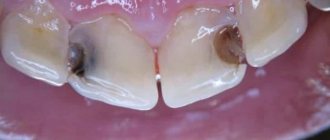
Liver disease can manifest itself not only through external signs, including changes in facial skin tone, fragility, brittleness of nails, and hair loss. It signals problems with the internal organ through an unpleasant liver odor from the mouth. Rotten odor is not considered a disease. The appearance of a stench becomes a symptom of halitosis, which occurs when the body's metabolism fails. Harmful bacteria are not eliminated, but accumulate and enter the circulatory system. Metabolism is an important component of the body's functioning.
Bad breath - causes and treatment
The cause of this situation may be poor nutrition, carious teeth, as well as some diseases of organs and systems. In order to understand why bad breath occurs for no apparent reason and to know how to eliminate it, you need to familiarize yourself with the main causes of this phenomenon.
What can cause bad breath
Bad breath in the morning and at other times of the day can occur for a number of reasons. You can get rid of this problem only by eliminating the root cause.
The smell of iron
A metallic odor from the mouth may indicate the development of the following problems:
- Lack of vitamins (hypovitaminosis). This problem is especially relevant in the autumn-winter period, when the body experiences an acute lack of vitamins. In addition to a metallic smell from the mouth, hypovitaminosis is indicated by general weakness, increased fatigue, irritability and insomnia.
- Diseases of the digestive system. Diseases of the liver, intestines, gall bladder and stomach can cause this problem. A person may experience stool disorders, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite and abdominal pain.
- Iron-deficiency anemia. When hemoglobin decreases, a person experiences a metallic odor from the mouth. In addition to this symptom, the development of anemia is indicated by symptoms such as dry and pale skin, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, increased drowsiness and weakness, impaired sense of smell and dry mouth. Iron deficiency anemia is a serious condition that requires medical attention.
- Taking certain medications. The problem often occurs when taking drugs such as Metronidazole, Tetracycline and Lansporazole.
Very often, bad breath develops after tooth extraction, which goes away over time if you follow medical recommendations.
Smell of acetone
If a person smells ammonia from the mouth, then this condition may indicate the development of the following pathologies:
- Thyrotoxicosis. This disease is characterized by increased production of thyroid hormones. In addition to bad breath, a person is worried about stool disorder (diarrhea), as well as a constant feeling of thirst.
- Diabetes. With the development of diabetes mellitus, a person’s urine and sweat acquire a pronounced odor of acetone.
In addition to the above reasons, the following factors can provoke the smell of acetone from the mouth of a child and an adult:
- digestive disorders;
- eating predominantly protein foods;
- violation of the functional state of the liver and kidneys;
- diseases of an infectious nature.
The smell of bile
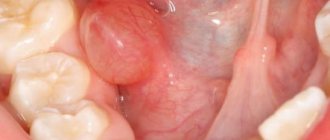
This symptom often indicates abnormalities in the liver and gallbladder.
Important! If the smell of bile is accompanied by bitterness in the mouth, yellow lumps on the tongue and a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium, the person is advised to immediately consult a medical specialist.
Such a symptom may indicate the presence of one or more stones in the gall bladder, as well as the development of an inflammatory process (cholecystitis).
Putrid odor from the mouth
This symptom is characteristic of pathologies of the digestive system. Foul, putrid odor from the mouth due to gastritis is a very common problem.
It is also typical for people suffering from gastroduodenitis and intestinal diseases (dyspepsia, enterocolitis, irritable bowel syndrome). In addition to a bad odor, a person may notice a white coating on the tongue, which indicates the development of chronic gastritis.
If the smell of pus occurs due to intestinal diseases, then the clinical picture is complemented by stool disorders (constipation or diarrhea), increased gas formation (flatulence), as well as fatigue and irritability.
Odor during pregnancy
During the period of bearing a child, many women face such an unpleasant problem. This problem during pregnancy occurs for a number of reasons:
- Violation of the integrity of teeth. In 95% of cases, expectant mothers face the problem of increased calcium consumption in the body. All reserves of a pregnant woman’s body are used to ensure the full development of the fetus. A lack of calcium leads to damage to the integrity of tooth enamel and the appearance of caries.
- Eating foods that can cause bad breath (beans, garlic, onions).
Smell due to diet
Many women prefer to follow strict diets in order to lose excess weight. A low-carbohydrate diet often leads to bad breath. So-called starvation diets also lead to bad breath.
I recommend reading articles about health:
How to lead a healthy lifestyle, where to start
Oral care
Choosing the right toothbrush
Cirrhosis of the liver
The appearance of connective tissue nodes in the liver tissue is accompanied by dysfunction of the organ and the appearance of clinical signs of the disease. The cause of cirrhosis in most cases is alcohol abuse and infectious hepatitis. In addition, among the predisposing factors it is worth highlighting:
- autoimmune hepatitis;
- Slerosing cholangitis;
- bile stagnation;
- narrowing of the bile ducts;
- metabolic pathology (cystic fibrosis);
- Wilson's disease;
- taking hepatotoxic drugs;
- surgical interventions on the intestines;
- parasitic infection of the digestive tract.
