Difference between progeny and prognathia
Bite with prognathism - the upper teeth are pushed forward relative to the lower ones
Prognathia and progeny are the names used in speech therapy and orthodontics for pathological changes in the bite that occur as a result of disturbances in the development and formation of the jaw bones and lower dentition. In Latin - prognathia, progenies.
Prognathia or distal occlusion is a consequence of insufficient development of the lower jaw bones. The upper jaw protrudes noticeably forward, the chin is small, almost merging with the neck.
Progenia or lower prognathia is excessive development of the lower jaw bones and dentition. In a person with this pathology, the chin and lower jaw protrude noticeably forward, the lower lip is noticeably larger than the upper. This type of bite is called mesial.
Correction techniques
The choice of technique for eliminating the progenic type of bite depends on the age of the patient at the time the pathology is detected, as well as the degree of its development.
Thus, treatment of incorrect jaw alignment in young children is based on the following measures:
- elimination of bad habits that affect the correct formation of the bite - giving up pacifiers, measures to stop sucking fingers and lips, the basis of which is the use of the vestibular plate;
- formation of the correct way of breathing by performing training of the orbicularis oris muscle, using special lip activators;
- massage of the alveolar arch of the upper jaw;
- trimming the frenulum of the tongue , if its length is a factor provoking the formation of malocclusion;
- the use of the Bruckle apparatus and devices with a chin sling and extraoral traction to change the position of the lower jaw with deep incisal overlap;
- wearing suitable activators and functional devices for the treatment of pathologies of the alveolar processes.
During mixed and permanent bites, it is much more difficult to get rid of pathology, but the possibility of returning an orthognathic bite still exists.
Dentists recommend using the following fixed orthodontic appliances:
- bracket systems;
- Bruckle's apparatus;
- arc devices;
- devices with jaw rods.
The use of the listed devices helps to eliminate gaps and interdental spaces, move the elements of both jaw rows in the required direction, and correct the position of the rows relative to each other.
In case of complete absence of teeth and the development of senile progeny, orthopedic treatment is carried out, which has many features associated with jaw deformation and bone tissue atrophy.
One of the methods for treating progenic bite is presented in the video.
True and false progeny, prognathia
In dentistry and medicine, progeny and prognathism are divided into true and false forms.
True progeny is a complex anomaly in which the position of the anterior and lateral teeth is disturbed. There is a large gap between the molars. The person cannot chew solid food. This is a genetic pathology in which the upper jaw is very large. The problem can only be eliminated in children with the help of a Frenkel function regulator. The device inhibits the growth of the upper jaw bones. In adults, the problem can only be eliminated through surgery.
False progeny is characterized by a violation of the position of only the front teeth. The lower jaw sinks, sometimes quite far. It often occurs in older people, which is why the disease is called senile progeny. In young people, the cause of the problem is improper fusion of the jaw bones after an impact or fracture. Treatment is carried out using orthodontic or surgical methods.
All newborns have a false distal prognathic bite. As the child grows older, it is corrected if the child is placed correctly at the breast and is not allowed to suck his fingers or constantly keep the pacifier in his mouth.
The combined type of malocclusion is a combination of false and true forms of pathology.
Types of mesial occlusion
Mesial occlusion is an anomaly that has three forms of manifestation. In accordance with this, in modern orthodontics, true, false and combined varieties are distinguished.
Features of true progeny
The diagnosis of true progeny in children is quite common: the lower jaw is developed much more than the upper jaw, which causes an overlap of a number of teeth. Usually in this case, the person has clearly expressed all the main signs, and there are serious problems with speech and diction.
- The defect, as a rule, becomes noticeable in a child from childhood, since abnormal bite is very often inherited.
- True progeny can also occur during fetal development if the mother has suffered a serious illness or difficult childbirth.
- It is best to start treatment of mesial malocclusion as early as possible; the results of correction largely depend on this. Unformed facial bones can be effectively treated until about 12-13 years of age; after this age, it is much more difficult to correct a mesial bite.
- The anomaly in a child can be eliminated using removable structures: trainers and mouth guards, as well as by performing special gymnastics and massage. In the case of teenagers, correction of the mesial bite with braces will be more effective.
