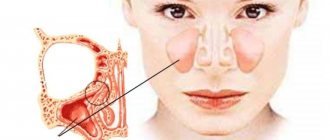
The maxillary cyst is most often located in the nose area
The maxillary sinus cyst consists of epithelial cells of the mucous membrane. Inside it can be filled with mucus, serous contents or pus. Most often it is localized in the area of the sinuses, that is, the paranasal sinuses, which is why the pathology is also called a maxillary sinus cyst.
A maxillary cyst is often called a maxillary sinus cyst.
Endoscopic maxillary sinusotomy: surgery
Removal of a cyst in the maxillary sinus photo
The operation to remove the formation can be performed in the traditional way, that is, through an incision in the facial tissue, or using endoscopic equipment. In recent years, the second method is usually preferred, since it does not involve making soft tissue incisions.
Removal of a cyst from the sinus using an endoscope is carried out under local anesthesia. The surgeon inserts the device into the affected sinus through the nasal passage and, skillfully manipulating the micro-instruments on its head, removes all existing tumors, and, if necessary, the affected areas of the mucous membranes, that is, he performs a maxillary sinusotomy.
Control over the progress of the manipulation is carried out through a miniature video camera on the endoscope, which transmits the image to the monitor.
Endoscopic removal of a maxillary sinus cyst, the price of which is approximately 15 - 25 thousand rubles in Moscow , is a low-traumatic procedure with minimal health risks. Therefore, after its implementation, long rehabilitation is not required, which justifies the higher cost compared to classic maxillary sinusotomy.
There are several types of pathology
Cysts of the maxillary sinuses are different:
- odontogenic: inflammation begins to form at the root of a poorly treated or completely untreated tooth located in the upper jaw. As the tumor increases in size, it destroys bone tissue and gradually grows into the sinuses. Such neoplasms are most often filled with pus,
- retention: formed due to disruption and obstruction of the glands that produce mucus.
Doctors also classify false cysts as a separate category - such formations do not contain epithelial cells and appear due to pathologies and structural disorders of the maxillofacial apparatus.
The essence of pathology
Cyst formation is a benign process. It is not typical for it to be complicated by the development of dangerous malignant neoplasms. The paranasal sinuses are cavities formed by the bony structures of the skull. They have communications with the nasal passages. Therefore, when there is a volumetric formation in the sinuses or fluid accumulates, this will certainly affect the condition of the nose.
The maxillary sinus is located in the maxillary bone. The bone walls are lined with mucous membrane. It consists of epithelial cells and cells that produce mucus. Under certain conditions, a disturbance in the outflow of mucus occurs, which causes excessive stretching of the mucous membrane with the development of a secondary cavity. This is the mechanism for the development of cysts in the maxillary sinus. Symptoms appear in situations when its size increases, and conditions are created for disruption of the anastomosis between it and the nasal passages.
Causal factors
The etiology of cyst formation is varied. Infectious processes, accompanied by inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane of the nose and paranasal sinuses, take first place among the causative factors.
Viral respiratory diseases cause a pronounced drop in local defenses, and also weaken mucociliary clearance - the cleansing process. Therefore, both pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms can colonize weakened mucous membranes and cause inflammation there, including purulent inflammation. Ultimately, a violation of the outflow from the cells that form the mucous glands is formed. They become the causes of cyst formation.
It is discussed that a possible etiological factor is . In addition, a cystic cavity in the maxillary sinus can form due to untreated teeth, trauma to the maxillary bone, including during attempts to extract teeth. In the latter case, the cyst in the nasal sinus is called odontogenic.
Dysplasia of the facial skeleton affects the condition of the paranasal sinuses. Deformations such as flattening and underdevelopment of cavities may occur. A deviated nasal septum is also considered a predisposing factor for cyst formation.
One of the most common causes of tumor is a bad tooth.
A maxillary sinus cyst can form due to a reason such as dental disease. More precisely, when treatment was not carried out, or it was performed poorly. Most often, the development of pathology is provoked by advanced caries, pulpitis and periodontitis on molars and premolars (these teeth are separated from the paranasal sinuses by a thin septum).