If the cause of cirrhosis has not been established, it is usually called cryptogenic. Cirrhotic changes occur against the background of impaired cell nutrition, which is accompanied by the proliferation of connective tissue. The formed nodules compress the blood vessels, which further impairs tissue trophism.
Why liver failure may develop
Fulminant (fulminant) liver damage can occur against the background of autoimmune and viral hepatitis, exposure to toxic substances, taking medications and some chronic diseases. The mortality rate reaches 80%, but this is a fairly rare occurrence. According to statistics, about 2,000 people worldwide die from fulminant liver failure per year.
Causes of acute forms of the disease:
- Poisoning with poisons (for example, phosphorus, arsenic, inedible mushrooms).
- Viral hepatitis (severe forms).
- Side effect when taking certain medications.
- The appearance of chronic liver failure is affected by diseases such as oncology, cirrhosis and others.
Other causes of unpleasant odor
The following factors can cause the formation of such a delicate problem:
- Failure to comply with oral hygiene rules. If a person brushes his teeth less than twice a day, then as a result of rotting food debris, an unpleasant odor develops.
- Diseases of the oral cavity, nasopharynx and oropharynx (sinusitis, inflammation of the gums, sore throat, adenoids, and also due to tonsils).
- Tobacco smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Wearing dentures, crowns and braces. Food particles get into the dental structures, resulting in a foul odor. Proper oral care gives you a chance to avoid this problem.
- Diseases of the salivary glands. Inflammatory damage to the salivary glands provokes bad breath.
- Helminthiasis. Medical experts have proven that bad breath is the fault of parasites living in the intestinal lumen. If the problem is caused by parasites, then an integrated approach is needed.
- Eruption of wisdom teeth. This physiological process is accompanied by the formation of a hood from the gums, under which food particles fall and rot. All this is accompanied by an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
- Carious teeth. When teeth are damaged by caries, pathological holes form in the teeth. These holes accumulate food particles, which, when decomposed, emit an unpleasant odor.
By undergoing a free medical examination, you can prevent many diseases, including finding out the cause of bad breath.
Diagnosis
The treatment of hepatic bad breath is carried out by a hepatologist. But not all clinics have such specialists, so you can contact a gastroenterologist. When visiting a medical facility, a specialist examines the medical history and asks questions to the patient. Then he prescribes the following procedures:
- biochemical analysis of blood and urine. With liver diseases, a change in characteristics occurs because the composition of the blood depends on the cleansing by the organ. If the functionality of the liver is impaired, this will be visible in the results of a blood test;
- examination of stool for the presence of incompletely digested food. An unpleasant odor may indicate a disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, and sometimes the liver;
- gastroscopy (if necessary). Fibragastroduodenoscopy is necessary for examining the gastrointestinal tract;
- ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal cavity.
In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Stages of development of liver diseases
Symptoms may differ depending on the stage and severity of the process and the nature of the disease. The chronic form develops over several weeks or even months. Its main danger is the risk of coma, especially in the presence of additional provoking factors (infections, fatigue, gastrointestinal bleeding, alcohol intake, etc.). The acute form develops over several days, and in some cases hours.
Timely diagnosis and effective therapy will help reverse this process!
With this disease, there is a decrease in appetite, fatigue, nausea, aversion to tobacco, alcoholic drinks, food, and emotional disorders. If the cause of liver problems is poisoning, a crimson color of the tongue is observed.
How to detect bad breath
In order to detect this problem in a timely manner, you need to pay attention to your condition. You can determine if you have bad breath by doing the following:
- While at home, you need to go to the mirror and look at the condition of your tongue. If it is covered with a white coating or there are white lumps, then this sign in 95% of cases indicates the presence of bad breath.
- This indicator can be assessed with the help of relatives or close people. It is enough to ask them about it.
- You can independently assess your breath odor by applying a small amount of saliva to your wrist. After application, it is recommended to let the saliva dry, after which the smell is assessed.
- To determine the smell, you need to bring a cupped hand to your mouth. After this, you should exhale sharply through your mouth, while inhaling through your nose. This smell corresponds to the smell of your mouth.
- For a similar purpose, you can use dental or regular floss, which should be passed between the teeth. The smell of the thread matches the smell of your mouth.
Additional measures
If the liver pathology progresses, then it is quite difficult to remove the liver odor. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the root cause, and not deal with the consequences. While the underlying disease is being treated, you can take some measures so as not to feel uncomfortable while being around people.
Rinsing helps get rid of odor. After each meal, rinse your mouth with water or mouthwash. Disinfecting solutions help to cope with odor by reducing the number of pathogenic microorganisms found on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. A weak solution of potassium permanganate has a good bactericidal effect.
To irrigate the oral cavity, you can use decoctions of medicinal plants. You need to choose herbs that have a disinfectant effect. These include: chamomile, lemon balm, St. John's wort, oak bark, scrofula, eucalyptus.
Halitosis in combination with other signs may indicate severe liver pathologies, so if you are plagued by constant bad breath, you should be examined by a doctor.
Condition of mucous membranes
If the liver does not function sufficiently, then additional stress is placed on the skin. The skin is able to filter and remove toxins, and when the liver does not cope with its task, this is sure to affect the condition of the skin and mucous membranes.
