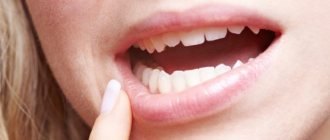
Gum pain after anesthesia
For many people, visiting the dentist's office is a tragedy. Often the patient needs to mentally prepare to dare such a medical event. But it’s not enough to just cure a tooth. What if my gums hurt for a long time after an anesthetic injection? In this case, you should consult a doctor again.
Symptoms
The anesthetic is injected into different places in the mouth depending on the location of the problem. Painful sensations appear during the injection and after its effect ends. This happens because the doctor may have hit the nerve ending.
The action of the anesthetic suppressed the pain during the procedure, but after the end of the effect, disturbing sensations appeared. The pain can be mild or severe.
If this continues for a long time, then you should consult a doctor, as complications could arise.
Types of anesthesia
Local anesthesia is divided into the following categories:
- Infiltration anesthesia . It can be direct or indirect. Direct anesthesia is administered directly under the mucous membrane of the diseased tooth, while indirect anesthesia occupies a large infected area and depends on the tissues that surround it. It is convenient to carry out anesthesia of the lower and upper jaw.
- Application anesthesia . It is applied with a cotton swab and does not require an injection. Suitable for children as it is difficult for them to inject.
- Conduction anesthesia . Aimed at turning off nerve endings. The method is used for extensive dental procedures that include the treatment of two or more teeth. The substance acts within 1-2 hours.
- Intraosseous anesthesia . It is used rarely, and usually in cases where previous anesthesia did not work. Often used for tooth extraction.
- Intraligamentary anesthesia . It is inserted into the tooth ligament under high pressure, using a small amount of anesthetic. The effect is achieved in 20-30 seconds.
- Intracanal anesthesia . It is injected into the pulp or canal, sometimes into a carious cavity.
Causes of pain
The reasons that provoke pain after using an anesthetic are:
- Soft tissue hematoma . Causes pain after an injection into the gum. Due to needle damage to small vessels and nerve endings, after which blood appears, a hematoma is formed. The intensity of the pain depends on the size of the bruise. The consequence of the process is swelling of the gums. The process continues until the hematoma finally resolves, which takes an average of a week.
- Damage to the nerve trunk . It occurs more often during conduction anesthesia, since half of the jaw is subject to freezing. During the injection, the needle enters the nerve fiber. The pain may persist for a month.
- Allergic reaction to drugs . It manifests itself in swelling of the jaw, cheeks, gums and neighboring tissues. In difficult situations, the breathing process may become more difficult.
- Partial nerve removal . May cause pain for a long time. To eliminate your concerns, you should contact your dentist again.
- Infectious process . Appears due to inflammatory manifestations. Against the background of decreased immunity, infected microorganisms enter the injection site where the injection was performed, which can lead to the appearance of phlegmon and abscess. A person, in addition to pain and swelling of the gums, feels an increase in temperature and chills. In severe cases, inflammation spreads to neighboring tissues, resulting in swelling of the mouth, nasolabial folds, and facial muscles.
- The process of root canal cleaning or pulp treatment . This is a painful procedure, after which discomfort persists for some time.
Development of an infectious focus
After anesthesia, in the presence of decreased immunity and oral infections, bacteria enter the puncture site. Also, the reasons for the development of an infectious focus are:
- Jaw cyst.
- Inflammatory process inside the gums.
- Periodontitis.
- Inflammation of the periosteum.
- Hematoma.
- Benign tumor.
Elimination of these manifestations occurs under the supervision of a physician.
Nerve trunk injury
The risk of damage to the lingual, mental, alveolar, and infraorbital nerves appears due to infection, inflammation, and direct trauma to the nerve ending.
The consequence of nerve injury is numbness of the cheeks, lips, teeth, and chin. Leads to discomfort while shaving, eating, and applying makeup. The same manifestations occur when a wisdom tooth is removed.
For minor injuries, the pain goes away on its own and lasts up to 3 months. If pain bothers you, you need to take painkillers.
In case of serious violations, the consequences are eliminated surgically.