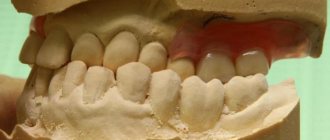
Only in particularly severe cases is surgery or preliminary tooth extraction required. However, with age, surgery may become the only method that can be used to correct mesial malocclusion in adults. By paying attention to the photo, you can see what a jaw with an advanced anomaly looks like.
Specifics of false progeny
In this case, the mesial bite may be practically invisible visually, since there is no significant increase in the lower jaw. Disharmony is observed due to the fact that the upper jaw is not fully formed or the lower jaw is shifted forward.
- False progeny is formed due to improper functioning of the muscular system. It occurs due to the fact that a person involuntarily protrudes the lower jaw.
- Also, false progeny is provoked by early change of teeth, chronic inflammatory processes, bad habits or a very short hyoid frenulum.
False progeny is easier to correct; the use of special orthodontic appliances is usually sufficient. After braces, as a rule, there is no trace left of the mesial bite. In rare cases, surgery is necessary. However, despite the positive prognosis, it is better not to delay treatment of false progeny, so as not to create serious health problems. Looking at the photo, you will note what a mesial occlusion of the false type looks like.
Combined type
When mesial occlusion combines signs of true and false progeny, a combined type is diagnosed. It involves a completely individual approach, which depends on how serious the degree of development of the anomaly is. In difficult cases, surgery to correct mesial malocclusion cannot be avoided.
Forms and types of progeny
Micrognathia before and after bite correction
With physiological progeny, the jaws are positioned normally in a dynamic and static state and work correctly. The periodontal tissues are healthy and the jaw joints bear moderate load.
With a pathological mesial bite, the functioning of the jaws is disrupted, the dentition is straight, but various disorders in the gastrointestinal tract and dental diseases develop.
Betelmann classification:
- micrognathia of the upper jaw;
- micrognathia of the lower part;
- mixed form.
Doroshenko classifies the disease according to its anatomical features: as a consequence of underdevelopment of the lower jaw or insufficient development of the upper part of the face, or as a consequence of the anterior position of the lower jaw in the joint.
Symptoms
Senile progeny is a diagnosis that has quite pronounced symptoms, especially those that are considered external. These include:
- the lower jaw is more protruding in comparison with the upper;
- ingenious angle of inclination - in case of illness it is greater than normal. This symptom can only be determined by a doctor, and it is one of the basic signs of diagnosing progeny;
- the appearance of fragmentary facial asymmetry and the formation of dents;
- an increase in the size of the lower lip relative to the upper lip - while it is slightly swollen and slightly turned outward;
- the lower part of the facial apparatus becomes more massive;
- the chin in its lower area narrows and looks pointed;
- the lower labial fold stretches and becomes almost invisible, while the nasolabial recesses, on the contrary, have more pronounced features.
Internal pathologies that progress against the background of the underlying disease, unfortunately, are not so noticeable, but upon closer examination, they can still be identified.
The patient can observe:
- the appearance of the first signs of a lisp;
- protrusion of the lower jaw row forward, while a gap appears between the upper and lower organs, which, as progeny develops, increases;
- internal asymmetry;
- chaotic direction of growth and position of organs. The jaw row becomes like a wavy line;
- secondary dental diagnoses – caries, gingivitis, excessive accumulation of stone deposits;
- increase in the volume of individual teeth. Basically, these are the upper fragments;
- the size of the alveolar arch is not normal;
- partial dysfunction of the chewing reflex. This symptom appears much earlier than others.
Types of prognathia
Forms of prognathia
There are 2 types of prognathia – physiological and pathological.
With physiological prognathia, the alveolar processes and the front teeth of both jaws are tilted forward. There is no need to correct such a bite. In the pathological form, the lower jaw moves forward, the lower dental arch is larger than the upper.
Classification depending on jaw position:
- The first is insufficient development of the lower jaw against the background of a normal upper jaw.
- The second is the excessive size of the upper dentition, the lower part remains in its normal position.
- The third combines the features of previous forms.
- The fourth is a slight protrusion of the upper ones and twos.
Additionally, crowding or severe discrepancy of teeth is observed.
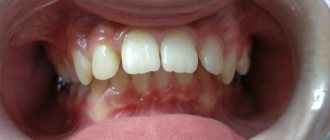
Characteristics of correct bite
The doctor determines the correct bite based on a number of signs
- no gaps or crowding in the row;
- proportionality of the oval of the face;
- clear, intelligible speech;
- comfortable chewing of food;
- aesthetic appeal of a smile.