A yellowish or excessively pale skin color may indicate liver disease. Yellowness is observed in hepatitis and gallbladder diseases, and indicates a high level of bilirubin. White skin color, especially noticeable on the fingertips and face, can also indicate a diseased liver.
In liver pathologies, the mucous membranes and eye sclera also change color. Swelling of the skin and mucous membranes may occur. The skin becomes dry, pustules and pimples appear on them.
Why does an unpleasant odor appear?
If a person has a smell from the oral cavity, then one can suspect the development of complications.
When the liver is unable to process toxic substances coming from the intestines, a rotten or sweetish odor emanates from the mouth.
In addition, a person may notice the appearance of a different colored coating on the tongue, indicating that, for example, congestion has formed in the liver.
It is worth taking a closer look at the diseases that provoke such symptoms.
How to get rid of odor
The issue of getting rid of this problem must be approached comprehensively, taking into account the cause of this condition. If these symptoms are associated with diseases of the digestive system, then the primary task is to normalize the diet. For gastritis and intestinal diseases, it is recommended to constantly follow the following dietary recommendations:
- It is recommended to eat a minimum amount of foods containing simple carbohydrates (sugar, confectionery).
- You should limit your consumption of meat products.
- It is also necessary to temporarily exclude coffee, cottage cheese, whole milk and foods containing large amounts of fat from the diet.
- It is recommended to avoid eating fruits that cause fermentation in the intestines (grapes, apples and plums).
- It is necessary to consume more fermented milk products (kefir, acidophilus, yogurt).
If bad breath is caused by diseases of internal organs and systems, then in order to eliminate it it is necessary to fight the disease. In all other cases, it is recommended to follow these rules:
- Completely quit smoking and limit the consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Drink increased amounts of fluid. For this purpose, mineral water in the amount of 1.5-2 liters per day is useful.
- Periodically use special sugar-free lollipops and chewing gums.
- Brush your teeth at least 2 times a day.
- Clean dental gaps daily using dental floss.
- After each meal, it is recommended to rinse the mouth with boiled water or special rinses containing an antiseptic component. Hydrogen peroxide has a good effect against bad breath, which should be added 5-6 drops per glass of water for rinsing.
- Visit your dentist regularly, have carious teeth treated, and have tartar removed professionally.
- When brushing your teeth, it is recommended to pay attention to tongue hygiene. You can clean it with a toothbrush or a teaspoon.
- If a person wears dentures, it is recommended that they be removed and cleaned daily with a toothbrush, followed by rinsing in an antiseptic solution.
In the fight against this problem, folk remedies for bad breath help, which are recommended to be used as an addition to the main treatment. For rinsing, it is recommended to use an infusion of chamomile and sage.
If the recommendations described above do not answer the question of how to kill bad breath, then the person is advised to seek advice from a dental specialist. The doctor will be able to identify diseases of the oral cavity of an inflammatory and non-inflammatory nature, and prescribe a medicine that corresponds to the problem.
To eliminate the problem, special sprays are used that not only freshen breath, but also disinfect the oral cavity.
Remedies for bad breath in the form of balms for rinsing have a pronounced effect. The range of these products includes balms based on the following components:
- Zinc compounds. These components have an antiseptic and astringent effect.
- Extracts of medicinal herbs. Natural extracts of medicinal plants have anti-inflammatory, wound healing and antiseptic effects.
- Chlorhexidine. This component kills bacteria that cause unpleasant odor in the mouth.
- Ethanol. Oral balms that contain ethyl alcohol have antiseptic properties. The only downside is that these substances dry out the oral mucosa.
You can read about dental myths here.
Why the liver is bitter: reasons for how to eliminate the bitterness and cook the liver deliciously
Liver is an incredibly useful product that should be included in your diet, even if only rarely.
But, despite the benefits and low calorie content of liver, there is one drawback - if cooked incorrectly, the liver becomes bitter. Why is this happening? What to do about it? In this article we will find out why beef, chicken, pork and cod liver is bitter.
We will share tips on how to get rid of bitterness and give practical recommendations for preparing this product.
Why liver is bitter: chicken, pork, beef, cod
The liver takes an important part in metabolism. Any living organism needs this organ to cleanse the blood and the body as a whole of harmful substances.
Why is the liver bitter? The unpleasant taste of liver is caused by bitter enzymes that are found in the organ and are needed to break down fat. Experienced housewives know a lot of ways to hide an unpleasant aftertaste, or even get rid of it altogether. But these methods do not always work, since the cause of bitterness may lie elsewhere.
Bile is the cause of bitterness
Why is pork liver bitter? It, like the liver of a cow, chicken and other animals, in addition to bitter enzymes, also has a gall bladder. Bile is a bitter substance that, when improperly processed, gets into meat and completely spoils its taste. Getting rid of the taste of bile is very difficult!
Even if you carefully remove the bubble when cutting the carcass or buy a ready-made, processed organ, there will be no guarantee that the bitterness of bile will not be present even with the most careful preparation.
Damaged product
Why does cod liver purchased as canned food in a jar taste bitter? Most likely, this is a spoiled product that is dangerous to eat. If you feel an unpleasant bitter taste after tasting a piece from a jar, then rush to throw away the product or return it to the store where you bought it; for this you will need a receipt confirming the purchase.