Teeth with cysts and granulomas were previously more often removed than treated. Today, in some clinics, high-precision tooth-preserving operations are carried out, where all stages of treatment are accompanied by work on a dental microscope. A competent endodontist carefully removes the cyst under a microscope using special instruments, then the canals are sterilized to their entire length and filled with filling material. Treatment under a microscope is accurate, fast, without risks or complications, and, most importantly, the natural tooth remains intact.
The prerequisite for the appearance and growth of a tumor may be the individual anatomical characteristics of the patient, for example, a deviated nasal septum or jaw abnormalities. Another reason is the systematic blockage of the ducts of the glands located in the nose, against the background of rhinitis, runny nose, and allergic reactions.
Prevention
To prevent the re-development of the cyst, the patient must follow preventive measures:
- regularly monitor the condition of the teeth (treat caries) and the oral cavity;
- avoid hypothermia, do not breathe through your nose in cold weather;
- if there is difficulty breathing due to a crooked septum in the nose, correct it;
- treat infectious diseases of the nasopharynx in a timely manner;
- exclude possible injuries to the nose and skull;
- take antihistamines for allergic rhinitis;
- At the first negative symptoms, visit a doctor.
A maxillary sinus cyst is often painless and, with timely treatment, does not pose a threat to the health and life of the patient. The main thing is to notice its symptoms in time and seek help from specialists.
A small cyst can only be detected by x-ray
When the neoplasm is small, less than 10–15 mm, it is almost impossible to find out about its existence, since no alarming signs are observed. At this stage, the only option to identify pathology is to do a computed tomography scan. A dentist may also suspect its presence during a routine examination or other doctors if a person needs to visit them.
At the initial stage, the problem can only be detected on an x-ray
Signs of a large cyst are similar to signs of acute sinusitis
When the cyst begins to grow, a person develops alarming symptoms, which, based on clinical manifestations, can be confused with acute purulent sinusitis. Let's list them:
- severe headache: unpleasant sensations spread to the cheekbones, temples and the back of the head. The pain intensifies when the head is tilted forward, pressure surges, or diving under water. Discomfort may persist even after taking analgesics,
- difficulty breathing through the nose, constant nasal congestion,
- nasal discharge: clear, less often yellow,
- a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the areas under the eyes,
- the presence of a viscous mucous lump in the throat immediately after sleep and in the morning.
The signs of a cyst are similar to the signs of sinusitis.
However, the signs become more pronounced when the lumen in the nasal sinus is practically blocked. Facial asymmetry and swelling of the cheek may appear. If there are associated problems, for example, a bad tooth, swelling of the gums, pain when chewing food and any mechanical impact are disturbing.
Maxillary sinus cyst - symptoms
The presence of a maxillary tumor may not bother a person. It does not manifest itself and is often detected by CT, X-ray or MRI when diagnosing another disease. Size does not affect the intensity of symptoms. A large tumor on the upper wall may not bother the patient, but a small one near the excretory anastomosis may lead to severe pain in the teeth and head.
Patients notice signs of the presence of maxillary formations when they reach significant volumes or acute inflammation occurs (associated with exacerbation of sinusitis or another disease). The time it takes to fill depends on the intensity and frequency of the inflammatory process and the individual structural features of human organs.
Nasal congestion
During illness, the patient may feel discomfort in the area of the wings of the nose. Congestion is a constant symptom: with a unilateral process, the right or left nostril does not breathe; with a bilateral lesion, a person cannot draw in air through the nose at all. This indicates a strong growth of the formation and its filling of the entire sinus space.
Mucous contents are discharged from the nose. The incidence of ENT diseases is significantly increasing. They are much more difficult for humans to tolerate and last longer than before the formation of a tumor.
Headache
In 50% of patients, the cyst manifests itself as nasal congestion and headaches. The pain syndrome extends to the ocular and temporal region.
In patients who engage in water sports, the symptom may worsen when diving to depths. Headache can be constant or periodic; changes in the condition often occur in response to stress or climate change; a person may suffer from dizziness.
