1883
The aesthetics of dentures is no less important than functionality. For a long time, dentists were unable to create a material that would satisfy both aesthetic and strength requirements.
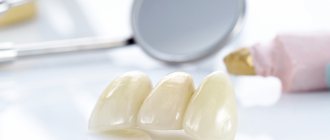
Combined crowns were the solution that allowed us to combine beauty and strength in one design.
Product characteristics
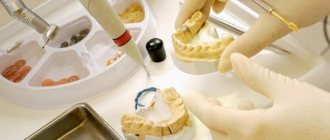
Combined crowns are those consisting of a metal base (frame) and a non-metallic lining applied to it.
These designs represent a compromise between functionality and aesthetics. Metal makes products durable, not subject to cracks and destruction; the facing material gives them a look similar to natural enamel.
The production of combined crowns consists of two stages:
- stamping or casting of a metal frame;
- lining it with ceramics, plastic or composite.
Frame
Dozens of grades of noble and base metals and their alloys have been developed for the manufacture of frames of combined models.
The most commonly used materials are:
- Cobalt-chrome alloy. The material has high strength and rigidity, which makes it possible to make the frame thin - 0.3-0.4 mm. But its casting properties are low, and its high rigidity makes stamping difficult.
- Nickel chrome alloy. It has good casting characteristics, but due to low rigidity it requires a frame thickness of 0.4-0.5 mm.
- Stainless steel.
- Titanium and its alloys.
- Noble metals - platinum or gold and their alloys.
It is advisable to use materials containing gold for manufacturing hidden under the lining of the frame for two reasons - due to the high biological compatibility with human tissues, and the yellow color, which does not show through from under the lining.
To obtain the required aesthetic effect, gold alloys can be replaced with base metals coated with titanium nitride (“gold-like”).
The thickness of the frame wall should not be less than 0.3 mm. Metal bases are made by stamping or casting. Stamped structures are cheaper, but solid ones have a number of advantages:
- They are more accurately adjacent to the stump. This makes the fixation more reliable, since a thin layer of glue holds better than a thick one.
- They are less subject to deformation than stamped ones , which increases the strength of fastening of the cladding to the base.
- It is possible to manufacture a frame with a ledge for facing material. This eliminates the traumatic effect of the microprosthesis on the gums.
- Cast structures can be cast together with bridge prostheses. Stamped types have to be connected to MP soldering, which is undesirable due to the chemical reaction of the solder to certain substances contained in saliva.
The technology for manufacturing cast and stamped frames at the first stages is the same and provides for:
- turning the tooth;
- taking impressions from it and antagonist teeth;
- making plaster models from casts;
- checking them on an occluder.
Further production of stamped and cast bases differs. The first ones are usually made from dental sockets. To do this, a metal die (mold) is cast using a plaster model, on which a metal crown is forged using free forging.
To produce a solid-cast frame, wax modeling and casting of the product from a nickel-chrome alloy or other metal is performed.
Facing
Ceramics and plastic composite are used as cladding.
The most widely used is ceramics, which can have different properties depending on its composition.
Ceramics based on lithium disilicate and leucite and aluminum-magnesium spinel have good strength properties.
Advantages and disadvantages of stamped products
Stamped metal products for oral prosthetics have their advantages and disadvantages. In addition to ease of manufacture and relatively low price, several more positive qualities can be highlighted:
- since the thickness of the stamped crown does not exceed 0.3 mm, there is no need to remove a large layer of hard tissue from the diseased tooth;
- this type of prosthesis can be installed without first removing the nerve;
- Thanks to quick production and easy fixation in the oral cavity, the prosthetic procedure takes little time;
- the versatility of the prosthesis allows you to install a crown even when other methods of prosthetics are not possible.
In the last century, medical presentations and scientific reports were devoted to the topic of metal dental crowns. Modern methods of dental correction and the use of the latest materials in orthopedic dentistry have almost completely replaced “stampings” from the field of dental prosthetics. Stamped products are abandoned for several reasons:
- the medical cement composition, which serves for reliable fixation of metal caps, quickly dissolves under the influence of external factors, which leads to the formation of gaps between the tooth and the crown;
- a loose fit of the “stamping” is fraught with clogging of the resulting gap with consumed food and the development of caries;
- metal does not have the same high strength characteristics as modern materials and wears out over time.
In addition, metal teeth present in the mouth are unlikely to brighten anyone's smile. Today it is quite difficult to find a clinic that manufactures and installs such prostheses.
Indications and restrictions
Combined microprostheses are recommended for the restoration of teeth that are visible when smiling and speaking (primarily maxillary frontal and premolar teeth) that have the following defects:
- Significant destruction of the coronal part due to caries or trauma, when fillings and inlays cannot solve the problem.