Hematoma formation
After the injection, due to damage to small capillaries, a hematoma appears, in other words, hemorrhage into the mucous tissue. This manifestation can resolve on its own, but in case of a long period of elimination of the hematoma, you should consult a doctor, since the infection can lead to tooth loss.
Necrotization of soft gum tissue
This process happens extremely rarely. The death of gum tissue occurs for the following reasons:
- Rapid administration of medication. This can lead to necrosis, as well as compression of nerve endings and blood vessels during the procedure.
- Infectious inflammations.
- Poor circulation after injection, injection inflammation at the injection site, due to chronic diseases, for example, diabetes, vasculitis.
- Doctor's mistake. This occurs when other substances are introduced into the anesthetic site.
Allergy to anesthetic
In dentistry, during anesthesia, an allergic reaction of the body is rare, but still occurs. One of the reasons may be medical negligence, when the doctor chose the wrong dose of a substance or the wrong drug.
Another reason is that the patient did not say during anesthesia about an allergy to certain components. It may also be the body’s genetic predisposition to anesthesia, mental disorders, vegetative-vascular diseases, etc.
Allergies are divided into mild, moderate, severe and very severe. The most dangerous manifestation is anaphylactic shock and Quincke's edema. To relieve painful symptoms, the doctor prescribes antihistamines.
Radiation of pain from the site of dental surgery
After the anesthesia wears off, pain begins to appear. They can spread to the area next to the puncture, to the mucous tissue. But the patient seems to be worried about the injection site. After a few hours the pain will subside.
Preventing complications
After visiting the dentist, you will be under anesthesia for several hours. During this period, it is not recommended to consume food, especially alcohol. You can eat only after two hours.
At first, you should avoid hot foods to prevent bleeding. If there is an inflammatory process, use antibiotics as prescribed by your doctor. Thanks to them, pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity are destroyed.
If painful sensations bother you, use antiseptic mouth rinses.
If the pain is too much
If the pain does not go away and bothers you for a long time, and the sensations are strong, do not self-medicate. Consult your doctor as there are several reasons for this phenomenon. Please note that infectious processes can spread to the head and other organs, so urgent consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Remember, the key to strong and strong teeth is prevention and periodic examination of the oral cavity by a doctor.
Source: https://simptom.guru/rot/bolit-desna-posle-anestezii
Why can a tooth hurt after root canal filling?
So, what causes unbearable, shooting and tugging pain and swollen gums?
- Repeated caries or pulpitis. If necrotic tissue was not completely removed, if a piece of nerve remained in the canal, or if the infection spread from neighboring, not yet cured teeth, these pathologies may develop under the filling and cause pain.
- Tool fragment. The dentist himself may not notice that the needle has broken and a piece of its tip remains in the dental canal. Sometimes a person lives with it for months or even years, and only then the tooth becomes inflamed and hurts. To detect such a medical error, it is necessary to take an X-ray.
- Cyst. This neoplasm is also not always visible even on an x-ray if it is covered by large tooth roots. Very often, a granuloma or cyst is discovered only after tooth extraction, so there is no need to rush to accuse the doctor of incompetence or negligence.
- Burns to nerves and pulp while using a drill. Modern equipment is equipped with special cooling devices, since during prolonged cleaning with a drill, both the bur and the tooth tissue overheat. If they are not cooled with water, a burn of the pulp may occur, which is very painful and also threatens the development of inflammation.
- Insufficient or excessive filling of dental canals with filling solution. Both the first and the second are equally bad. In the first case, access is opened for bacteria to penetrate into the pulp and periosteum, in the second, cement or composite material removed outside the canals injures the soft and hard tissues of the tooth and also provokes inflammation. It can also be difficult to determine exactly how much filling composition is needed because many solutions shrink greatly after hardening.
What to do to get rid of pain? There is only one answer - make an appointment with the doctor again, take an x-ray and have the tooth re-treated.
Neither pulpitis, nor a fragment of a dentist's instrument, nor excess filling material will resolve on their own, and the more time passes, the more difficult and lengthy the treatment will be.
It is important to know:
zubsite.ru
After anesthesia, gums hurt
- Causes of pain
- Ways to relieve pain
- Possible complications
Anesthesia is used in dentistry. There are several ways to relieve pain in the mouth.
