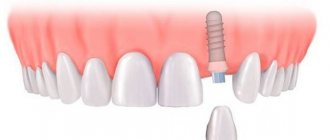
A wisdom tooth is an ordinary tooth, the structure of which is no different from the multi-rooted other teeth. Doctors call wisdom teeth “eights,” because if all the teeth are conventionally divided into 2 symmetrical halves by a vertical line, then such teeth in the lower and upper dentition will be eighth in a row. Therefore, the answer to the question “how many wisdom teeth can a person grow” is four (one on each side, bottom and top). But this does not mean that all four wisdom teeth will necessarily erupt in every person. The whole reason is that during human development, the size of the jaws decreased significantly (by 10-12 mm). This is due to their transition to thermally processed, softer foods. Because of this, the chewing load on the jaw is reduced. As a rule, the rudiments of wisdom teeth can be found in all people, but in some people all 4 teeth erupt, while others do not even know if they have them at all.
At what age do wisdom teeth erupt?
Milk teeth are replaced by permanent teeth starting from the age of 6, this process ends around 12-13 years. The eruption of wisdom teeth most often occurs no earlier than 16-25 years of age. True, the literature describes cases where wisdom teeth erupted at the age of 40. But such cases are extremely rare.
Why did wisdom teeth get such a name?
Permanent teeth begin to erupt in a child at the age of 6-7 years, and the eruption of wisdom teeth occurs at the age of 16-25 years. It is by the age of 25 that the growth of all organs and systems of the human body, as well as their development, has completely ended, and then the process of aging of the body begins. Thus, the time when the eruption of the eighth teeth occurs can be considered the period of maturity of the organism, hence the last permanent eighth teeth got their name.
How many baby teeth should there be?
We all know that a child is born without teeth, and their first appearance is observed at 6-7 months. Let's talk about how many baby teeth a child should have. First of all, it is worth noting that, like permanent teeth, baby teeth consist of a root system, nerve endings and blood vessels. This is why many children suffer so much pain when their first teeth appear.
Already at the age of 6 months, a child may first encounter severe and aching pain, which is the cause of the appearance of the first tooth. This is considered the norm.
On average, a child’s teeth grow until they are two and a half years old, and their order is as follows:
- 7-9 months – 4 teeth: two upper and two lower.
- 1 year old – 8 teeth, some children have 12 teeth.
- 1.5 and 2 years old – 18-20 teeth.
- 2 years – exactly 20 teeth.
The development and appearance of primary teeth also directly depends on a number of factors, which may include genetic characteristics. If you observe certain abnormalities in the development of teeth in your baby, do not rush to draw your conclusions. It is better to immediately contact a pediatrician who will examine the baby’s jaw and be able to give an accurate answer as to why this or that slowdown in growth occurred.
Children also have molars; there should be 8 of them, with 4 teeth in each row. At a time when an adult already has 20 molars, 10 in each row of the jaw.
Why do people need wisdom teeth?
As you know, in nature there is nothing superfluous. Although wisdom teeth are considered to be vestiges (parts of the body that have lost their function during the process of evolution), they can often be necessary in old age. The eighth teeth can serve as a support for bridge prosthetics, and also partially take over the chewing function if, for some reason, it becomes necessary to remove adjacent teeth. If wisdom teeth are healthy and correctly positioned, then they perfectly complement the dentition. But very often, “eights” can cause problems, because many complications arise during their eruption.
Complications that occur during the eruption of wisdom teeth
In some cases, various complications may arise during the eruption of wisdom teeth. Most often, inflammation of the tissues that are located around the tooth occurs. During the growth of a wisdom tooth, a mound appears on the surface of the gum, which is covered by a mucous membrane - the so-called “hood”. The wisdom tooth covered with this “hood” is subject to constant traumatization by solid food, due to which infection subsequently develops and inflammation develops. As a result of food debris getting under the “hood,” favorable conditions arise for the life of pathogenic flora, resulting in purulent inflammation—pericoronitis.
Clinical picture of pericoronitis
The disease begins with increasing pain in the area of the wisdom tooth. The pain is very intense, it can radiate to the temple and ear. Pain may occur when opening the mouth, yawning, or swallowing. Sometimes you feel like your throat and cheek hurt, not your wisdom tooth. The process may also involve the facial muscles and lymph nodes. If a wisdom tooth becomes inflamed, the general condition of the whole body also suffers: a headache occurs and the temperature rises. The mucous membrane in the area of the diseased tooth is painful and red; as a result of “pressure” on the hood, pus may be released and swelling may occur.