Other symptoms
The neoplasm sometimes causes symptoms that are difficult for a person without medical education to associate with diseases of the olfactory organs. Depending on the location, size of the cyst and the structure of the maxillary sinus, the patient may complain of discomfort:
- discomfort in the upper jaw,
- the appearance of mucus or draining pus in the throat,
- cheeks and eyes hurt,
- the temperature rises.
READ ALSO: what to do if all the teeth on the left side of the jaw hurt?
If left untreated, vision and more can seriously deteriorate.
Cysts of the maxillary sinuses are dangerous because if they are not treated, they can become a source of very serious health problems.
The infection can spread to the nearby teeth of the upper jaw and along the chain take over the entire row, as a result of which you can lose all your teeth. Pathology can lead to deformation of the skull bones and jaw fracture, the development of purulent processes - abscess, phlegmon, osteomyelitis, meningitis.
The tumor provokes the development of sinusitis and chronic sinusitis. Its presence is always accompanied by a runny nose and inflammation of the sinuses.
If the problem is not addressed, it can affect vision
The growth of the tumor often leads to blurred vision, “double vision.” If the cyst is purulent, it can lead to brain damage and encephalitis. When a tumor grows, there is a risk that it will completely block oxygen and complicate breathing, which is especially dangerous during sleep, since a person may not wake up.
What is the threat and what can it lead to?
It is important to know why a cystic tumor in the cavities of the upper jaw is dangerous and what complications it can provoke.
The most dangerous threat comes from infection of the exudate in the cystic capsule; a chronic infection can develop in it, which in turn leads to the accumulation of pus inside the capsule. At a certain point, the walls of the cyst cannot withstand the pressure of purulent fluid and burst, at which point yellowish exudate with a pungent odor flows out of the patient’s nose. Some patients think that a burst cyst brings them relief, but this condition is dangerous, as it can lead to exacerbation of chronic pathologies and cause other equally serious consequences. The spilled contents of the cystic capsule contain a large number of pathogenic bacteria that can penetrate the ear and cause inflammation of the middle ear.
Even if the capsule remains intact, it can cause complications and deteriorate the patient’s quality of life. When it grows and occupies the entire sinus in the upper jaw, this leads to difficulty breathing through the nose and to the following equally serious consequences:
- severe pain in the head;
- spasm of blood vessels, including cerebral vessels;
- reduced oxygen content in the body, which is fraught with complications for expectant mothers and their fetus;
- development of heart and vascular diseases;
- breathing may stop during sleep;
- the image before the eyes may double;
- the patient's general well-being worsens.
The pressure inside the skull may also increase, the body temperature rises, and inflammatory processes spread to nearby tissues, which in an old state leads to necrotization of the bone.
The main method of treating pathology is surgery
To treat a tumor, doctors combine therapeutic and surgical methods. First, surgery is used to remove the tumor, then drug therapy is used to eliminate signs of the inflammatory process and avoid complications, speed up rehabilitation and tissue healing.
If the maxillary sinus cyst is small (less than 1 cm), then drug therapy is used for treatment and dynamic observation is carried out, and there is no need for surgical removal of the tumor. But there are two important points. The first is that rarely do any patients go to the clinic until the cyst has grown and began to cause significant problems. Secondly, therapy can take a long time (4-6 months) and the result will not always be positive.
When treatment is carried out in dentistry
Most often, patients go to clinics when the cyst reaches 1 cm or more in diameter. In this case, its removal can be carried out in different ways. If the cause of the problem is a diseased tooth, then treatment is carried out by a dental surgeon. The doctor removes the tumor by performing a cystectomy if its size is no more than 1–2 cm. Or by cystotomy1, when the size is more than a few centimeters and the tumor has grown into the sinus.
The photo shows an operation to remove a cyst.
The main tasks of the dentist in this case:
- eliminate the source of inflammation in the oral cavity and stop the inflammatory process,
- ensure the outflow of purulent contents, if any, using drainage,
- save the diseased tooth, if possible: in cases where the root is slightly immersed in the tumor, its resection (removal of the apex) is carried out, and the tooth itself is preserved. When the root is immersed in the cyst by more than 1/3, its complete removal is recommended to avoid relapses,
- fill the cavity left after tumor removal with bone material,
- close the communication between the oral cavity and the sinus.