One of them is an injection of anesthetic. Consequences may occur in the form of discomfort and pain at the injection site.
Let's consider the causes, methods of control, possible complications after anesthesia injection.
I believe that you can still save a lot on visits to the dentist. Of course I'm talking about dental care. After all, if you carefully care for them, then treatment may indeed not come to pass - it won’t be necessary. Microcracks and small caries on teeth can be removed with regular toothpaste. How? The so-called filling paste. For myself, I highlight Denta Seal. Try it too. Injection anesthesia is the most common method of anesthesia in dentistry
Causes of pain
Why does pain occur after anesthesia? There are several reasons, including the following:
- Allergy. Appears on drug components. Painkillers are medications that can cause negative reactions.
- Traumatization. It all depends on where the puncture was made. If the goal was to treat dental pulp or clean root canals, the body’s reaction is natural; these procedures are painful.
- The nerve remained in the gum cavity. Sometimes it seems as if the problem is concentrated at the puncture site, but in fact it is a “nerve ache”.
- Infection. Bacteria and microorganisms that are in the oral cavity enter the puncture site. The situation arises due to decreased immunity, exposure to concomitant diseases and other problems. The result will be inflammation, abscess, phlegmon. An accompanying symptom is increased body temperature, weakness, and poor health.
Each person's reaction to an injection may be different.
- Hematoma. It can last for a week - it all depends on the area of damage and health characteristics. It occurs due to an incorrect puncture when a doctor or nurse inserts a needle into the point where the vessel is located. Experienced doctors sometimes encounter a similar situation; all people are individual and it is difficult to predict the location of blood vessels. At the site of the rupture, blood flows out and enters the soft tissue, causing the affected area to become dark, slightly swollen, and aching. The blood resolves on its own, but healing accelerating agents can be used.
- Damage to the nerve trunk. When a nerve fiber is injured, the pain goes away within a month. A situation may arise during conduction anesthesia, when the effect is on half of the jaw.
- Circulatory disorders are a rare cause. Leads to tissue necrosis.
- Compression of blood vessels. This may occur with rapid administration of the drug.
- Spasms appear due to the use of a high dosage of the drug, which the patient needs in large quantities.
The last three reasons are uncommon, but are more dangerous and require a medical response.
Ways to relieve pain
If there is no pus, and the place where the injection was given looks normal (slight redness is acceptable), you can wait a few days without going to the doctor. If the problem persists, it's time to see your dentist.
The situation will be dangerous when the problem does not go away after a week. This indicates either damage to soft tissues during injection, reasons that the doctor can analyze.
Recommendations to help cope with unpleasant sensations:
- Avoid eating salty and spicy foods. The components enter the wound and irritate it.
- Buy an anesthetic, use an aerosol based on Lidocaine, Diclofenac and general anesthetics. The frequency of use and frequency must correspond to the information indicated in the instructions.
- Do not heat food to high temperatures or drink hot or cold drinks. The optimal temperature is room temperature.
- Alcohol and carbonated drinks negatively affect the inflamed area.
- Until you get rid of the problem, do not touch the affected area with the brush. You can apply toothpaste to a cotton pad and wipe your teeth and gums.
- You need to avoid solid foods or those that can damage the surface of the gums.
- It is advisable not to smoke. Nicotine increases inflammatory processes.
- After eating, you should rinse with water or with the addition of herbs (for example, chamomile, oak bark).
- Stock up on antipyretic medications. If inflammation increases, body temperature will also rise.
Anesthetics affect the functioning of the liver, so you should consult your doctor before taking painkillers. It is highly likely that he will prescribe a medicine for the liver that protects it from harmful effects.
If a person can chew on the other side without affecting the problem side, this will aid recovery. Mouth rinsing is not done actively, but simply by collecting liquid and keeping it in the mouth. If a powerful stream of moving fluid is created, it can dislodge or destroy a blood clot that has formed as the site begins to heal.
What can you take for pain caused by an injection in the gum:
- Analgin, Paracetamol, Ibuprofen. These are complex-action drugs, they help relieve pain, normalize body temperature, and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Nise and Ketanov are powerful tools for fighting pain. They have an effect quickly. Available in pharmacies in different release forms. Aerosols and tablets taken orally are relevant for this problem.