- Anomaly in the size, shape and position of the teeth.
- Change in enamel color (as a result of fluorosis, for example).
- Mobility of teeth (in this case they are used as an element of splinting structures).
- Hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of teeth.
- Destruction or deterioration of previously installed microprostheses;
- Reduced lower facial height due to worn teeth.
Combined products can also be used as components of bridges.
Why is a metal-free tooth crown popular among patients?
Come here to view the types of metal coated crowns.
At this address https://zubovv.ru/protezirovanie/nesemnyie-p/koronki-np/mozhno-li-stavit-na-zhivoy.html we will find out whether it is possible to put a crown on a living tooth.
Contraindications
Most contraindications for combined crowns are associated with their significant thickness (due to the presence of two layers - metal and cladding), which requires extensive grinding of the supporting teeth.
Combined designs are not used in the following cases:
- The location of the pulpous chamber is close to the surface of the tooth. When grinding, the pulp can become burned and necrotic.
- Lower incisors. Due to the thinness of the bone tissue and the risk of damage to the pulp.
- Deep bite combined with oral inclination of the upper incisors. In this case, there is simply not enough space for the thick walls of combined microprostheses.
- Age up to 16-18 years. The teeth have not finished forming.
- Bruxism and other parafunctions. Increased excitability of the masticatory muscles leads to distal and lateral displacements of the LF, which can lead to failure of the microprosthesis.
- Pathologies of marginal periodontium. This contraindication applies only to metal-ceramic teeth, which, due to their low abrasion over time, can cause overload of the periodontium.
Dental crown - what is it?
A dental crown is a structure that replaces or restores the coronal part of a tooth. By analogy, the crown can be compared to a soldier’s helmet. A crown on a tooth covers its upper part, like a helmet, on a soldier's head.
A dental crown has three main functions:
- Aesthetic (visually retains an appearance indistinguishable from your own teeth)
- Functional (promotes chewing, as it is fully capable of withstanding and distributing the chewing load in full.)
- Protective (preserves the tooth’s own tissues from mechanical and carious damage)
Why do you need to cover (restore) teeth with crowns?
- Tooth decay is the most common reason for crowning. If the coronal part of the tooth is destroyed by more than 50% or the presence of circular caries, restoration of the coronal part of the tooth with an orthopedic crown is indicated. If this rule is not followed, unfortunately, within several years the tooth is destroyed and further restoration is not possible (the tooth will be removed).
- Depulped (nerves have been removed from the teeth) chewing teeth should be covered with orthopedic crowns to avoid chips and fractures of the walls of the crown part of the tooth. The thing is that when depulping (removing the nerve of a tooth), in addition to the nerve, the entire nutrient bundle is removed. In other words, the tooth does not receive nutrition and the materials used to fill the root canal have a strong drying effect on the tooth tissue, that is, they dry out the tooth, and therefore the tooth becomes very fragile.
- Aesthetic defects, such as dental discoloration due to fluorosis, enamel hypoplasia, tetracycline teeth, etc., require restoration through the manufacture of crowns.
- Injuries, in case of traumatic damage to the coronal part of the tooth (fracture, chipped tooth crown), there is often a need for restoration with an orthopedic crown.
- The need for total or partial jaw prosthetics. That is, if it is necessary to replace part of the missing teeth or correct dentofacial deformations, the supporting teeth are covered with crowns, which are part of bridge or splinting prostheses.
- Also, if we are talking about removable dentures, then the supporting teeth are covered with crowns to avoid mechanical damage from excess pressure from the removable denture.
Why depulpate teeth before dentures?
Before prosthetics, the dentist must grind (remove part of the dentin and enamel) the tooth by 1.5 - 2 mm (depending on the material of the future crown) around the circumference. It is impossible to maintain absolute sterility during this process, due to the fact that the oral cavity is not sterile. Therefore, by leaving your teeth “alive” you preserve microbes in your tooth, and over time (from several months to several years) the problem will make itself felt and the tooth will have to be removed.
"Pros and cons"
The cladding is made from different materials, which determine their main characteristics. Therefore, we can only talk about the advantages and disadvantages of combined structures with a specific cladding in mind.
The most popular metal-ceramic models have the following advantages:
- High degree of functional restoration – from 80 to 100%.
- Greater strength due to the metal frame (much stronger than non-metal structures).
- Satisfactory aesthetics (less than all-ceramic products, but quite high).
- Reasonable price considering their high characteristics.
- Possibility of use as elements of bridges , orthodontic structures, splinting devices.
Flaws
- Limitations associated with large thickness, in particular, undesirability of use for lower anterior teeth.
- Significant weakening of supporting teeth due to severe grinding.
- Not the smallest price - higher than that of purely metal models.