When treatment is carried out at the direction of an ENT doctor in a hospital setting
Maxillary sinus cysts are not always associated with diseased teeth. But regardless of the cause of their appearance, advanced tumors almost always lead to inflammatory processes in the nasal mucosa, congestion, sinusitis, and mucus discharge from the nasal passages. Therefore, many patients with such symptoms turn to an ENT doctor.
In this case, the tumors are removed through surgery. For example, using a classic operation, when a deep incision is made in the upper jaw, through which the formation is removed. This method is the most affordable, but it is quite traumatic, and the patient then requires a long postoperative recovery.
“Two years ago I had a maxillary cyst removed. My background was like this: snot was either pouring out of my nose, or there was constant congestion, and for a long time I could not smell or breathe normally, so I went to an otolaryngologist. The doctor sent me first for an x-ray, and then for tests and surgery. The operation was performed in a hospital and under anesthesia, I was very afraid of how everything would go, and especially how I would recover from the anesthesia, but everything was tolerable. Then I was in the hospital for about 4 days, but some people stay longer. I felt discomfort for another ten days after that.”
[email protected] , fragment of a review from the site woman.ru
However, today the most common surgical method is endoscopy. The operation is performed through an opening in the facial wall of the maxillary sinus, or through the nasal passages. The entire treatment process is monitored on the monitor screen, so the doctor can control his actions. The technology is considered the most gentle, atraumatic; after its use, the patient has no stitches, incisions or scars on his face. The procedure is quick (duration is about 40 minutes), tissue restoration takes about 7 days.
An endoscope is an optical device used in all areas of medicine for high-quality examination and treatment of hollow internal organs. Endoscopes can be inserted through natural body openings (in this case, the nose) or through surgical incisions.
The operation can be performed using an endoscope through the nose
The operation can also be performed using a laser. This approach almost completely eliminates the likelihood of developing postoperative complications. But due to the use of laser equipment, the cost of treatment increases significantly.
Treatment options
Often, a neoplasm in the sinuses does not require emergency measures. In each case, methods for eliminating the disease are prescribed individually. The doctor chooses procedures depending on the patient’s complaints, concomitant diseases and the severity of the problem. If there is a small cyst, experts advise monitoring its development and eliminating pathologies that could lead to its occurrence. If there is a dental cyst in the sinus, there is a good chance that it will disappear on its own after complete treatment of oral diseases.
Conservative
Patients are offered to undergo treatment without surgery. The conservative method is aimed at reducing the rate of cyst growth. It is prescribed when a small formation is detected. Most experts are confident in the insufficient effectiveness of such treatment and its negative consequences. Attempts to get rid of tumors at home can lead to new sources of tumor formation and create a favorable atmosphere for the development of bacteria.
If inflammation worsens, even if the formation has reached a size sufficient for surgery, surgical intervention is prohibited. To suppress the infection process, the patient undergoes a course of therapy consisting of drugs:
- saline solution for rinsing Physiomer, Aquamaris,
- drug for the outflow of fluid from sinuses Sinuforte,
- cortecosteroids Beconase, Nasonex,
- vasoconstrictor sprays Tizin, Nazol, Otrivin,
- local antibiotics Isofra or Bioparox,
- general antibiotics Amoxicillin, Lincomycin.
Surgery
The choice of type of surgery depends on the size and location of the tumor. Indications for surgical intervention appear if the cyst worsens the patient’s quality of life. Previously, the Caldwell-Luc method was considered the standard for removing maxillary sinus cysts, but due to the use of general anesthesia, the formation of coarse scar tissue and the consequences of sinusitis and rhinitis, it is rarely performed. Today patients are prescribed:
- Denker's maxillary sinusotomy. Access to the formation is through the front wall. The advantage of the intervention is the ability to remove the tumor in a hard-to-reach place. The only way to perform surgery is on the posterior wall of the maxillary sinus.