- Promedol, Fentanyl, Morphine - these drugs are very powerful, they are produced on the basis of narcotic substances used in medicine. They are sold only with a doctor's prescription.
- No-shpa, Papaverine are antispasmodics, relevant in the fight against many types of pain.
Do you feel nervous before visiting the dentist?
To ensure that medications do not cause side effects or allergies, they are taken strictly according to the instructions. If we are talking about treating a child, in any case, you first need to consult a doctor.
Possible complications
To avoid complications after the injection, you need to reduce the level of consumption of hot, cold, spicy, salty foods, alcohol, and soda. To prevent small pieces of food from becoming lodged in the wound, you should not eat food for three hours after the procedure. Despite following all the rules, complications are possible:
- The spread of the inflammatory process, covering the area of the nasopharynx, sometimes the ear.
- Tissue death, and this process, once it has begun, is irreversible. In the initial stages, you need to determine the cause of severe pain.
- Infection leads to a purulent process. If action is not taken quickly, the circulatory system may become infected.
Consequences and complications depend on the original cause of the pain syndrome. You should consult a doctor if you have pain, when mild medications to relieve discomfort do not work, and when the situation does not change for several days. Already on the third day, a visit to a specialist can no longer be postponed.
Loading…
Source: https://zub.expert/polost-rta/bolit-desna-posle-ukola-anestezii
The main causes of pain after injection in the oral cavity
It should be understood that when a needle passes through soft tissues, it injures them and the occurrence of unpleasant sensations is always present. This is considered normal and can persist for even 1-2 days, and even longer in more sensitive people.
It all depends on the individual characteristics of the person and his neuropsychic perception. This condition does not require treatment and goes away on its own after a certain time.
Another question is when the pain does not subside, and also intensifies in direct proportion to the period of limitation of the treatment. This condition may indicate the development of a complication that can result in a serious complication. The symptoms of such problems are varied and depend on what led to the pain reaction.
Development of an infectious focus
A person, even without the development of inflammation, has a huge number of bacteria in the oral cavity. In a normal position, they do not develop, but are in a certain balance.
Attention. If any complication develops after anesthesia, it is prohibited to use warm compresses and self-medicate. This can lead to even more serious consequences that will require long-term hospital treatment.
When a pathological focus appears, there is a sharp increase in the number of pathogenic microbes. This is especially noticeable against the background of decreased immunity. When an injection is given, they easily penetrate into the resulting wound and cause inflammation.
Gradually, an abscess or phlegmon begins to form, which captures more and more areas of healthy tissue. In principle, we can say that the problem arose due to a violation of pain relief according to the rules dictated by generally accepted instructions.
My gums hurt after an injection: how to relieve the condition?
If a person's gums hurt after an injection given during dental treatment, this is often a cause for concern. But usually experts say that minor discomfort as a result of this anesthetic procedure goes away after a few days.
But this is not always the case - sometimes the patient feels a burning sensation, itching, or even sees that a tubercle has formed on the mucous membrane. The first thing you need to do is visit a doctor. He will prescribe treatment that will eliminate the unpleasant consequences.
When not to panic
Modern dentistry focuses not only on effective treatment, but also on ensuring patient comfort. If a person is relaxed, manipulations are easier. This is why local anesthesia for dental treatment is the norm.
Even whitening and removing tartar involves its use. Modern methods of pain relief have virtually no effect on the body, after which the person continues to lead his usual lifestyle.
But it happens that the gums hurt after an anesthesia injection due to periodontal damage in the following ways:
- Infiltration - assumes that the injection is made as close as possible to the inflamed area. The sensitivity of the remaining zones is maintained. This anesthesia ends quite quickly - after 1-2 hours.
- Conductive - the injection is placed inside the nerve trunk, which leads to loss of sensitivity of the entire periodontium, affecting the inside of the cheeks. It goes away in 8-10 hours.
In advanced cases or for large-scale implantation, anesthesia is used. This also applies to children. Even the most careful and professional treatment does not guarantee that the recovery period will pass without problems.
But doctors say that the gums at the injection site almost always hurt within 1-2 days after the procedure.