Frozen cod, beef, pork or chicken livers are also often spoiled. This will be indicated by unsightly dark blue or greenish spots located in some places.
Unfortunately, it is almost impossible to notice this before defrosting. Some people cut out spoiled areas of the product and cook the rest.
But we would not recommend risking your health and the health of your household this way.
Choose only chilled meat products for purchase; traces of spoilage in such products are simply impossible to hide. Inspect your liver before purchasing.
If nothing can be done about the spoiled product, then a number of culinary tricks will help to overcome the bitterness from bile or eliminate the taste of the bitter enzyme.
Having figured out why the liver is bitter, you can begin to eliminate the unpleasant taste. There are many methods for this, and each can save your culinary masterpiece!
- Do not cook freshly purchased refrigerated liver. There is blood in it that tastes bitter. To get rid of it, you need to freeze the product, then cut it, removing all the films, and then rinse well under running water. Frozen blood is washed out easier!
- Fresh liver has a uniform, slightly purple, dark red color. if the product is pale, or, on the contrary, too purple, then this will indicate that it is expired, and it cannot be prepared.
- Greenish-colored spots on a well-colored liver are traces of bile, and not a delay. You just need to cut out such places, so you won’t get a bitter taste when cooking.
- If there are too many green spots, then do not cook the product, it is not of high quality, and the bile has already spread throughout the liver.
Removing bitterness by soaking
You can soak it in milk, which needs to be cooled beforehand. To do this, first cut, rinse the product in running water, and then place in a bowl of cold milk for an hour. Fold the pieces so that they lie freely.
If there is no milk, then plain cold water with salt will do. The soaking method is simple:
- Chop and rinse the liver in cold water.
- Pour only cold tap water into a bowl and add a teaspoon of salt.
- Place the liver in water so that the pieces are not stacked on top of each other.
- After 30 minutes, rinse the pieces under running water.
Masking the Bitterness
If you don’t understand why the liver tastes bitter even after processing and soaking, then there is only one way out - to mask the unpleasant taste. To do this, we suggest remembering a few tricks:
- Add more onions when frying, but do not take carrots. Fry, then add tomato paste, wait until it turns orange, add water and simmer until done.
- Herbs and spices with a pronounced aroma and taste will help hide the unpleasant taste.
- Adding a walnut to the dish will perfectly enhance the taste of the liver. It itself is slightly bitter, but this will hide the bitterness of the liver and give the dish a zest.
- You can sprinkle the finished liver with a small amount of lemon juice.
- Don't try to mask the bitterness with sweetness, it will only make things worse. It is unlikely that any eater will like bittersweet meat.
Finally
Buy only chilled offal, and only from a trusted seller in a butcher shop. Before purchasing, inspect the liver from all sides, turning each piece without hesitation.
Avoid buying offal, and meat products in general, frozen in supermarkets. Fresh products are sold only chilled. Frozen is something that was not sold refrigerated on time and had to be frozen. Or the products have been transported for a long time, which means they are no longer fresh!
When buying a jar of cod liver, pay attention not only to the manufacturer and expiration date, but also to the quality of the jar itself. It should be free of dents and scratches.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/401672/pochemu-pechen-gorchit-prichinyi-kak-ustranit-gorech-i-vkusno-prigotovit-pechen
Menu adjustments
When liver pathologies are detected, treatment is necessarily accompanied by the prescription of a special diet. The frequency of food intake, the method of processing it, and the temperature matter. You need to eat food in small portions at fairly short intervals. Food should not be too cold or hot. You should not eat fried, canned, smoked, overly salted or spicy foods.
These measures help not to overload the liver, distributing the load evenly. You should also avoid eating fatty foods, confectionery, marinades, and sausages. No seasonings are used during cooking; salt is added in minimal quantities. Food is steamed, boiled or baked. You should stop eating bread. You can eat biscuits or toasted baguette.
It is healthy to eat honey, nuts, dried fruits
Fermented milk products should be consumed with caution, little by little. Whole milk is excluded
Animal fats must be replaced with vegetable fats. Moderate but obligatory consumption of vegetable oils is beneficial for a diseased liver.
Prevention of bad breath
If a person has encountered a similar problem and was able to understand how to quickly get rid of it, then it is important for him to adhere to preventive measures that will avoid a relapse of the condition. Preventive measures include:
- Visit the dentist at least 2 times a year;
- Timely treatment of diseases of the oral cavity, nasopharynx and oropharynx;
- If you have dry mouth, it is recommended to use special moisturizers:
- Complete smoking cessation;
- Prevention and timely treatment of chronic diseases of internal organs and systems;
- Normalization of lifestyle, revision of the diet in favor of light and plant-based foods;
- Compliance with the rules of oral hygiene, regular brushing of teeth, use of balms and dental floss;
- Regularly clean the surface of the tongue from accumulated plaque.
Breathing, like appearance, is the calling card of every self-respecting person. Every person, regardless of gender and social status, should pay attention to oral health. The cause of the disease determines which doctor treats the problem.
Video - bad breath, Dr. Komarovsky’s school
Medical specialists such as a gastroenterologist and dentist can provide assistance in this matter.