Symptoms of complicated eruption of third molars
The process that begins with painful sensations in the jaw leads to the appearance of more serious symptoms:
- the pain increases and begins to radiate to the ear or temple;
- the wisdom tooth erupts, swell greatly;
- due to its inflammation, pain appears when swallowing;
- facial muscles begin to ache;
- temperature rises and headache occurs;
- a “hood” appears on the gum, under the shell of which, when food gets in, pathogenic microflora begins to multiply and pus forms.
Increasing throbbing pain, accompanied by an increase in temperature, indicates the presence of an inflammatory process, pericoronitis. To prevent the formation of a purulent abscess at the site of the “hood,” you should contact the clinic as soon as possible. Otherwise, the inflammation will spread to the tissue surrounding the tooth and lead to blood poisoning.
The surgeon opens the gingival “hood” to release the infiltrate that has accumulated underneath it, and rinses the resulting cavity. The patient is prescribed mouth rinses with antiseptic solutions to prevent wound infection. If necessary, anti-inflammatory therapy with antibiotics is carried out. Otherwise, you may need to have your wisdom tooth removed in Moscow.
If the wisdom tooth cuts slowly, relapses are possible. In this case, the surgeon may decide to remove it. “Eights” are also removed in a number of other cases, when during the process of eruption the trigeminal nerve becomes inflamed, a jaw cyst is formed, when they grow “into the cheek,” etc.
What you should not do if your wisdom tooth is sick:
- Under no circumstances should you apply any heat to your cheek (including heating pads), or rinse your mouth with warm water. As a result of any warming, the infection can spread even more, even suppuration of the bone tissue is possible.
- It is not recommended to put painkillers on the tooth area, because as a result, not only will the pain not be relieved, but an ulcer may form on the gum.
- Under no circumstances should you use advice given by friends and relatives. This or that remedy can help them, but the exact cause and diagnosis are unknown, as a result of which your wisdom tooth is swollen.
What to do if your gums are inflamed
Contact your dental surgeon immediately. Before you plan to do this, you can take an anesthetic (ketorol, analgin, etc.) orally. It is advisable to rinse the oral cavity with a cold solution, which is prepared at the rate of 1 teaspoon of soda and the same amount of salt per glass of water.
Treatment of such a pathology consists of incision (opening) of the mucous “hood”, further washing of the cavity and taking anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs. If a large amount of pus is removed during the autopsy, the patient must also take antibiotics. If the gums surrounding the wisdom tooth become inflamed again, then most often the dentist advises removing the wisdom tooth.
Caries
Carious lesions are another common problem that occurs during the eruption of wisdom teeth. The development of this pathology is due to the fact that the eighth teeth are located in a hard-to-reach place, which prevents good daily oral hygiene. Often, a wisdom tooth may erupt with initial signs of caries and damaged enamel. Due to the fact that such teeth are always pressed tightly against neighboring teeth, caries can quickly spread to them. In this case, after an examination, the dentist will decide whether the wisdom tooth can be treated or whether it is better to remove it.
Diagnosis of “crowded teeth” – what does it mean?
Dental crowding is a pathology characterized by close positioning and rotation of teeth. Because the teeth are too close together, some of them erupt outside the arch and overlap each other. This anomaly has several degrees of severity:
- mild
- when the crowding of teeth within one jaw is approximately 2-3 mm; - medium
- when it reaches 4-6 mm; - strong
- more than 7 mm.
Crowding can form on one or both jaws, as well as simultaneously in the anterior and lateral regions. In addition, the curvature, if left untreated, worsens over time, which leads to very sad consequences and requires more serious treatment. An interesting fact is that crowding of the lower teeth is several times more common than the upper teeth.
Crowding of teeth and malocclusion
Due to the fact that there is usually not enough space for a growing wisdom tooth, it begins to prop up the adjacent molar and shift it towards the center, and it, in turn, also moves towards the center of the teeth adjacent to it. As a result, crowding of teeth occurs and their correct alignment is disrupted. If this process goes too far, the bite may be disrupted.
Pressure on the adjacent tooth
Quite often, as wisdom teeth grow, pain may occur (constant dull or intermittent), radiating to the ear, temple or lower jaw. If there are no external signs of inflammation (redness and swelling of the gums), then you need to take a photo of the tooth. After all, this is the only way to understand whether the wisdom tooth is growing correctly and whether it will be necessary to remove it.