If it does not go away after the specified period, you should consult a doctor, since this condition is considered a deviation from the norm.
Each person has an individual reaction to treatment. This also applies to anesthesia. Complications can arise if the area becomes infected. The gums often hurt after an injection if, when inserting a needle, bacteria penetrate into the microscopic wound.
A person feels a burning sensation, throbbing pain, which indicates infection. Another common cause is hematoma, which occurs when capillaries are accidentally damaged. Blood accumulates under the soft tissues, forming a small lump.
Basically, it goes away without complications.
If your gums hurt after an anesthetic injection, you may be talking about injury to the nerve trunk. This can happen to anyone - even experienced dentists make mistakes.
Moreover, when the patient is nervous and twitches at the most crucial moment, the needle can hit another area, damaging the nerve fibers. The facial muscles suffer, which leads to severe pain radiating to the ears and temples.
In addition to the fact that the gums hurt at the injection site, a person experiences asymmetry in the face and watery eyes. Sometimes the problem goes away after a few weeks.
When removing a fistula, it is often necessary to make an incision into the soft tissue. This leads to discomfort. It seems to a person that it is after the injection that the gums are swollen, but the reason lies in the fact that the cut parts have not yet healed. It will take a few days for everything to return to normal. Usually the doctor recommends rinses to the patient, medications that speed up the recovery process.
One of the most serious problems is the death of mucous membranes. If the gums are swollen after anesthesia, and a whitish or dark spot has formed on the surface, it is important to immediately visit a doctor, as this is one of the signs of necrosis.
It is caused by too rapid administration of the anesthetic, which damages the blood vessels, and incorrect selection of the dose of the drug for pain relief.
The patient may also have diabetes or other diseases that increase the sensitivity of the mucous membranes to pain relief.
How to deal with unpleasant sensations?
If your gums are swollen after anesthesia, but there is no pain, you should wait until the next day - the symptoms should decrease. But when an abscess forms, you need to go to the dentist, who will prescribe antibiotics. They are worth taking to cope with the infection.
Perhaps the patient will be prescribed Ammoxiclav, Lincomycin, Sumamed. The duration of the general course of treatment depends on the degree of damage to the oral cavity.
But after the injection, the gums are swollen; you cannot use these drugs yourself without identifying the underlying cause of the problem.
To cope with pain, you can take Ketanov, Ibuprofen, Nurofen. Diclofenac, which can be combined with Paracetamol, helps with jaw pain. This will remove swelling and reduce inflammation.
The patient will then be able to eat normally, because until this point he will experience severe pain. Rarely, when the gums hurt after an anesthesia injection for a week, people sit at home and wait for everything to go away - most visit a doctor.
Thanks to this, it is possible to quickly stop the development of inflammation.
The resulting abscess must be opened, cleaned, and an application with an antiseptic is made. At home, the patient can rinse his mouth with Miramistin or Chlorhexidine. No one can say for sure how much the gums hurt after an injection in complicated cases.
But usually 3-7 days after the start of treatment, people completely return to normal. It is permissible to use folk remedies in combination with the main therapy. Rinses based on chamomile, sage, and oak bark are excellent in reducing pain.
Applications with sea buckthorn oil work well.
Remember, if your jaw hurts after an injection of anesthesia into your gums, you should not heat the affected area or use alcohol-based products to treat wounds. It is also worth giving up smoking and drinking alcohol for faster recovery.
Do not forget to be especially careful about oral hygiene after surgery - this will reduce the likelihood of complications. If they appear, be sure to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Modern drugs and treatment methods will help to quickly cope with the problem.
Source: https://vzube.com/bolit-desna-posle-ukola.html
When to see a doctor
Often complications after treatment have to be eliminated with a second visit to the dentist:
- persistence of cheek swelling after tooth treatment for 2-3 days and the formation of a seal at the site of swelling is a cause for concern;
- if for several days, in addition to the tumor, you feel a general malaise, the temperature remains above 37 C, then you should consult a doctor;
- the appearance of a tumor 2-3 days after treatment is a sign of the development of inflammation;
- the appearance of a strong odor from the mouth indicates suppuration and accumulation of pus;
- Clicking sounds while chewing and discomfort in the jaw area indicate minor nerve damage.