The doctor determines the correct bite by a number of signs. The doctor determines the correct bite by a number of signs.
The structure of the jaw arch
The teeth, united in special arches, form a functional system for biting, breaking and grinding food. In its structure, it is necessary to highlight features that influence resistance to pressure and the relationship of teeth during chewing.
The lower dental arch has the shape of a parabola, the upper - a semi-ellipse. Due to the slight inclination of the teeth towards the vestibule of the mouth, the outer part of the upper arch is larger than the inner one. Accordingly, the outer part of the lower arch is smaller than the inner part due to the dental inclination towards the oral cavity. If the rows are closed, an occlusal curve is formed.
Location of incisors and canines
Teeth are the main part of the masticatory apparatus. In adults there are from 28 to 32 units. In the center of the upper and lower jaw there are incisors designed for biting food. There are two lateral and two front incisors. Their distinctive features are a sharp cutting edge, one spine and a flat crown. With a correct bite, the upper incisors are larger than the lower ones.
With a correct bite, the upper incisors are larger than the lower ones
The canines follow immediately behind the incisors and serve to hold and tear food. They are located one on each half of the jaw at the corners of the arches. The canines have a cusp along the cutting end and can withstand more force than the incisors. When you clench your teeth, the cusp of the upper canines should be between the lower canine and the first premolar.
Chewing teeth
After the canines come the molars. First, the premolars grow, having two cusps on their chewing surface. They serve to grab and tear food and are slightly reminiscent of fangs with a wide crown. In adults, there are two premolars on the right and left half of the upper and lower arches.
Behind the premolars grow molars - the largest teeth in the mouth. On each half of the jaw there are 2-3 molars with a massive crown and a wide chewing surface with several tubercles. With a correct bite, the cusps of the upper molars are projected in the groove between the cusps of the lower ones.
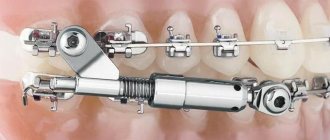
Treatment methods for malocclusion
A method for changing the shape of the jaw and bite
In orthodontics, radiography, teleradiography, tomography, and orthopantomography are used to accurately determine the shape of prognathia of the upper jaw or progenia of the lower jaw. For diagnosis, a special bite roller and bite models are used.
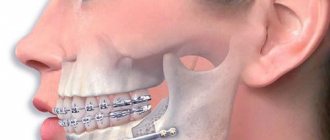
It is better to correct the bite in childhood, up to 10 years. For children, braces and plates cause virtually no discomfort. Adults often require surgical intervention; wearing orthodontic devices is accompanied by pain.
Orthodontic devices for correcting malocclusion in children:
- mouthguards;
- braces;
- dental plates and trainers;
- Frenkel device;
- Klammt or Wunderer activator;
- Bruckle's apparatus;
- masks, hats with a chin garter.
In addition to special devices, children can undergo plastic surgery of the lingual frenulum and massage of the alveolar process. Special myogymnastics helps.
To correct occlusion in adults, a permanent brace system is required. Surgical treatment consists of straightening, removing, and prosthetics of teeth. Sometimes complex operations on the lower jaw and facial plastic surgery are required.
It will take 1.5-2 years to correct a child’s bite. In adults, a full correction course lasts at least 2.5-4 years.
Causes of pathology
The occurrence of this disease is influenced by genetic, congenital and acquired factors. About a third of cases of anomaly are caused by hereditary structural features of the skull.
During the period of intrauterine development of the fetus, diseases of the pregnant mother can lead to the development of pathology in the child. Progenia is also accompanied by birth injuries and hypoplasia of the premaxillary bone. The condition of the oral cavity plays a major role:
- the presence of a complete set of teeth in the lower row;
- absence of teeth in the upper row;
- small teeth both above and below;
- too big tongue.
Among the causes of progeny of the lower jaw, experts name artificial feeding of a child, early diseases, pathologies of the oral cavity, etc. A separate group of causes includes components of a behavioral nature. These include:
- habit of sucking the upper lip, fingers and various objects;
- pressed head to chest during sleep;
- resting your chin with your hand while sitting at a table, etc.
The emergence and development of progeny is caused by inconsistent teething, delayed formation of the upper jaw, osteomyelitis, correction of cleft palate and other pathologies.