproate, stashchepin. They reduce the excitability of neurons, resulting in pain subsiding.
- Muscle relaxants: baclofen, mydocalm. Elimination of muscle spasms, pain-relieving effect.
- B vitamins. Promote the regeneration of nerve sheaths.
- Unsaturated fatty acids (Omega-3). Material for restoring neuron myelin.
- Sedatives: glycine, aminazine, mitriptyline. Calming and antidepressant effect, improves sleep.
- Antihistamines (antiallergic): diphenhydramine, pipalfen. Suppress the immune response, enhance the effect of antiepileptic drugs.
- In severe cases and severe pain, the doctor may prescribe narcotic analgesics: forfin, sodium hydroxybutyrate.
Physiotherapy
Any neuritis is recommended to be eliminated using physiotherapeutic procedures.
Physiotherapy is a treatment and rehabilitation methods based on the use of natural and artificially created natural factors on the human body.
Types of physiotherapy:
Features of the treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
The main symptom of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve (neuritis, trigeminitis) is pain (neuralgia). Strong, sharp and burning, it does not allow you to lead your usual lifestyle. The patient’s psychological state, sleep, and appetite are disrupted. This determines the dominant role of symptomatic drugs in the treatment of the disease, such as:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen) also have an analgesic effect;
- glucocorticosteroids (Hydrocortisone, Methylprednisolone, Dexamethasone) effectively and quickly fight inflammation;
- anticonvulsants (Carbamazepine, Tegretol, Phenytoin), reduce impulses in the nerve fiber;
- non-narcotic painkillers (Ketanov, Voltaren) and narcotic painkillers (Tramadol, Promedol);
- muscle relaxants (Mydocalm, Baclofen) eliminate spasms of the facial muscles;
- antidepressants (Amitriptyline) normalize the psychological state.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Which braces are better: ceramic or metal?
Drug treatment is usually combined with physiotherapeutic procedures designed to enhance and prolong the analgesic effect:
- cutaneous laser irradiation of the face;
- ultraviolet irradiation of the face;
- ultra-high frequency therapy (UHF);
- diadynamic currents;
- electrophoresis with B vitamins or with diphenhydramine, platiphylline, novocaine.
Guaranteed, but short-term relief is achieved by using alcohol-novocaine blockade at the nerve exit points on the face. The effect of each subsequent blockade is weaker than the previous one.
To finally get rid of the disease, it is necessary to influence the cause of the disease.
The source of the problem is often:
- viral infections (herpes, in particular herpes zoster, and multiple sclerosis);
- pathology of the nose and paranasal sinuses (rhinitis, sinusitis or space-occupying formations - cysts, tumors);
- facial injuries and their consequences (hematomas, bone fragments, post-traumatic edema can compress nerve fibers);
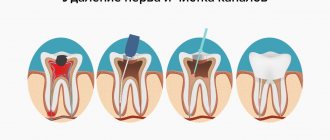
- diseases of the oral cavity (periodontitis, pulpitis, periodontitis);
- dental procedures: tooth extraction, inaccurate filling (the filling material is located outside the tooth root and is in contact with the nerve); errors when administering anesthetic;
- compression of a nerve by an artery or vein (most often by cerebellar vessels), which leads to destruction of the nerve fiber sheath (dimyelination) and its pathological excitability;
- allergic or toxic swelling of facial tissues;
- local and general hypothermia;
- depletion of the body's protective abilities due to physical or psychological overstrain, deficiency of essential nutrients;
- malocclusion, accompanied by permanent injury to the temporomandibular joint;
- narrowing of the bone canals where the branches of the trigeminal nerve pass, osteomyelitis;
- pathology of the cervical spine (osteochondrosis).
Some causes can be treated medicinally using the following drugs:
- antiviral (for herpes infection, acyclovir and its analogues are used);
- antibiotics (for sanitation of foci of infection in the nose and paranasal sinuses, oral cavity);
- antihistamines (to relieve post-traumatic, allergic, toxic edema);
- B vitamins (actively promote the restoration of nerve sheaths).
With cervical osteochondrosis and displacement of the facial bones, manual therapy gives good results.
However, more often the source of irritation can only be eliminated surgically. The following options are possible:
- If the cause is a tumor that can be operated on, surgery is performed to remove it.
- In the case of narrowing of the infraorbital canal, in which the branch of the trigeminal nerve passes, a low-traumatic operation to widen it is highly effective.
- When a nerve is compressed by an artery or vein, microvascular decompression of the trigeminal nerve root is performed (a spacer is placed between the vessels and the nerve root).
Unfortunately, sometimes the cause remains unclear, and symptomatic treatment does not produce a noticeable result. In such a situation, disruption of nerve fiber conduction is achieved surgically.
The following types of interventions are currently used:
- Percutaneous radiofrequency destruction (destruction) of the trigeminal nerve roots. It is performed under local anesthesia. The method is highly effective and has a minimum of contraindications and can be performed on an outpatient basis.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery (cyber knife, gamma knife) – the sensitive root is destroyed using gamma radiation.