Why does gum pain occur due to anesthesia?
After treatment and tooth extraction, pain often occurs at the site of injection of the anesthetic. Patients begin to worry if pain in the gums lasts more than a day. Sometimes pain can be accompanied by swelling and impaired sensitivity of the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Pain in the gums after administration of anesthetic
In dentistry, infiltration and conduction anesthesia are often used, which are performed by injecting (injecting) an anesthetic into a certain area of the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
If the anesthetic is administered by infiltration, the injection is performed in the gum in the area of manipulation.
When conduction anesthesia is performed, the injection is performed in the area of the nerve trunk innervating the surgical site.
Causes of pain
After anesthesia, all patients have gum pain. This is a normal reaction of tissue damaged by the needle during pain relief. Pain after an injection can be of varying intensity and duration, it all depends on the individual characteristics of each organism.
For one person it will be mild and go away after a few hours, for another it can be intense and last for several days. In both cases, this is a normal condition, it does not require treatment and will go away on its own.
But sometimes the gums hurt due to complications of anesthesia.
Infectious process
A healthy person’s oral cavity contains a huge number of microorganisms; during inflammatory diseases, their number increases even more. If a person has a reduced immune system, microbes, penetrating through the injection wound, can cause an infectious process in the soft tissues (abscess, phlegmon).
With this complication, in addition to pain, which will be intense, body temperature and/or local temperature at the site of inflammation may increase. Often with abscesses, patients note that the gums are swollen.
Depending on the severity of the process, swelling can spread to the facial muscles, causing asymmetry of the nasolabial folds and mouth.
Cheek swelling
Soft tissue hematoma
If during anesthesia the needle damages a small vessel, the leaking blood can form a hematoma in the gum tissue.
Depending on the size of the resulting hematoma, it will put pressure on the surrounding soft tissue with varying intensity, irritating nerve receptors and causing pain.
If the bruise is located in the superficial layers of the mucous membrane, the patient may also notice that the gums are swollen. The pain from a hematoma will persist for several days (up to a week) and will go away on its own after the blood is absorbed.
Damage to the nerve trunk
Just like a vessel, a nerve fiber can be injured by a needle during the procedure. After a nerve injury, the gums hurt for a long time, up to several months. The duration and intensity of pain will depend on the size of the injured nerve trunk.
With infiltration anesthesia, small endings in the mucosa can be damaged, and therefore the pain will be localized and will go away after a few days.
If conduction anesthesia was performed, then there is a risk of injury to a larger nerve that innervates half of the lower jaw at once, so after such an injury, as a rule, the entire innervation zone hurts at once. The pain may radiate to other parts of the oral cavity.
Often the pain prevents you from opening your mouth, chewing and talking normally, and it lasts for several months. Facial features may become asymmetrical; in the first days, the patient may also feel that the gums at the injection site are swollen.
Irradiation of pain from the surgical wound
At the site of the operation, tissue and nerve endings are also damaged, accompanied by pain that occurs after the anesthesia wears off. The pain may radiate to neighboring parts of the mucous membrane, and the patient feels that the gums hurt at the site of anesthesia.
Necrosis of the mucosa
In rare cases, anesthesia may be complicated by necrosis of the tissue of the gum mucosa. Necrosis develops as a result of tissue death that occurs for various reasons.
- Poor blood circulation at the injection site, usually due to some chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, systemic vasculitis).
- A sharp spasm of blood vessels after the administration of a large dose of adrenaline along with an anesthetic can also cause necrosis.
- Too rapid administration of the drug can lead to compression of blood vessels and nerve endings and also lead to necrosis.
- Infectious processes at the injection site, especially those caused by anaerobic flora, can also cause tissue necrosis.
- Medical error when another aggressive agent (alcohol, calcium chloride) is administered instead of an anesthetic.
If calcium chloride is incorrectly administered instead of an anesthetic, mucosal necrosis may develop.
As a rule, the development of tissue necrosis is accompanied by acute pain already during the injection and forces the doctor to take emergency measures. At the site of tissue necrosis, a wound forms, which hurts and heals for several weeks.
