7178
© zea_lenanet / Fotolia
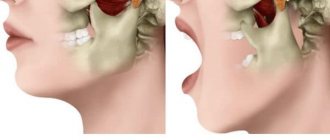
Malocclusions are characterized not only by the presence of pathological dentition, but also by improper development of the jaw. One of the most common problems of this type is a small lower jaw.
A pronounced discrepancy between the jaw and normal dimensions leads to the formation of an aesthetic defect and disruption of the basic functions of the dentofacial apparatus.
Definition
The concept of “small lower jaw” in orthodontics is not clearly defined.
This diagnosis is classified into several types, differing in the clinical picture of the anomaly.
Micrognathia
Mandibular micrognathia is a defective or too long-term development of an organ that goes beyond the norm.
The defect can affect both the entire jaw and its individual areas, for example, affecting only one lateral part.
Prognathia
It is considered a phenomenon directly opposite to the case described above.
The organ corresponds to the normal parameters, but with the pronounced size of the upper jaw, it seems that it is too small.
Experts often call this disease false prognathia.
Main symptoms
How can a patient understand that he has a disease such as jaw prognathism? It all depends on the individual characteristics and form of the disease itself. Most often, patients complain of the following inconveniences:
- it is very difficult to bite into food, since the incisors protrude very much forward;
- in some cases, serious difficulties arise with the speech apparatus;
- there are difficulties in mouth breathing;
— the oral cavity is reduced in volume, so the patient cannot chew food thoroughly enough.
Signs
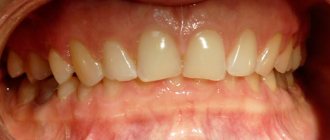
The main sign indicating the presence of this disease is the visual observability of an anomaly - such a defect is visible to the naked eye, and you do not need to be a specialist in orthodontics to determine such a deviation in a person.
In addition, pathology deforms the natural proportions of the maxillofacial apparatus. The chin becomes sharp and slightly raised upward. Doctors even defined this phenomenon as “bird beard.”
It is important to understand that this is not just a cosmetic defect; micrognathia threatens its “owner” with the development of the pathology of tongue retraction, which is considered a serious disease.
The anomaly causes frequent uncontrollable attacks of suffocation and poses a serious threat to the patient's life.
The disease is often diagnosed based on this characteristic feature - excessive retraction of the chin leads to wrinkling of the skin in its area, and the horizontal fold between the chin and lip is smoothed out.
In addition, underdevelopment of the lower jaw often goes hand in hand with chromosomal mutation processes, which leads to Patau syndrome.
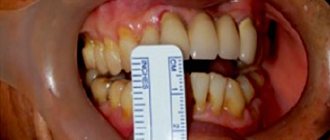
A clear sign indicating the presence of this defect is also the incorrect location of individual fragments of the dentition.
In the case when some organs are missing, neighboring teeth change the direction of growth, trying to spontaneously fill the free space.
Signs of the disease
Prognathia is a pathology that has the following symptoms:
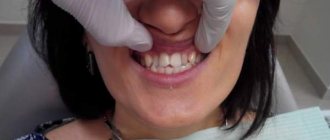
— In a sick person, the middle part of the face is very prominent. The lower lip shortens, and the muscle tissue of the mouth is constantly in a tense state.
— The upper teeth noticeably extend beyond the boundaries of the oral cavity, biting the lower lip. This condition is characterized by the fact that the patient cannot completely close his mouth.
— Another sign of this disease is a large gap between the upper front teeth, as well as their crowding.
Causes
This type of anomaly can be triggered by the following factors, some of which are external, and some are internal:
- unbalanced diet of a woman during pregnancy - in this situation, the defect is formed already at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus;
- chromosomal mutations that cause deviations in the normal growth and development of the baby during pregnancy;
- genetic predisposition;
- Robin's syndrome is a congenital anomaly of the anatomical structure of the facial apparatus;
- too early loss of baby teeth or permanent organs in adulthood , as well as a fairly long change from a temporary bite to a permanent one;
- difficulty breathing through the nose , associated with the structure of the nasal septum or chronic diseases of the nasopharynx;
- mechanical organ injury.
Everything about correct orthognathic occlusion, its signs and characteristics.
Let's talk here about the treatment of dental dystopia.