Prevention of facial nerve diseases
A patient who has experienced diseases of the facial nerve can accurately report unpleasant sensations and constant pain in the facial area. The constant feeling of pulling on the face does not leave the patient indifferent. Therefore, once a nerve has caught a cold, it is necessary to carry out proper prevention.
Among the preventive ones are:
- In the winter season, it is necessary to wear hats;
- The face should be covered with a warm cloth - a scarf;
- Drink warm drinks. When drinking cold drinks, your teeth and throat get cold, which subsequently leads to the appearance of neuralgia.
Important: if a nerve gets cold, it can lead to pain in the teeth, face, and hearing loss.
Diagnostics
Signs of papilledema are characteristic of all eye diseases. Doctors cannot immediately find the cause. Research begins with an examination by an ophthalmologist using an ophthalmoscope and visometry - determining visual acuity using a table.
The following are hardware research methods:
- perimetry - study of the boundaries of vision;
- tonometry - determination of intraocular pressure.
An MRI of the brain may be required. Sometimes a patient with papilledema is referred for consultation with a neurologist or neurosurgeon.
We recommend further reading: Causes and treatment of eyeball swelling
Intercostal neuralgia
Between the 12 pairs of ribs there are a large number of nerve endings. If the peripheral nerves are pinched in the thoracic region, severe pain occurs under the scapula. If the clamping occurs on the left side, the symptoms of a neurological disease are often confused with pain in the heart. The causes of inflammation of nerve endings can be:
- osteochondrosis and compressor fracture;
- hypothermia and hormonal imbalance;
- lung disease and anemia;
- multiple sclerosis and diabetes mellitus;
- scoliosis and kyphosis.
What symptoms indicate inflammation if a person has a cold on the nerve under the scapula?
- pain in the thoracic spine, radiating to the neck or lower back;
- impaired sensitivity of the skin at the site of inflammation;
- burning and itching in the area of the shoulder blade;
- increased pain when sneezing, coughing and moving.
Surgical intervention
If drug treatment does not help, the patient is prescribed surgery. During surgery, the nerve is freed from compression and inflammation.
Negative aspects of the operation:
- The surgery takes place under general anesthesia. Not every patient can tolerate it;
- After the operation, a scar remains.
But besides the negative aspects, there are also positive ones. The patient feels much better and is not bothered by facial pain.
Following the recommendations of a specialist in the postoperative period is the key to health.
Treatment
When treating facial neuralgia, the main goal is to stop the inflammatory process and eliminate it. Therefore, treatment should be comprehensive and include medication, massage, special gymnastics and folk remedies.
Medication
Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Nise, Meloxicam will help relieve acute pain.
Taking Prednisolone will help relieve swelling and improve blood circulation. It is advisable to start taking it from the first days of illness.
To relieve spasms of the facial nerve, anticonvulsants are prescribed, such as Tegretol, Trileptal, Diphenin.
Taking antidepressants will help you endure pain more calmly and improve your psychological state, because each of us has a different pain threshold, and maintaining calm is extremely important.
Exercise No. 3. For lips
Purse your lips into a tube, slowly draw in the air, and also exhale slowly. Relax your mouth. Repeat the exercise 5-10 times. Move your lower jaw in the direction where the nerve is frozen. Press your finger on your cheekbone. Return your jaw to its original position. Repeat 2-3 times. Do not press too hard, as your jaw may become sore after the numbness subsides.
To get the most complete effect from gymnastics, rub a little fir oil into the painful side (you can buy it in pharmacies). This way, facial expressions return to normal faster. It would also be a good idea to drink rose tea for a week or two. Brew red or burgundy rose petals, add a little sugar to taste. This brew will have a calming effect on the entire nervous system and reduce the symptoms of the disease. At night, you can place geranium leaves in the ear on the sore side, which will relieve pain. Together, all these procedures help very successfully if the facial nerve is cold. Symptoms, treatment, gymnastics - all this should be observed by a neurologist, since only he can track the dynamics of the disease. In some advanced cases, surgery is required.
conclusions
How to treat a cold nerve?
Neuropathy in 90% of cases is accompanied by severe pain in the affected areas of the body. Timely treatment helps prevent tissue abscess and complications.
To eliminate neuralgia I use antidepressants, multivitamins, antibiotics and analgesics. They relieve symptoms of neuropathy and promote decompression of nerve roots.
The facial nerve is responsible for the functioning of the facial muscles. When its branches become inflamed, a person loses the ability to control the movements of facial muscles, and paralysis occurs. This condition is called neuritis. Symptoms of the pathology may appear if a person has a cold on the facial nerve or has suffered severe nervous stress. What measures to take if neuritis of the facial nerve has developed, is it possible to treat it with folk remedies and what are the chances of recovery, you will learn from our article.