As already noted, the main properties of combined microprostheses are determined by the type of lining. The indications, characteristics, durability and price of combined structures depend on it.
Three types of cladding are mainly used: plastic (metal-plastic), ceramic (metal-ceramic) and composite (metal-composite).
Metal-plastic
This is the most “modest” type of microprosthesis in terms of its characteristics. Polymers, usually acrylic, are used as cladding.
The main advantage of metal-plastic structures is their low cost. This is the most inexpensive of all existing options, excluding purely plastic ones, which are used only as provisional ones.
The advantages include satisfactory aesthetics, which is maintained during the first years of operation.
Disadvantages of metal-plastic products:
- Transmission of the base through the polymer. To combat it, the metal frame is coated with titanium nitride or special opaque coatings (EDA-02).
- Staining that appears over time.
- Detachment of plastic from the base. If this happens, food gets stuffed into the gap between the polymer and the metal with all the negative consequences of this phenomenon - rotting, proliferation of microorganisms, odor.
But metal-plastic models are quite capable of serving for several years, remaining functional and aesthetic.
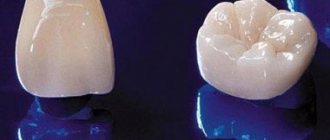
Metal-ceramic
Ceramics of different compositions can be used for cladding metal frames.
Based on the totality of their properties, metal-ceramic microprostheses can be called a leader not only among combined structures, but also among all crowns in general.
A cast frame is usually made for ceramics. Before cladding, it is sandblasted, steam cleaned and oxidized at a temperature of 980°C.
After sintering and cleaning are completed, the microprosthesis is fitted to the tooth, modified if necessary, and sent to the laboratory for the final operation - glazing.
Metal composite
A dental composite consists of a binder (organic resin - about 20%) and a filler (small particles of ceramics up to 80% of the volume). The ceramic fraction gives the material hardness, the resin gives elasticity and manufacturability. The material polymerizes (becomes hard) when exposed to light.
The main advantage of the composite over ceramics is the absence of fragility due to the presence of resin.
Disadvantages - high abrasion, color change, polymerization shrinkage, plaque formation.
The lack of fragility allows for a thinner metal base. As a rule, it is most often made from a cobalt-chromium alloy.
In appearance, metal-composite crowns are similar to metal-ceramic crowns, but they are inferior in strength and service life. The color in the initial period is very natural, but over time the composite darkens due to the absorption of pigments contained in food and drinks.
Metal-composite microprostheses are relatively strong and durable, their service life is 5-10 years. They can be installed on any teeth and implants.
An important feature of composite products is good maintainability. They can be repaired in the patient's mouth.
Manufacturing technology
A Belkin crown is a metal-polymer structure in which a stamped metal base has a window on the vestibular side. This allows you to ensure the natural color of the cladding and reliable fastening of the plastic to the frame.
Belkin crowns are installed on the upper frontal teeth and premolars. The stages of their production include:
- tooth preparation using standard technology;
- taking impressions from the stump and antagonist teeth;
- production of a stamped frame based on an impression;
- fitting it to the tooth;
- drilling a hole on the vestibular surface, filling it with wax and installing it on the tooth (excess wax mass is squeezed out through the hole);
- obtaining an impression of a tooth with a crown installed;
- removing wax from the frame by heating, cutting out a window on the vestibular surface with teeth around the perimeter (for more reliable fastening of plastic to metal);
- degreasing the frame, coating with white varnish to mask the color, installing on a plaster model, modeling with wax;
- casting of polymer cladding (plastic takes the place of wax), polymerization, grinding, polishing.
- Fitting the microprosthesis onto the tooth, modifying it if necessary;
- fixation with cement.
The advantage of Belkin’s models is their ease of manufacture and good aesthetics. But the structure is not strong enough, so it is not used as a support in bridges that replace more than 3 frontal teeth.
The video shows the technique for making a combined crown.
Crown according to Pogodin
Pogodin’s model differs from Belkin’s design in that the metal is cut out not only from the vestibular side, but also from the oral side. At the top, only that part of the metal remains that is in contact with the antagonist teeth. The front and back, as well as the cutting edge of the tooth, are covered with one piece of plastic.
The model, freed from excess metal, is degreased, coated with white varnish, placed on a plaster mold of the tooth, modeled with wax, a plastic part is cast, polymerized, processed and fixed to the tooth with cement.
The product contains even less metal than the Belkin microprosthesis , so it cannot be used at all as an element of bridge prostheses.
a) manufacturing according to Belkin; b) manufacturing according to Pogodin.