Inflammation of the branches of the trigeminal nerve
The pathology is manifested by attacks of pain in the neck, as well as twitching of some muscles. Painful attacks can be triggered by normal daily activities such as washing, brushing teeth or shaving. Most often, the symptoms go away after the wisdom tooth is removed and proper anti-inflammatory treatment is administered.
Jaw cyst
Since the growth of a wisdom tooth occurs very slowly, it can cause the formation of a cyst in the lower jaw. In the event that the cyst does not grow, the course of the disease may be asymptomatic, and the cyst can be discovered by chance when a picture of the jaw is taken for completely different reasons. If the cyst grows, this causes pain in the area of the wisdom tooth. There may be an accumulation of fluid in the cyst, which will gradually corrode the walls of the teeth. If an infection gets into the cyst cavity, a gumboil (ulcer) of the wisdom tooth occurs. In this case, you can definitely answer that the “eight” must be removed.
Problem: Parents with a teenage girl contacted the orthodontist. The girl grew permanent fangs, but there was not enough room for them in the row, and the fangs grow as if in the second row. The desire of the patient and her parents is to straighten her teeth .
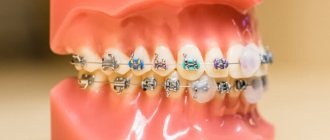
Solution: treatment was carried out using Damon braces without removing teeth, crowding of teeth was eliminated and the dentition was aligned.
Quite often, children whose baby teeth were straight develop orthodontic problems after changing teeth - the teeth grow out of line or grow crooked. This may be due to the fact that children did not eat enough solid foods, their jaws were not stimulated to grow, and the permanent teeth grow larger than the baby teeth, and now there is not enough space for the permanent teeth, causing crowding of the teeth. In addition to an unaesthetic appearance, protruding teeth can cause injuries to the mucous membranes of the lips or cheeks. Violation of the position of the teeth leads to excessive wear of the opposing teeth and overload of the temporal joints. That is why it is necessary to show the child to the orthodontist during the period of teeth change in order to identify the problem as early as possible.
In a teenage girl, after a comprehensive diagnosis, the orthodontist revealed a neutral bite (tendency towards class 3), a high position of 13 23 teeth (canines of the upper jaw), a lack of space for 13 23 teeth, protrusion of the incisors of the upper jaw (the front teeth are excessively deviated forward relative to jaws), narrowing of the dentition, upper retrognathia. Parents were told in detail about the appropriate brace systems in this situation, the cost of treatment with various brace systems and the approximate duration of treatment (1.5 - 2 years).
Initial situation:
The peculiarity of this case is that there is very little space for placing teeth in a row, and Olga Baranova’s ORTHODONT PROJECT is in no hurry to remove teeth; they try to carry out treatment while preserving all the teeth. The experience of doctors helps to discern hidden opportunities. Timely treatment in many cases saves teeth from removal.
Orthodontic treatment in adolescence has its advantages: before the final change of teeth (the outer chewing teeth, the sevens, have not yet grown in), the child has a so-called growth potential. Impact on the jaws and teeth during this period gives the greatest effect. Orthodontic treatment for adolescents often requires less time than for adults, and tooth movement is less painful. Many parents worry about their child’s oral hygiene, but this problem can be solved by hygienic preparation before installing braces, using products specially selected by our hygienists for cleaning teeth with braces, as well as regular, once every three months, professional teeth cleaning using the Air Flow method.
Damon -Q braces were chosen for treatment .
The patient visited the orthodontist every 1.5-2 months to monitor the progress of treatment and change equipment.
In parallel with the orthodontist, patients of Olga Baranova's ORTHODONT PROJECT are led by an osteopath who helps relieve stress in the temporal joints and articulations of the skull bones caused by orthodontic correction. An integrated approach to orthodontic treatment provides a more stable result.
Orthodontic treatment lasted 2 years and 1 month. A total of 15 visits to the orthodontist were required.
After removing the braces, a non-removable wire retainer was fixed on the lower teeth, which should hold the new position of the teeth until it is finally fixed. A removable transparent mouthguard was made for the upper teeth, which must be worn at night. You should visit the orthodontist every 2-3 months to monitor the condition.
The result of orthodontic treatment with braces :
The cost of treatment with Damon-Q braces was 115,700 rubles.
More examples of orthodontic treatment for crowded teeth can be found here.
Make an appointment
When is it necessary to remove wisdom teeth?