After undergoing diagnostics and identifying the cause, the person will be given recommendations that will help him learn how to get rid of bad breath caused by diseases of the oral cavity and beyond.
Today we learned about how to detect bad breath, the causes and treatment of the disease. If this bothers you and prevents you from living a full life, don’t delay, look for the reason. I wish you good health and good mood.
Timely contact with specialists
According to statistics, people who seek qualified medical help have diseases that are already in advanced stages. Therefore, if prevention, oral care and diet do not give the desired results, then you should definitely go to the doctor and the sooner the better - the early stages of illnesses are much easier to identify and cure.
The state of a person’s internal organs, in particular the body’s main filter, the liver, determines a person’s appearance: the color and condition of the skin, hair, nails, and tongue. This organ also directly affects breathing, which is felt by others. If liver odor appears from the mouth, this indicates possible disturbances in the functioning of the organ. In addition to the unpleasant odor from the mouth, other problems appear - the condition of the skin, nails and hair worsens. If a liver odor appears from the oral cavity, you must urgently consult a hepatologist and find out the cause of this symptom.
Diagnostics
In order to determine the cause of halitosis, it is necessary to conduct a number of studies. The liver, stomach, and intestines are examined. The doctor examines the patient, assesses the condition and color of the skin, mucous membranes, and tongue.
A general blood test is required . In case of liver cirrhosis, liver failure and other severe pathologies, the blood changes characteristics, since its composition depends on the quality of purification. If the liver is not functioning sufficiently, this is immediately revealed by the state of the blood.
Symptoms confirming liver disease
It is possible to determine that liver disease is the cause of the unpleasant odor by comparing a number of specific symptoms:
- Pain in the right side, namely in the hypochondrium. Occurs because the liver becomes inflamed and enlarges.
- Jaundice – changes in the color of the whites of the eyes and skin; urine acquires a pronounced color, and feces, on the contrary, become discolored.
- Nausea, vomiting, bitter taste in the mouth - due to improper functioning of the liver, bile is poorly released.
- Abnormal stool – with liver problems, constipation is common, since bile is released into the body in uneven portions.
- Skin problems – changes in skin color are a specific sign of improper liver function. Also, some patients note excessive dryness of the skin, cracks and peeling.
It is important to know! Early contact with a specialist is necessary if any such signs appear.
In some sources, liver odor from the mouth is usually called halitosis. But the latter term has a broader meaning - it refers to any stench that exudes from the human body through the oral cavity. The presence of halitosis is an inevitable consequence of diseases, disorders of physiological cycles, and disturbances of normal activity. This can occur in any segment of the human body - in the respiratory, digestive organs, and in cases of disorders of the endocrine system. We cannot talk about halitosis as a separate disease, because it is not a disease, but a consequence of its presence, a characteristic symptom. Based on odorological associations, it is often possible to determine the cause itself.
Cirrhosis
If connecting nodes begin to appear on the liver, this leads to its improper functioning and characteristic symptoms of the pathology. Most often, cirrhosis is caused by a passion for alcoholic beverages and the presence of infectious hepatitis in the human body.
Doctors identify several main factors that provoke the development of cirrhosis:
- Autoimmune hepatitis.
- Stagnation of bile in the body.
- Too narrowed bile ducts.
- Metabolic problems.
- Treatment with hepatotoxic drugs.
- Surgery on the intestines.
- Infestation with parasites.
Cirrhosis, the causes of which could not be identified, is called cryptogenic. In this case, changes in the liver are observed due to improper nutrition of its cells and the appearance of excess connective tissue.
Due to the fact that the nodules on the organ put pressure on the vessels, blood circulation in the body worsens.
And this, in turn, leads to the fact that the veins of the esophagus and abdominal wall become full, and the person is diagnosed with varicose veins.
Cirrhosis manifests itself in different ways, depending on why it appeared and how advanced it is.
In 25% of all cases, the process is asymptomatic, periodically making itself felt by increased bloating and general fatigue.
As the disease progresses, the person begins to feel pain in the right side. It is especially acute after drinking alcohol and fatty foods.
The pain is accompanied by the following symptoms of liver damage: itching of the skin, bad breath, increased body temperature to subfebrile levels, ascites, dilated veins in the esophagus, swelling of the legs, problems with nails, “stars” from the vessels on the legs, sudden weight loss, gynecomastia and atrophic phenomena on the testicles.
If any of the above symptoms appear. You should immediately contact a specialist for a thorough diagnosis of the body and a correct diagnosis.
The future fate of a person depends on timely treatment.
Halitosis as a symptom
In non-professional sources, liver odor from the mouth is usually called halitosis, just as the latter term is considered the name of the disease. The appearance of a bad taste and stench from the mouth is indeed called halitosis, however, this is a general collective term for the name of an unpleasant odor of any etiology. In clinical medicine, this is regarded as an undoubted sign of a disease, evidence of the presence of a pathological process occurring in the body with sufficient intensity. This is not an independent disease, but its consequence, a symptom by which one can only assume the origin and localization of inflammation or decay, rotting or critical stagnation.