What measures should be taken if the pain bothers you for a long time?
If your gums hurt for several days and the pain does not decrease, the mucous membrane is swollen and hot to the touch, you should immediately consult a doctor.
You should not try to treat yourself, as different causes of pain require different approaches to treatment.
You cannot perform warming compresses and physical procedures on your own, since if purulent foci or tissue necrosis appear after the injection, such treatment can lead to the spread of the process and even the development of sepsis.
Source: https://NarkoZzz.ru/stomatologiya/desna-posle-anestezii.html
Treatment
Complicated hematomas may require surgery. In this case, the gum in the area of the bruise is cut, a mass of coagulated blood is removed from it, and the cleaned area is washed with antiseptic solutions.
When a pyogenic infection is attached, a drainage is placed in the incision area on the gum - a special polymer tube or a sterile bandage tourniquet, which serves as a drain for pus and exudate. Drug treatment is mandatory if the bruise after tooth anesthesia shows signs of infection or an inflammatory process.
The list of medicines may include:
- Gentamicin, Lincomycin, Amoxicillin, etc. to eliminate a bacterial infection or to prevent its occurrence.
- Miramistin, Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, etc. for rinsing the mouth and antiseptic treatment of the mucous membrane.
- Metrogyl Denta, Cholisal, Solcoseryl - used as applications to the gums, they promote faster resorption of hematoma, elimination of swelling and prevention/treatment of the inflammatory process and microbial complications.
- Nimesil, Nise, Analgin and other drugs that have an analgesic effect.
Which drugs should be used and in what combination is decided by the attending physician, taking into account all the features of the clinical case and the severity of complications.
Sore gums after anesthesia at the dentist, pain in the jaw, head, cheeks and injection site
Treatment and removal of teeth is an unpleasant and very painful procedure. To prevent a person from feeling pain during dental procedures, anesthesia is used. Today, tooth extraction, oral surgery and even simple treatment cannot be done without pain relief.
Anesthesia is an integral part of dental treatment; after a certain period of time, the unpleasant sensations disappear, the injection site stops hurting, and the patient continues to go about his business, forgetting about the problem. But for some people these feelings do not go away - their gums still hurt after the anesthesia injection.
In this case, a second visit to the doctor is inevitable.
Features of anesthesia
Anesthesia during dental treatment and other surgical interventions allows the patient not to feel pain, while the dentist can calmly carry out the manipulations associated with the treatment.
Today, special syringes with very thin needles are used for injections, which cause the least harm to soft tissues. The dentist irrigates the injection site with an aerosol anesthetic, so the injection is painless. But sometimes it happens that the jaw begins to hurt after anesthesia.
This effect can occur if the dentist gave the injection incorrectly.
For pain relief, dentists use conduction or infiltration methods, which affect a specific painful area, so anesthesia does not have a toxic effect on the entire body.
Conduction anesthesia is used for deeper medical operations; it affects the entire nerve, which is responsible for the immediate area of excitation. The gum is pierced directly into the area of branches of the branches of the trigeminal nerve.
Conductive anesthesia is practiced during the removal or treatment of molars, removal of the nerve trunk, and operations on the gums.
Infiltration anesthesia is done directly into the mucous membrane of the gums. The injection time is limited to one hour, so this anesthetic is used when cleaning dental canals.
Application anesthesia is used in the form of a gel or spray, which is applied to a small area in the form of applications.
Its duration of action is limited, so this anesthesia is used during simple dental operations or as an auxiliary anesthesia of the gums before piercing it with a needle.
The main causes of pain after an injection
After a puncture of the gums in the soft tissues, a violation of the integrity of the integument occurs, the patient feels a pain syndrome in the area of the injection, which will go away on its own after some time. After anesthesia, the gums may hurt from several hours to two days, it depends on the person’s condition.
This is a natural effect of the body on the injection, which does not require any treatment; after some time, the puncture site gradually stops hurting.
If the pain does not subside, but on the contrary, becomes more and more unbearable, you should contact a dentist who will determine its cause and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Reasons why the mucous membrane or gums continue to hurt:
- Development of infection;
- Trauma to the nerve trunk;
- Hematoma formation;
- Necrosis of soft tissue on the gum;
- Allergy to anesthetic;
- Increasing pain at the site of dental surgery.