Whether it is necessary to remove a wisdom tooth or not is the most common question that interests every person who is faced with the problematic eruption of “eights”. For wisdom tooth removal, as for any other surgical procedure, there are indications. Wisdom teeth are removed if:
- There are impacted “eights” - those that are incorrectly positioned in the jaw and cannot erupt, since they rest partially or completely on other teeth
- The “eight” has partially erupted, but there is pain and inflammation in the gums (recurrent pericoronitis).
- For pain along the trigeminal nerve.
- Presence of a mandibular cyst.
- Periodic pain in the area of the wisdom tooth, accompanied by headache, pain when swallowing or other painful conditions.
- Trauma to the oral mucosa as a result of improper tooth positioning.
How to fix crowded teeth in children
The absence of spaces between the primary canines in a small child is a sure sign that there is not enough space in the jaw. And if even baby teeth can’t fit on it, then molars definitely won’t be able to fit either. Treatment at such a young age is usually not carried out, since it is difficult to force very young children to wear orthodontic appliances, even removable ones. However, it is during this period that one very important thing needs to be done - get rid of bad habits that cause crowding: wean the baby from sucking his finger and pacifier, teach him to swallow correctly and eliminate the cause of mouth breathing.
Treatment of crowding of the upper and lower teeth in the early mixed dentition, that is, starting from 6 years of age, is carried out with the help of plates, as well as trainers, LM-activators, palatal expanders and other functional devices. At this age, it is especially effective to correct the size and position of the jaws, but it is not always necessary to correct crowding during this period. Of course, it will be possible to straighten the dentition, but there is a high probability that they will return to their previous position after the remaining molars erupt. This is why many orthodontists recommend delaying treatment until 11-13 years of age, when the bite is fully formed.
A specialist can prescribe a young patient a set of myogymnastic exercises that normalize the functioning of the oral muscles. To achieve the necessary results, it is enough to devote only 7-10 minutes a day to gymnastics. This way you can avoid not only the development of malocclusion, but also problems with the musculoskeletal system in the child.
Examples of myogymnastic exercises
✔ Button.
Hold a large flat plastic button horizontally between your lips, first for 1 minute, then for 3-5 minutes.
✔ Ruler.
Press the edge of a ruler 8-10 cm long with your lips, while holding it horizontally. Next, increase the load by placing a small object on the ruler.
✔ Air.
With your lips closed, blow air first under the upper and then under the lower lip.
✔ Cheeks.
With your lips closed, puff out your cheeks, and then slowly squeeze out the air with your fists through your clenched lips.
To eliminate anomalies in adolescence, inexpensive designs are used - the price of ceramic braces is quite justified in terms of aesthetics and treatment effectiveness, and the most disciplined children are even fitted with aligners - removable transparent aligners that must be worn at least 22 hours a day. However, even at this stage, specialists are faced with certain difficulties in the form of wisdom teeth that have not yet appeared, so they are faced with a very important question - is it worth carrying out treatment before they erupt or not?
Consequences of wisdom teeth removal
In almost all cases, removal of wisdom teeth is traumatic, which can result in slow healing and various complications. Pain after such a procedure may occur due to alveolitis, an inflammatory process in the socket. Normally, the hole is covered by a blood clot, which protects the wound from pathogenic microbes entering it. That is why it is strictly forbidden to rinse your mouth after tooth extraction! When a blood clot is washed out, an infection may develop or a dry socket may occur, which may require further surgery. In some cases, after removal of the “eight”, numbness of the tongue, chin or lip may occur in the first days. If this condition does not go away within a week, you need to consult a doctor again, who will prescribe the necessary treatment.
Useful recommendations for the postoperative period
During the process of tooth extraction, surrounding tissues are inevitably injured. In addition, the vacated hole represents an open wound. Therefore, it is so important to strictly follow the doctor’s instructions during the rehabilitation period, as well as monitor oral hygiene and the integrity of the blood clot formed in the socket. Otherwise, the risk of complications and alveolitis in particular will increase significantly.
If you ignore the doctor's recommendations, alveolitis may occur.
As a rule, experts provide the following recommendations for the rehabilitation period:
- refuse to eat in the first 2-3 hours after the procedure,
- do not touch the hole with your tongue or fingers,
- avoid intensive rinsing and anything that can create a vacuum effect in the mouth - to use antiseptic solutions, it is better to use oral baths,
- temporarily avoid visiting saunas and steam baths, hot baths and intense physical activity,
- take antibiotics, painkillers and other medications strictly as prescribed by the doctor,
- if the area where the tooth used to be hurts too much, swelling has increased and bad breath has appeared, as well as if a blood clot is damaged - in all these cases you need to urgently consult a dentist.
