How to dilute a mouth rinse solution
It is necessary to rinse the mouth using a syringe, into which the required amount of medicinal liquid should be drawn.
A very important point is that the drug does not enter the stomach. Before using the medicine, you should read the instructions, and if there are none, then you should contact your doctor for recommendations.
Stomatitis (lat. Stomatitis) is the most common disease of the oral cavity. It affects approximately 1/5 of the world's population, of which almost half are pregnant women. There are many reasons why the disease develops. Among the most popular are violations of hygiene rules, allergies, burns, mechanical trauma, and hormonal imbalances.
During the illness, ulcers appear, which, subject to adequate treatment, completely disappear after a maximum of 2 weeks and do not bother the person in any way.
The following forms of stomatitis are distinguished:
- aphthous;
- herpetic;
- candida;
- allergic;
- bacterial;
- catarrhal;
- ulcerative;
- traumatic;
- vesicular.
To treat some forms of stomatitis, doctors prescribe the antiseptic Chlorhexidine to their patients. The use of this medicine significantly speeds up the healing of aphthae and destroys bacterial growth in the oral cavity.
In the pharmacy you can find the drug with a concentration: from 0.05% to 20%, such implementation is due to different therapeutic purposes and indications.
For rinsing the mouth and throat, it is optimal to use a solution with a concentration of the active substance of 0.05%.
There is no need to dilute anything with water here.
In other cases, the drug is diluted with water, based on its concentration according to the instructions or recommendation of the doctor.
There are foreign analogues of the drug on sale that cost 10 or more times more. Their use is absolutely unjustified, since they are based on the same chlorhexidine digluconate, which means the effectiveness is the same at a significantly different cost.
Can Chlorhexidine be used to treat stomatitis?
According to the instructions supplied with the drug, Chlorhexidine bigluconate is an antiseptic with predominantly bactericidal properties. The action of the drug is based on its ability to disrupt the structure of bacterial cell membranes, thereby provoking the death of microorganisms. Fungal spores and viruses (with the exception of herpes viruses) exhibit increased resistance to the components of the drug.
A wide variety of infectious agents can act as causative agents of stomatitis. Considering that Chlorhexidine is active only against bacteria and herpes viruses, it is advisable to use this medicine only in the following cases:
- inflammatory processes provoked by gram-positive or gram-negative bacterial microflora;
- complicated forms of viral, mycoplasma or fungal stomatitis caused by the addition of a secondary bacterial infection;
- herpetic inflammation of the oral mucosa.
For inflammatory lesions of the epithelial tissues of the mouth, occurring in the aphthous, candidal, allergic or vesicular form, this method of treatment is not effective.
Description and release form
Chlorhexidine is available in the form of alcohol and aqueous solutions, suppositories, cream, spray, gel, and patch. Pharmacies sell containers with different concentrations of the active substance; they are designated by the numbers 0.05%, 0.01%, 0.1%, 1%, 5% and 20%. For stomatitis, the liquid form of the drug is most often used; gel and spray are used less frequently.
The main active ingredient is chlorhexidine bygluconate, a local antiseptic with a bactericidal effect. It has a destructive effect on the cells of pathogenic bacteria, but is absolutely safe for viruses. After tissue treatment, the drug remains on the surface of the skin or mucous membranes for a long time, which prevents the penetration of infections. The auxiliary component is water.
Chlorhexidine is a completely clear liquid.
The main active substance is chlorhexidine bigluconate. In addition to it, the composition includes purified water. As a rule, proper treatment of stomatitis involves regular rinsing of the mouth with antiseptic agents. And chlorhexidine is excellent for such therapy.
Thanks to its action, the mucous membrane is cleared of accumulated plaque and inflammation is eliminated. After freeing the oral cavity from bacteria, the solution has a healing effect, removing redness and ulcers.
Chlorhexidine is widely used for stomatitis due to its effective therapeutic effect. Therefore, doctors often recommend treating stomatitis with the drug Chlorhexidine. The active ingredient of Chlorhexidine is chlorhexidine bigluconate.
•Concentration of the substance is 0.01% - has a detrimental effect on gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria;
•A concentration of 0.05% has a negative effect on viruses.
- Cream;
- Spray;
- Gel containing lidocaine;
- Plaster with bactericidal action;
- Candles.
In some cases, the solution has a weakly active antimicrobial effect. The solution can be produced up to 20% concentration of the active substance, depending on the purpose of use. To treat stomatitis, a Chlorhexidine solution with a concentration of 0.05% is used.
What is chlorhexidine, how to rinse your mouth with it
Chlorhexidine is very popular in the treatment of stomatitis. The active component is chlorhexidine bigluconate .
It is sold in the form of an aqueous, alcoholic solution, or in gel form. This is a broad-spectrum antiseptic: it destroys germs, bacteria, and some viruses.
The effectiveness of the drug increases with increasing temperature, so it is necessary to warm up before use. Disinfectant property - it is used when treating medical instruments, hands, and surfaces.
Chlorhexidine - effective, safe and popular
Chlorhexidine is a proven remedy used for stomatitis for many decades in a row. Due to the low risk of side effects and a minimal number of contraindications, it is popular with both doctors and their patients.
The use of more expensive and modern antiseptics can be considered unjustified - cheap and easy to use Chlorhexidine copes well with pathogenic microorganisms, defeating stomatitis.