Halitosis can be temporary, acquired due to the consumption of persistent, pungently smelling food components. There is also pseudohalitosis, which occurs in stressful situations or psycho-emotional shocks. In most cases, it is felt only by the wearer himself - the subjective sensation of a sour, metallic or sweet and sour taste becomes a reaction of the nervous system, affecting the taste buds. An unpleasant odor may be associated with halitophobia - a panicky fear that others perceive a stench that exists only in a person’s morbid imagination.
There is an approximate classification of halitosis according to odorological sensations and olfactory characteristics:
- putrefactive, clearly reminiscent of rotten eggs, develops with bacterial infection of the oral cavity (local);
- a purulent or sour aroma indicates candidiasis in the same location, although they may also indicate caries;
- a stench, like that of rotten eggs or rotting cabbage, can also occur with dysbacteriosis and diseases of the digestive organs;
- clearly purulent – with painful processes in the ENT organs in a neglected state;
- the ammonia component is clearly felt in renal pathologies, thyrotoxicosis and some processes in the liver at an early stage;
- The distinct taste of acetone is characteristic of diabetes mellitus.
Hepatic bad breath appears when the liver is in a dangerous condition, and an experienced hepatologist always associates it with acute or chronic organ failure. The degree of concentration and clarity of manifestation can, in the presence of other symptoms that constantly accompany the clinical picture, give an idea of the stage of development.
Halitosis
Doctors use the term halitosis to define severe bad breath. The amount of pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity increases, which is why an unpleasant odor appears. It may smell like garlic, hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, or putrefaction, depending on the type of bacteria. This symptom can be observed in both adults and children, both in humans and in mammals. Halitosis can indicate liver disease, pathologies of the digestive tract, intestines, ENT diseases, dental problems, diseases of the throat and upper respiratory tract.
The causes and treatment of halitosis may be under the jurisdiction of physicians of different specialties. If ordinary hygiene measures do not help, such as thorough brushing of teeth and tongue, treatment of infectious diseases of the larynx and respiratory system, then you should be examined to identify the causes of the unpleasant symptom.
Bad breath in itself is not a disease, but it does indicate the presence of problems. Most often they relate to the pathological condition of the mucous membranes of the mouth, teeth, and gums. But if halitosis is accompanied by a number of other symptoms, then the stomach, liver, and intestines should be examined.
Liver damage
It is noted that with a high intensity of the process, the negative plume spreads not only from the oral cavity, but also from the entire body. This is due to the cause of the disease, which at a certain stage has a destructive effect on biochemical processes, disrupts relationships, affects the composition of biological fluid during sweating and the secretion of sebum. Just a few decades ago, a doctor could make quite reliable diagnostic assumptions based on smell. Of course, he paid attention to the accompanying symptoms, but the aroma exuded by the sick body was also very informative.
For liver diseases, a specific amber is characteristic, which at first comes only from the mouth, and then, at significant stages of development, is exuded by the entire body of the patient. The hepatologist, looking at the characteristic condition and shade of the skin, its lesions, spider veins, brittle nails and hair, can think about the localization of the disease in the hepatobiliary system. But having smelled a smell that is difficult to confuse with anything, he can unmistakably claim that the problem is the damage to the external gland. And not just in liver pathology, but in one that is accompanied by acute or chronic organ failure.
An approximate description will give little in the way of sensations, but for everyone who knows what we are talking about, it is accompanied by certain associations:
- some believe that it resembles the sweetish aroma of coagulated blood;
- for some, amber is associated with mice and the persistent presence of acutely and persistently stinking rodent droppings;
- the most common analogy is with the unique aroma of raw liver lying on a cutting board and being beaten by the hostess;
- when a negative scenario occurs, the liver odor from the mouth and from the whole body acquires a distinct aftertaste of rot or an unpleasant odor of sweetish pus.
External signs of liver problems
Let's take a closer look at some typical manifestations of liver dysfunction, in which it is necessary to consult a hepatologist and undergo additional examination.
Halitosis (bad breath)
Severe, fetid, putrid odor in the mouth can be associated with many reasons, including problems with teeth and mucous membranes, diseases of the ENT organs and gastrointestinal tract. In most cases, it is enough to sanitize your teeth and follow basic oral hygiene rules to solve this problem.
You need to be wary if, in addition to halitosis, you have the following problems:
- Characteristic sweetish “mouse” smell, reminiscent of raw liver;
- Lack of connection with the frequency of meals and the composition of foods consumed;
- The presence of accompanying symptoms (changes in the color of the skin, eyes, tongue, nails, the appearance of rashes, pimples, itching and others);
- The skin also emits a strong liver odor.
The occurrence of such a symptom complex is a typical manifestation of acute or chronic liver failure, which often requires urgent hospitalization and extensive drug treatment.
Condition of the skin and mucous membranes
Violations of the protective function of the liver lead to excessive load on the additional “filter” of the human body – the skin.
With liver problems, the skin may be:
- Pale, with pronounced swelling and sweating. Such manifestations are especially noticeable in the area of the extremities (white nails) and face.
- Dry with peeling of the epidermis, cracks and scratching. Hair and nails become thinner, brittle and dull.
Particular attention should be paid to skin color and the shade of the sclera of the eyes. Jaundice is caused by excess bilirubin, and its degree is an important indicator of diagnosis and differentiation of the causes of liver failure.