To somewhat reduce the intensity of pain after the procedure, the specialist will prescribe anti-inflammatory and painkillers, for example, Nimesil, Nise or Nimesulide. These medications are often prescribed after oral surgery. In addition, medications based on the active substance nimesulide have a moderate antipyretic effect, so they also help reduce temperature in the postoperative period1.
After the operation, the specialist prescribes anti-inflammatory and painkillers
Regarding whether it is necessary to remove a wisdom tooth, there is no clear opinion on this matter. In fact, these rudiments no longer carry any important functional load. On the other hand, if the upper or lower 8 grows vertically, and does not in any way affect the position of its “neighbors,” it is not at all necessary to remove it. In any case, the decision remains with the attending physician and is always based on the individual characteristics of the clinical picture.
- Bezrukov V.M., Sukachev V.A. Complications after tooth extraction, 2000.
How painful is wisdom teeth removal?
The question of the pain of wisdom tooth removal arises in all patients who need such an operation. The removal procedure is carried out under local anesthesia (various painkillers are used - ultracaine, septanest, ubistezin and others). The complexity of removal and pain depend on many factors: the structural features of the root system, the location of the tooth, the presence of complications in the form of cysts, suppuration and others, as well as the pain sensitivity threshold of a particular person.
What to do if your wisdom tooth hurts during pregnancy
Unfortunately, any pregnant woman may experience various unpleasant conditions and diseases. As with any other period, the eruption of wisdom teeth can occur during pregnancy and this can be a cause for concern. Many people wonder whether wisdom teeth can be treated during this period and how to deal with pain relief during this period. Gynecologists advise treating teeth (including “eights”) after the 16th week of pregnancy. It is during this period that all systems and organs of the fetus are already formed, so the use of painkillers will not negatively affect the child.
Folk remedies used to treat wisdom teeth
The following traditional medicine recipes will help reduce signs of gum inflammation and make teething less painful:
- The most common and simple method is rinsing the mouth with solutions of oak bark, sage, chamomile or soda solution.
- The inflamed gum above the figure eight can be lubricated with sea buckthorn oil.
- Rinsing the mouth with a decoction of chicory root. It has analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. Add 1 tablespoon of chopped chicory root to 250 ml of boiling water and boil it all for 5 minutes. Then the broth is infused for 1 hour, after which you can use it to rinse the mouth 3-4 times a day.
- A saline solution with camphor and ammonia will have an analgesic effect. To prepare it, add 1 tablespoon of sea or table salt, 100 g of 10% ammonia and 10 g of camphor alcohol to 1 liter of cool boiled water. Shake everything well, then apply a cotton ball dipped in it to the teething site for 10-15 minutes. The procedure can be repeated several times a day.
Do not forget that any traditional medicine methods can only provide short-term relief, so do not hesitate to visit a dentist. Only a specialist will be able to answer you whether the wisdom tooth is growing correctly or not and whether there is a need for its removal.
How many teeth does an adult have?
Very often, adults, knowing that there should be 32 teeth, panic after they count only 28 teeth. What is this connected with? Where did the other 4 teeth go? The answer is obvious, because 4 teeth are wisdom teeth that grow in an adult at an individual time, and after a few years require their removal.
If there are fewer teeth, this indicates that the wisdom teeth have not yet grown. Their development comes a little later than everyone else. Some people grow wisdom teeth at the age of 18, some live up to 30 years, and do not even suspect when they will be lucky enough to have 32 teeth.
To know how many teeth a person has at what period of life, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the statistics:
- Permanent teeth in an adult are formed at the age of 6 years, and complete their formation already at 12 years.
- At the age of 16, all teeth should be fully formed, their number is 28. Every dentist will confirm this.
- Some people live without wisdom teeth, their entire mouth has only 28 teeth, and this is quite normal. Wisdom teeth, or molar teeth as they are also called, may not appear in a person for the following reasons:
- Features of the oral cavity.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Low quality of food consumed.
If you look far into the history of the appearance of teeth, you can note a very interesting fact: initially, 44 teeth were considered the norm for an adult. The thing is that our distant relatives ate exclusively hard foods, for the processing of which they needed more teeth.
Wisdom teeth begin to grow abundantly at age 17, and by age 25 they should be fully formed. If before this time 32 teeth are not observed in the mouth, it means that the person belongs to that small percentage of the population who simply do not have wisdom teeth.