Follow the link https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/okklyuzii/glubokiy-prikus.html if you are interested in methods of treating deep bites in adults and children.
Main reasons for development
Prognathia is a disease that can be accompanied by many different factors. Let's look at the most common of them:
- Constant nasal congestion and breathing through the mouth. As a result, the jaw begins to stretch forward.
— Development of various diseases of the jaw apparatus that occur during breastfeeding.
- The child has bad habits such as thumb sucking and lower lip sucking. This may cause the lower teeth to protrude.
— The jaw will form incorrectly if the baby has incorrect posture and walks with his head down.
— Consequence of diseases associated with bone tissue.
— Very early removal of baby teeth.
As you can see, basically, prognathia is a disease that begins to develop in childhood.
Treatment
Methods for eliminating micrognathia depend on the degree of development of the pathology, the age of the patient and can be gentle or radical.
In the first case, treatment is carried out gradually through the use of special bite-leveling structures, and in the second, surgeons are involved in the work.
In children
In childhood, this deviation is easy and in most cases, successfully, treated mainly with therapeutic methods, and with rare exceptions, surgically:
- sanitation of the oral cavity – complete restoration of damaged tooth segments, as well as removal of affected root areas. Restoring the integrity of periodontal tissues using general and targeted spectrum agents;
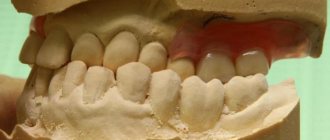
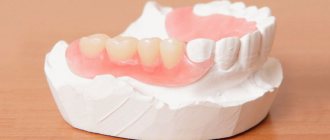
- pediatric prosthetics – indicated for early loss of mammary organs. The voids are filled by splinting or attaching temporary devices that maintain the correct position of growing teeth and correct the size of the jaw arch;
- correction of language function and normalization of the respiratory system - in the first case, this is surgical cutting of the frenulum, which is done quickly and almost painlessly. In the second - surgical alignment of the partitions, followed by rehabilitation exercises;
- myogymnastics – tonic effect on the muscle tissue of the organ through special gymnastic exercises.
It is advisable to carry out with children 4–6 years of age, when in case of underdeveloped pathology this method can be used as the main method of treating the defect.With positive dynamics, the need for subsequent installation of orthopedic structures, as a rule, no longer arises;
- leveling the unevenness of the chewing surface using the method of grinding (fissures) - an ideal solution for a slight deviation in jaw closure;
- the use of leveling systems and structures is carried out when the anomaly is too pronounced, when other correction methods are ineffective. Wearing mouth guards and plates, and in infancy special nipples, gradually brings the deviation back to normal.
In adults
Treatment of patients whose bite has already been formed takes longer, and methods for correcting it are most often more radical.
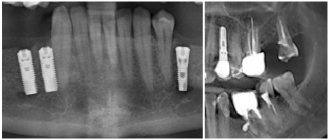
Bone grafting
The essence of the method comes down to artificial extension using a graft. Bone tissue is taken from other areas of the patient’s tissue, which guarantees good survival of the material.
Fixation of the grafted fragments is carried out using screws made of high-quality, durable alloy of titanium components. This is done as follows:
- the lower organ is incised;
- the hard tissue is moved apart and the osteoplast is immersed inside;
- fixed with screws;
- intermediate voids are filled with special plastic chips;
- implantation of the membrane and suturing of the organ.
The main advantages of the method are the rapid survival rate and reliability of the procedure; the jaw augmented in this way retains its functionality for many years.
Disadvantage: individual intolerance to components and osteoplast fixatives.
In the video, watch the process of bone grafting for anomalies of the lower jaw.
Bone grafting plus liposculpture
Plastic surgery of hard bone tissue is carried out similarly to the option described above, with the difference that in parallel, aspiration of the local accumulation of fatty tissue is carried out using a vacuum method.
The technique qualitatively solves the aesthetic problem of underdeveloped chin caused by this pathology, corrects its shape, evens out the oval of the face and, in a sense, resembles the effect obtained from lifting the chin area.
The advantage is a high aesthetic result, the disadvantage is the high cost of the procedure and the presence of a large number of contraindications to its implementation.
Causes of open bite development and its dangerous consequences.
In this article we will discuss treatment methods for microdentia.
At this address https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/ryadov/suzhenie.html we offer details about the treatment of narrowing of the dentition.