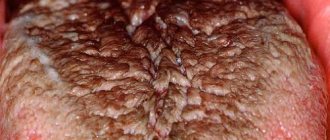
Tongue color and coating
Problems in the functioning of the hepatobiliary system can be signaled by such an indirect sign as a yellow coating on the tongue. Stagnation of bile leads to the fact that the coating on the tongue, which is normally white, becomes yellow or greenish-yellow; a yellow-brown tint is also possible.
Another characteristic symptom that clearly “signals” about problems with the liver is the rich crimson color of the tongue and mucous membranes of the mouth (occurs during poisoning). Also, a similar type of tongue occurs with cirrhosis and severe stages of intoxication.
Rash and itchy skin
Liver diseases have a detrimental effect on the immune balance and cause the occurrence of various pustular elements (pimples, boils).
As a result of toxicological damage to the body, allergic rashes (spots or pimples) may appear even in normal environmental conditions. At the same time, the allergy panel is steadily expanding.
Pinpoint hemorrhages (hemorrhages) and hematomas due to protein metabolism disorders are also noted.
Excess bilirubin and toxins in the skin cause, along with various rashes, incessant, persistent itching. Upon examination, you can identify scratches on the face (especially in the area of the eyes and mouth), stomach, and arms.
In some cases, knowledge of dangerous symptoms and timely seeking medical help can save a person’s not only health, but also life!
So, if a pronounced, sharp liver odor appears from the mouth, you should immediately consult a doctor!
This symptom may indicate the rapid development of acute liver failure, which is fraught with encephalopathy and coma.
The reason for the appearance of such an odor (in a comatose state, the skin can also acquire it) is a violation of the demithylation process, the accumulation of methionine and its conversion to methyl mercaptan.
Liver failure
In considering the causes of the characteristic odor of mouse droppings or raw liver, the authors pay attention to listing the diseases usually diagnosed with such a symptom. But the fetid amber that exudes from the mouth or the whole body is not a separate disease and not a fundamental sign of a separate type of pathology. This is the result of a process that the organ comes to under the influence of a developing disease. Acute or chronic liver failure is caused by disturbances in the synthesis of protein compounds, blood clotting and severe intoxication.
The difference between acute and chronic is only in the timing of the process. In the first case, massive death of hepatocytes can be observed in the fulminant form of viral or toxic hepatitis, acute hepatosis, pregnancy and Reye's syndrome (in addition to liver failure, there is also fatty liver infiltration and encephalopathy). The prolonged form gradually becomes dangerous until it develops into hepatargia.
Reasons for development
The rate of development of the pathology depends on the provoking factors and the underlying cause. In hepatology, three types of PN are distinguished, with different pathological processes, which in a single form are timidly presented by incompetent authors as the main causes of the appearance of a negative aroma. Hepatocellular and mixed can have an acute and chronic course, while exogenous is always gradual in nature, because it develops in the portal vein, under the influence of external causes.
- Hepatocellular is always the result of necrosis or damage to hepatocytes, which occurs under the influence of poisons, most often penetrating the body through human fault. This is the consumption of inedible mushrooms, viral infections, alcohol abuse, unfavorable environment or working in hazardous industries. Although there are cases of poisoning with salts of heavy metals, household chemicals, and chemical compounds, this happens much less frequently.
- Exogenous - the result of disturbances in the circulatory system. Entering the azygos organ through the portal vein for purification, the humoral fluid flows under strong pressure. By breaking the connecting veins, the blood is not purified, but returns to the systemic circulation.
- Mixed - the result of the simultaneous action of the first and second causes.
Bad breath due to a diseased liver
Clean breathing indicates the adjusted mechanism of the body. However, the cloying smell of raw meat almost always indicates a diseased liver. Confirmation is the presence of the following symptoms:
- skin rash on the body;
- itching;
- liver odor from the skin;
- icteric color of the skin, sclera of the eyes, tongue;
- pain in the right hypochondrium.
Excess toxins damage the liver.
Reactive changes in the body are accompanied by a sweet smell from the mouth due to the liver and are the cause of intoxication of the body with medications, organic compounds or food. The body may be covered with pale pink spots, which do not cause concern. A cloying, slightly rotten smell occurs with excess bilirubin. The skin and organs covered with mucous membranes change pigmentation, acquiring yellowish tints. A pungent, bitter odor can be caused by stagnation of bile or malfunction of the biliary tract. The tongue turns yellow-brown and there is a bitter taste in the mouth. Pain appears behind the right rib. When liver disease is in a severe stage, there is an unpleasant smell of rotten meat from the body and from the mouth, bright red or white pimples appear, which cause severe itching, including scratching and bruising.
Toxic type hepatitis
With this disease, organ damage can be rapid or chronic, lasting for a long time.
The pathology is characterized by the ingestion of various toxins into the body, which provoke the death of hepatocytes (liver cells) and disrupt the functioning of the organ in question.
Toxic substances that have a detrimental effect on the liver are divided into several groups. They are:
- Chlorinated carbon, found in mechanical engineering and used in the manufacture of fire extinguishers, shoes and for disinfection of premises. This substance enters the body through the skin, mouth, nose or gastrointestinal tract.