- Endoscopic removal. The process lasts 20-60 minutes, the doctor does not make any incisions. The method does not imply the presence of complications, damage to the maxillary sinus or the occurrence of inflammation.
- Puncturing. It is carried out through the nose by piercing the sinus with a needle. It is a temporary measure, ensures suction of the contents of the cyst, leaving its walls. The symptoms go away, but when the tumor fills, the patient again worries.
After removal of the cyst, you need to adhere to restrictions
Treatment of tumors in most cases involves their surgical removal. And naturally, after surgery the body needs time to recover. Usually 7–14 days. During this period, swelling, soreness, and difficulty breathing are normal. To make unpleasant symptoms go away faster, you must follow these tips:
- use antibiotics, antiseptics and vasoconstrictors prescribed by your doctor,
- avoid actions that provoke active use of facial muscles: long conversations, laughing, yawning, blowing your nose,
- do not visit saunas, steam rooms, do not take hot baths,
- follow a gentle diet with a predominance of soft and not too hot food,
- reduce the intensity of physical activity as much as possible; it is better to avoid visiting gyms altogether for a while,
- buy a high pillow: when sleeping, your head should be higher than your body level.
Sleeping on a high pillow promotes a speedy recovery after treatment.
Doctors consider the main measure to prevent maxillary sinus cysts to be timely treatment of dental problems and ENT diseases, sanitation of the oral and nasal cavity, as well as correction of jaw and nasal abnormalities (for example, the nasal septum), if they occur. be.
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 2 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
flux
- Sirak S.V. [and others] Surgical treatment of odontogenic cysts of the upper jaw penetrating into the maxillary sinus, based on clinical and morphological research data // Medical Bulletin of the North Caucasus. – 2014.
Expert “In advanced dental diseases, such as pulpitis and periodontitis, there may be several mechanisms for the development of a maxillary cyst. The first is that the formation appears at the root of the diseased tooth, and then grows into the sinuses. The second is that the infection spreads upward through the root canals, and a cyst begins to form in the sinus. In this case, it is possible to prevent the development of pathology if “dental problems” are solved in a timely manner. Dentist-therapist Elena Vladimirovna Orlova
Consulting specialist
Dzhutova Aida Vladimirovna
Doctor rating: 8.8 out of 10 (5) Specialization: Implant surgeon, periodontist Experience: 8 years
When is surgery required?
Surgical treatment is necessary only for severe cases of the disease. There are several modern methods, from which the attending physician makes the choice depending on the characteristics of the patient’s body and the type of pathology.
The most common is the Caldwell-Luc operation, which is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. In this case, a small incision is made above the gum below the upper lip and the anterior wall of the sinus is opened. An endoscopic tube is inserted there for inspection. Then the shell of the formation and its contents are removed through the hole. However, after such an operation, negative consequences are possible for patients in the form of frequent rhinitis and sinusitis due to the development of scar tissue.
The most effective is the endoscopic method, when all instruments are inserted through the nasal passages. The optical fiber in the endoscopic tube allows you to see clearly and perform the necessary manipulations. There are no scars or scars left, and the patient is discharged from the clinic after 1-2 days. The advantage of the method is the absence of contraindications and the risk of complications.
Removal of an odontogenic cyst is performed through an incision under the upper lip under local anesthesia. If the inflammatory process develops, you need to undergo antibacterial therapy (before and after surgery). The probability of complete recovery after surgery is 85-90%.
Comments
The other day I visited LORA, because... I'm worried about constant nasal congestion. HE examined and diagnosed “odontogenic sinusitis” and prescribed symptomatic treatment. He said that in order for everything to return to normal, you need to go to the dentist and look for the cause. No cyst was found. Explain what could be the reason and why this is dangerous?
Tanyusha (06/03/2020 at 17:53) Reply to comment
- Dear Tanyusha, the diagnosis of odontogenic sinusitis indicates that the problem should be looked for in the oral cavity. The cause of its development is often periodontitis, perforation of the sinuses during dental treatment, impacted and dystopic teeth. If the exact cause is not identified and eliminated, then the formation of a cyst will not take long to occur.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (06/08/2020 at 09:16) Reply to comment