Endoprosthetics
It is made with harmless facial implants from non-biological components - silicone, porous polyethylene or cartilage extract. The desired shape is given to the device directly during the operation.
The implant is inserted through deep incisions in the mucous cavity, which leaves no postoperative traces. The product is inserted into the subperiosteum in lateral fragments into the chin area and attached to it with surgical sutures to fix its position.
The disadvantage of this method is the rather long recovery period.
Lipofilling
This option is considered to be a non-surgical correction, which is its main advantage.
The method allows you to give the chin the desired shape through pinpoint needle injection of fat cells into the subcutaneous area, in those areas where an increase in the size of the chin is required.
The entire procedure takes no more than an hour. The rehabilitation period passes quickly and without complications. The only drawback is that 30% of the implanted tissue fragments are rejected by the body, which requires repeated lipofilling 5-6 months after the first procedure.
To learn how chin augmentation is performed using lipofilling, watch the video.
How to correct this effect
Lower prognathia, just like the upper one, needs to be corrected in childhood. If the bite is already completely incorrectly formed, then correcting this defect will not be so easy.
Therefore, try to spot bad habits in your child in advance, such as sucking on foreign objects. At the initial stage of the disease, the doctor will be able to correct the bite of the baby teeth.
To correct this pathology, the following methods are actively used:
— sanitation of the nasopharynx and mouth;
— special compression bandages that stop the processes of improper jaw formation;
— activator tools that can stop the development of the upper jaw, and, conversely, stimulate the upper jaw;
- in some cases, the Frenkel apparatus is used, with the help of which the jaw acquires absolutely correct shape.
During treatment, parents should ensure that their baby does not put foreign objects in his mouth.
If the disease is eliminated surgically, then in this case the tissues are cut and the jaw is directed in the desired direction at a certain angle. This is done to ensure that the upper and lower teeth touch each other.
After this, the bones are splinted in the correct position and heal over the course of two months.
Prices
The approximate cost of treating a defect of abnormal development of the lower jaw is given in the table:
| Character of the bite | Correction method | Average price (in rubles) |
| Lactic | Sanitation of the oral cavity | From 3 500 |
| Lactic | Orthopedic therapy | From 30 000 |
| Lactic | Fissure grinding | From 11 000 |
| Lactic | Operation | From 15 000 |
| Constant | Bone grafting | From 19 000 |
| Constant | Bone grafting pole liposculpture | From 50 000 |
| Constant | Endoprosthetics | From 40 000 |
| Constant | Lipofilign | From 35 000 |
Narrowing of the jaws and teeth
The narrowing of the jaws or dentition is called a decrease in their transverse dimensions. It can be on one or both jaws, uniform throughout the entire jaw or uneven, that is, in some part of it. Narrowing is more often observed in the upper jaw than in the lower jaw. This is explained by the structural features of the jaws. The upper jaw, as is known, contains more spongy bone and borders the air sinuses.
The lower jaw is more compact. The narrowing of the jaws and dentition is most pronounced in the lateral regions, mainly in the area of the premolars. In the vast majority of cases, it is accompanied by deformation of the anterior jaw or dentition.
Korkhaus distinguishes three clinical forms of jaw compression. The first is characterized by narrowing in the lateral regions and crowding of the front teeth. In the second form, the front teeth are closely spaced, but with protrusion, that is, they protrude forward. The third form of jaw compression is accompanied by protrusion of the front teeth, between which there are gaps.
Narrowing of the jaws and dentition occurs during the period of primary, mixed and permanent dentition. It can occur with the correct mesiodistal relationship of the jaws and dentition and with a prognathic (distal) bite. Thus, narrowing of the dentition and jaws can be an independent anomaly or complicate other types of them.
Uniform narrowing of both jaws is rarely observed. In this case, the relationship of the dentition may not be disturbed. More often there is a narrowing of one jaw or dentition, unilateral or bilateral. When the upper jaw is narrowed on one side, a crossbite occurs. With bilateral narrowing, the buccal cusps of the molars and premolars of the upper jaw are located in the longitudinal groove of the lower molars, i.e., it is not the lateral teeth of the upper jaw that overlap the teeth of the lower jaw, but vice versa.