We will consider each of these reasons separately in order to have an idea of the possible risks of visiting the dentist.
Nerve trunk injury
Nerve tissue in the tooth canal
Even with an experienced dentist, major nerve damage can occur when administering anesthesia. In this case, the patient experiences pain after anesthetizing the tooth for a long period. Unpleasant sensations depend on the nature of the injury to the nerve ending.
When performing infiltration anesthesia, small nerve endings may be affected, so the damage will be minor and the pain will be minor.
Conductive anesthesia is performed directly in the area of advancement of the nerve trunk, which significantly complicates the procedure. If nerve damage occurs, the gums continue to hurt for a long time, often causing painful sensations that spread along the jaw.
The patient experiences the following symptoms:
- Unbearable pain that does not subside even when taking painkillers;
- Facial asymmetry;
- Problems with chewing food and speaking;
- Swelling of the gums, which does not stop hurting, can be observed at the injection site.
Treatment of dental pulp should be carried out only in a hospital, where modern medications and physiotherapy are used. In especially severe cases, when this treatment does not bring positive results and the patient continues to be ill, surgery is recommended.
Soft tissue necrosis
Necrosis is the death of soft tissue, a dangerous problem that requires immediate elimination. This rarely happens in dental practice, but it does happen.
The deviation can be identified independently if, after tooth extraction, the cheek does not stop hurting after anesthesia, a dark or white spot appears in the area of the injection, and there is a pulsating, ongoing pain.
Necrosis of mucosal tissue can be due to the following reasons:
- The administration of a large dose of adrenaline with incorrectly calculated anesthesia will lead to spasm and subsequent necrosis of soft tissues;
- If you quickly administer the drug , this can lead to injury to the blood vessels and their compression;
- Poor circulation due to chronic illnesses of the patient can cause necrosis of the soft tissues of the mucosa;
- If, as a result of an error, the doctor administers the wrong medicine , the gums and bone tissue may be damaged, which will continually ache, and if you do not consult a dentist in time, tissue death may occur;
- Infection of the injection site causes inflammation , which may result in necrosis.
Timely consultation with a doctor can reduce the consequences of necrosis on the gums. The process of wound regeneration occurs over the course of a month; after recovery, scars remain at the site of the wound.
Spread of pain from the site of dental procedures
During treatment, oral tissue or nerve endings may be damaged. After the effect of the painkillers wears off, the patient experiences pain in the area of manipulation.
It is possible that nearby places begin to hurt, but the person feels pain where the needle punctured.
Since after a visit to the dentist the reaction of the oral tissues is unpredictable, and a person’s gums continue to hurt for several days, the doctor should warn the patient about this.
He should advise what medications need to be taken if the pain continues to bother you, and recommend rinsing to reduce inflammation.
If the pain does not go away within three days, the patient needs to see the dentist again, he will prescribe x-rays and physiotherapeutic procedures.
The most common types of pain relief in dentistry
Most often, in order to cure caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, remove a tooth or perform other dental procedures (for example, dental implantation), the doctor administers local anesthesia, namely a pain-relieving injection into the gum. If it is painful for the patient to inject into the gums, and he experiences discomfort during the injection process, the specialist pre-treats the gums with an aerosol or spray (application anesthesia), which reduces the sensitivity of the soft tissues.
Dentists mainly use types of conduction and infiltration anesthesia. With the help of local anesthetics, it is possible to achieve a minimal toxic effect on the patient’s body, because medications administered topically affect only the area of preparation.
The doctor applies infiltration anesthesia to the problem area (for example, near the root of a diseased tooth). After its introduction, neighboring areas retain their sensitivity. The guidewire is effective for carrying out larger-scale interventions, because it affects directly the branch of the nerve that is responsible for a certain area. After the administration of a conductive anesthetic, all periodontal tissues are literally “frozen.”
How long does an injection into the gum last? Infiltration – up to 2-3 hours, conductive – up to 8-10 hours.
Read the article on the topic: anesthesia in dentistry. Find out what modern methods of anesthesia allow you to avoid an injection into the gum.