- Biphenyl, chlorinated naphthalene, which are used in the production of electrical capacitors or electrical wires.
- Benzene derivatives found in explosives and paints and varnishes. They enter the human body in the same way as chlorinated carbons.
- Various metals that negatively affect the liver, killing its cells and causing liver odor from the mouth.
- Natural hepatotoxins: mushrooms or substances from the field of household chemicals.
The degree of negative impact of the substances in question on the liver depends on their composition and the dose received by the person.
Damage to the organ occurs from the hepatotoxic effect of the substance itself or from an allergic reaction to any substance.
The symptoms of toxic hepatitis are quite extensive: yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes, increased liver volume, bad breath, pain in the right side, nausea and vomiting, the appearance of dark urine and light feces, severe weakness, diarrhea, slight increase in body temperature, shortness of breath, vision problems.
With more severe damage to the organ, a person may experience convulsions, bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, ascites, kidney dysfunction, loss of consciousness and even the development of coma.
Causes of unpleasant odor
The liver plays the role of a filter in the body and passes through itself all compounds and substances that come with food, water, and medications. Liver lesions that are characterized by an unpleasant odor are as follows:
- poisoning by alcohol, chemicals, poisons;
- reaction to taking medications;
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis.
Return to contents
General intoxication of the body
Toxins entering the body disintegrate, leading to the death of liver cells. The disease can occur in acute and chronic form. But in any form, the disease without proper treatment leads to serious consequences. The action of the allergic reaction affects the hepatoprotector, and the symptoms spread to different organs depending on the type of toxic substance. The main ones include:
- increase in liver size;
- nausea with vomiting;
- weakness;
- body temperature from 37 to 38 degrees;
- pain under the rib;
- photophobia;
- change in color of stool and urine.
In this case, the tongue acquires a bright red tint, bad breath appears, and nodular bruises on the legs are possible, which turn into trophic ulcers or weeping wounds. Their treatment is unproductive, since the released toxins act poisonously and support allergic manifestations in the active phase.
Drug allergies
Often, therapeutic agents cause an anti-effect, i.e., instead of therapeutic effects, toxicosis occurs. Antibiotics, anticonvulsants, antipyretics and analgesics should be taken with caution. For liver diseases, drugs of such groups are contraindicated or are taken according to a reduced dosage regimen, taking into account the type and degree of liver disease, as well as the inability of the diseased organ to perform its functions fully.
Hepatic hepatitis
Acute or chronic liver disease of viral etiology is called hepatitis. The main routes of transmission: through blood transfusion, from mother to fetus, fecal-oral and sexual contact. Viral hepatitis is divided into 6 groups:
- A - resembles the flu and is accompanied by a high temperature with the presence of aches, headaches, and no bad breath. With this type, it is necessary to observe bed rest, adhere to a diet and carry out detoxification therapy.
- B - low-grade fever, joint pain, and rarely skin rashes. Recovery occurs in 80% of cases and often develops into a chronic form, which is fraught with the development of cirrhosis or oncology. If the process is chronic, there is practically no cure. A daily routine and diet are followed, which is supplemented with drugs that act to improve metabolism in liver cells.
- C - characterized by decreased appetite, weakness, nausea, vomiting, pain in the right rib. An increase in the size of the liver and spleen, an increase in bilirubin and liver tests by 8-10 times is recorded. The treatment uses interferon-alpha, which prevents infection of hepatocytes.
- D - occurs against the background of hepatitis B, with the same symptoms. Antiviral treatment in hospital.
- E - nausea, headache present. This type is treated symptomatically, since the body's immune system is able to destroy the virus on its own. The recovery period is achieved after 1-1.5 months.
- G - similar to hepatitis C, but less dangerous. The route of transmission is mainly through non-sterile needles. Diet and immunomodulatory therapy quickly relieve all painful manifestations.
Return to contents
Cirrhosis of the liver
A disease characterized by the death of hepatoprotective cells of the body’s main “filter” with the replacement of its structure. In place of the voids, fibrous tissues and nodes form, reducing the functioning of the organ. The causes of cirrhosis can be: hepatitis, heredity, pathologies of the biliary tract, alcohol, poisoning, and disruptions in the immune system. Symptoms of the disease:
- bitterness in the mouth;
- rib pain;
- dystrophy;
- nausea and vomiting;
- amyotrophy;
- redness of the face and palms.
Return to contents
Other symptoms
In the chronic course of the disease, reactive changes occur in the liver, followed by its destruction. There are 4 stages of the disease, which have the following symptoms:
The onset of the disease is accompanied by a feeling of muscle weakness and fatigue.
- With grade 1 disease, signs may be absent or insignificant.
- At stage 2 there is:
- decreased ability to work;
- weakness throughout the body;
- dyspepsia;
- yellowness of the integument, swelling;
- ascites;
- bleeding.
- At the 3rd stage, deep disturbances in the body are observed:
- metabolic imbalance;
- organ dystrophy;
- severe exhaustion.
- Fourth stage. The following signs of an approaching hepatic coma appear:
- reduction in liver size;
- lack of appetite;
- neuropsychic disorders;
- tremor of the limbs;
- excitement followed by stupor;
- cold extremities;
- loss of consciousness.
Return to contents