The narrowing of the upper jaw is accompanied by a deepening of the palate and deformation of the dentition. The most common forms of the upper dental arch are the dentition, narrowed in the lateral areas with extension of the anterior section, and V-shaped, and other forms are also found. With a sharp narrowing of the lower jaw and dentition, on one or both sides, the buccal cusps of the molars and premolars of the lower jaw slip past the lingual antagonist cusps, coming into contact only with the oral surface of the latter.
This relationship worsens over time, since the lateral teeth of the upper jaw, when closing the jaws, experience pressure in the transverse direction and, as if along an inclined plane, deviate towards the cheek. In this case, the lower teeth deviate even more towards the tongue. Functional disorders due to narrowing of the dentition and jaws are expressed in difficulty in sagittal and transversal movements of the lower jaw.
The severity of functional pathology depends on the severity of the deformity and its clinical form. Thus, with a sharp narrowing of the upper jaw and a high palate, nasal breathing is disrupted due to the narrowing of the nasal cavity. In addition, the pronunciation of certain sounds is sometimes impaired. When the upper jaw is narrowed and the anterior teeth are crowded, their closure with the antagonists is disrupted, which complicates the movements of the lower jaw.
With a sharp narrowing of the lower jaw, its lateral teeth are blocked by antagonists and transversal movements are disrupted, as a result of which the grinding of food worsens. It should be added that when the dentition narrows, some teeth experience a load that is incorrect in magnitude and especially in direction, which often leads to pathological changes in periodontal tissues.
The narrowing of the jaws or dentition may be due to underdevelopment or deformation of the jaws in the transversal direction. Underdevelopment of the jaws is associated with a hereditary factor, congenital cleft palate, diseases of early childhood, endocrine disorders, trauma, osteomyelitis, premature loss of baby teeth and other reasons. The most common causes of jaw deformation, especially the upper one, are rickets, impaired nasal breathing, muscle imbalance, and bad habits (putting your hand under your cheek while sleeping).
“Childhood Dentistry”, A.A. Kolesov
Palatal lingual eruption of individual teeth
Palatal lingual eruption of individual teeth is observed in the primary, mixed and permanent dentition and concerns mainly the incisors, less often the canines, and even less often the premolars. These teeth erupt orally in relation to the others or only tilt towards the palatal (lingual) side with their crowns. When the incisors of the upper jaw erupt palatally, the incisors of the lower jaw are located in front of the upper ones and overlap them by a large...
Prognathic relationship of anterior teeth (treatment)
For the treatment of prognathic relationship of the dentition with protrusion of the anterior teeth of the upper jaw and deep bite, the Gulyaeva apparatus has been proposed. When it is used, the upper front teeth are deflected in a sliding arc towards the oral side, and the lower teeth of the same name and the entire lower jaw are moved forward along an inclined plane. With a prognathic relationship of the dentition in combination with a narrowing of the upper jaw and...
Deep bite (treatment)
It is necessary to begin treatment at the earliest possible age. It comes down to retarding the growth of the alveolar process of the jaws in the anterior region and stimulating it in the area of the lateral teeth. During the period of primary occlusion, it is first necessary to eliminate the cause of the anomaly, if it continues to act, and carry out general health and local preventive measures: sanitization of the oral and nasal cavity, elimination of bad habits,…
Vestibular and mesial eruption
Vestibular eruption, or inclination, is also more often observed in the anterior part of the dentition, that is, it concerns the incisors and canines. In this case, aesthetic disturbances are noted, speech is less often impaired, and sometimes there is injury to the mucous membrane of the lip. Treatment of vestibular teething is carried out using plates with elastic labial arches. For the same purpose, you can use a sliding arch and a high labial arch...
Abnormal placement of canines or premolars
Abnormal placement of canines or premolars is usually the main complaint of patients. As for the appearance of such children, there are no facial signs of a prognathic relationship of the dentition. This is due to the absence of a violation of the jaw relationship in the anteroposterior direction, as well as the correct closure of the upper and lower incisors. The most common causes of this anomaly in the closure of the lateral teeth are...
Prevention
In some cases, the development of such a defect can be completely avoided by following the following recommendations:
- preference should be given to breastfeeding , and if this is not possible, control the hole on the nipple - it should not be large in size;
- it is necessary to choose the right pacifier so that its position does not put constant pressure on the weak bone tissue of the gums;
- timely treatment of dental diseases.