Manufacturing stages
The creation of a prosthesis is carried out in close cooperation between a dental technician and an orthopedic surgeon. The technology for manufacturing stamped crowns includes several clinical and laboratory stages:
- a thorough examination of the oral cavity by a dentist and carrying out preparatory measures, which include caries removal and root canal treatment;
- removal of the upper tooth tissues with a drill;
- choice of crown color, depending on the patient’s wishes;
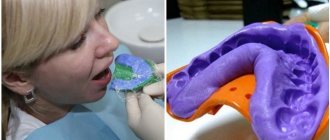
- taking impressions of both jaws, which is necessary for accurate fixation of plaster models;
- making models using the obtained impressions;
- installation of the resulting models in the position of central occlusion to determine the correct location of the upper and lower dentition;
- modeling of the future design by a dental technician;
- making a metal stamp;
- choosing a sleeve suitable for the tooth and giving the cap the desired shape;
- stamping the product and handing it over to the dentist;
- fitting of the prosthesis and carrying out corrective procedures.
The final stage is fixation in the oral cavity using dental cement. For some time after prosthetics, the patient may feel a feeling of discomfort in the oral cavity, which usually goes away after 2-3 weeks.
Installation steps
Metal-ceramic models are stopped in two stages:
- Temporary installation (for about a month) to identify negative aspects and errors.
- Permanent fixation.
After the trial period, the crown is removed, the patient is questioned about complaints, and the prosthetic bed and marginal periodontium are examined. If there are no complaints or damage, the microprosthesis is attached to permanent cement.
The glue is mixed thinner than when installing stamped structures. This ensures the necessary fluidity of the cement with small gaps between the crown and the tooth.
Let's figure out together which crowns are best placed on implants and why.
In this publication, we will find out what to do when a gap appears between the crown and the gum.
Here https://zubovv.ru/protezirovanie/nesemnyie-p/koronki-np/plyusyi-i-minusyi-farforovyih.html we will look at the technology for making porcelain crowns.
Common questions from clients
Why do the gums around the crown turn black (darken)?
- Error when preparing a tooth for a crown.
- Error in the manufacture of the crown (non-certified metals or the frame overlaps the ceramics on the outer surface).
- Root caries (a carious process has occurred under the crown), that is, the seal of the crown is broken.
- In all cases, urgent replacement of the structure is required. Failure to follow the recommendation will result in tooth extraction.
The ceramic on the crown chipped, why?
- Bruxism (teeth grinding).
- Technical shortcomings in crown manufacturing.
- Incorrect determination of occlusion by the dentist.
- In all cases, urgent replacement of the structure is required. It is impossible to repair high-quality ceramic crowns; replacement is required.
The crown fell out, how did that happen?
- Consultation with a dentist is required.
- If the crown falls out before a year after manufacture, most likely an error was made during prosthetics (subject to fixation with permanent cement).
- If many years have passed, then there are too many options, this requires immediate intervention from a specialist.
Why does the tooth under the crown hurt?
- In almost all cases, it indicates problems in the supporting tooth. Immediate consultation with a specialist (orthopedic dentist, therapist and surgeon) is required.
Life time
The service life of combined crowns depends to a greater extent on the lining material and, to a lesser extent, on the technology of its application and the installation location.
- For reference. Metal-free structures made of zirconium dioxide last the longest - up to 15-20 years.
- In second place are metal-ceramic structures - 10-15 years.
- The service life of metal composite products largely depends on the properties of the composite and can vary from 5 to 10 years.
- Metal-plastic crowns have the shortest service life, limited to 5 years.
The service life of combined microprostheses is affected by their care and the patient’s dietary preferences. Recommendations regarding the use of combined crowns are practically no different from those given for any type of prosthetics.
You need to brush your teeth at least 2 times a day, give up solid foods and smoking, regularly visit the dentist for preventive purposes, and, if necessary, resort to professional cleaning.
Price issue
The cost of combined crowns depends, first of all, on the lining material (its brand and manufacturer). Manufacturing technology, status and location of the clinic also affect the price, but to a lesser extent.
Approximate price of crowns lined with different materials.
| Cladding and frame material | price, rub. | Note |
| Ceramic + platinum/gold | From 18 000 | Taking into account the cost of the precious metal |
| Ceramic + Nickel-Chromium/Cobalt-Chromium Alloy | From 8 000 | When using materials from domestic manufacturers - from 5,000 |
| Ceramics + zirconia frame | From 15 000 | — |
| Plastic + Cobalt-Chromium Alloy | From 2 500 | — |
| GRADIA composite + cobalt-chromium alloy | From 8 000 | — |
Reviews
Of particular interest is the use of metal-composite crowns, since they are installed much less frequently than metal-ceramic and metal-plastic crowns.
If you have experience using crowns lined with composite, tell us what their features are, how many years did they last, and what condition were they in? The comment form is at the bottom of this page.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags dental crowns fixed dentures
Did you like the article? stay tuned
No comments yet