The only downside is the specific taste of the drug.
If you need a proven and inexpensive remedy against stomatitis, you can give preference to Chlorhexidine. Its effectiveness and safety when used in different age groups has been proven. In addition, the drug helps with dozens of other diseases, so it must be present in your home medicine cabinet.
Chlorhexidine is a popular local antiseptic in the Russian Federation and CIS countries, which is successfully used as a universal
disinfectant and antimicrobial agent.
The chemical compound chlorhexidine was discovered in the 50s of the 20th century in Great Britain, and after 4 years the first skin antiseptic based on this substance appeared. Later, urological lubricants, catheters, wipes and sponges, implants, and clothing for patients and medical personnel began to be impregnated with this substance.
Veterinarians also widely use this substance.
The active substance chlorhexidine bigluconate has strong disinfecting properties and successfully fights microbes, fungi and viruses. The effect is noticeable after the first use.
Dentists widely use Chlorhexidine to treat stomatitis. This drug forms a thin membrane on the ulcerated mucosa, which protects against the effects of bacteria. That is why rinsing the mouth with Chlorhexidine solution significantly increases the rate of healing of aphthae and ulcers.
The effectiveness of chlorhexidine is ensured by maintaining antiseptic properties; the properties of the drug are preserved even after contact with blood, saliva and pus, which is important in the treatment of necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis. The duration of action reaches several hours, the substance has a blocking effect, preventing further spread of bacteria. The drug belongs to the category of antiseptics; it has antimicrobial activity and is effective against fungi.
Properties of the drug
The first symptom of stomatitis is ulcers on the oral mucosa. They are painful and cause severe discomfort. Children often suffer from them. Kids refuse to eat, and sometimes even to communicate. A number of medications are used to combat stomatitis. Among them is chlorhexidine.
Among other drugs of similar action, chlorophyllipt should be noted. Chlorophyllipt for stomatitis is effective and safe. It is used for rinses and applications. An alcohol solution is used. Among folk remedies, baking soda is recommended for stomatitis.
Chlorhexidine is used for rinses and applications.
It can relieve inflammation, fight infection and promote healing of ulcers. You should consult your dentist regarding the use of any of these remedies. It is important to determine why stomatitis developed and prescribe treatment based on this.
Read also: Solution for toothache
Doctors prescribe chlorhexidine for stomatitis very often. Chlorhexidine (chlorhexidine bigluconate) is an antiseptic drug. It has the following properties:
- able to suppress microbial activity;
- fights fungus;
- effective against viruses.
The product suppresses the activity of three groups of pests at once, which cause many diseases.
The product is available in the form of a solution (alcoholic or aqueous), cream, gel, patch. To combat stomatitis, the drug is most often used in liquid form. This is due to the fact that it is used for regular rinsing. A gel may also be prescribed for application.
An effective analogue of Chlorhexidine.
Chlorhexidine is very often prescribed specifically for stomatitis. The powerful effect of the drug is due to the fact that it creates a protective film on the affected surface. It becomes a reliable protection for ulcers and inflammations from ubiquitous bacteria. Using the drug will significantly speed up healing. This has been proven by practicing dentists.
Therapy process
Chlorhexidine is available in various forms:
- aqueous and alcohol solution;
- gel;
- spray;
- cream;
- suppositories;
- patch.
In the pharmacy you can find containers with different designations - 0.05%, 0.01%, 0.1%, 1%, 5% and 20%. These numbers indicate the concentration level of the active substance in the solution.
For stomatitis, the liquid form of Chlorhexidine is most often used. Sometimes a spray and gel are used.
Depending on the form and severity of the disease, the course and dosage of the medicine is selected.
If this is a bacterial form of stomatitis, then an aqueous or alcoholic solution of Chlorhexidine in a 0.01% concentration is prescribed to rinse the mouth. For a complete cure, it is necessary to use solutions in which the active substance has a higher concentration. For therapeutic rinsing, medication at room temperature is suitable, and you should rinse the mouth for at least a minute.
When treating candidal stomatitis, the solution is used in a concentration of 0.05%. The drug should be at room temperature, and the procedure itself is recommended to take 8-10 minutes.
Doctors consider Chlorhexidine a universal medicine in the fight against stomatitis. The main goal is to determine the form of the disease and select the required concentration. In addition, the therapeutic effect continues after the rinsing procedure is completed.
There are basic oral care recommendations before rinsing your mouth with Chlorhexidine:
- before rinsing, you should carry out maximum hygienic cleaning in your mouth: remove food debris in the spaces between the teeth using a flosser, brush and other interdental products;
- then you need to rinse your mouth with boiled water, then you can treat with medicine.
We suggest you read: How teeth are counted in dentistry
After completing the procedure, you need to refuse food for about a couple of hours. If pain in the oral cavity does not bother you too much, then two rinses a day are more than enough. In case of severe discomfort, the number of procedures should be increased to 3-4.
A universal remedy for treating the oral cavity are such traditional medicines as Iodinol, methylene blue, and potassium permanganate. Chlorhexidine can be used doubly effectively along with them, as well as with folk remedies - soda and herbs (oak bark, sage, chamomile).
For what forms of stomatitis can it be used?
Chlorhexidine is used as an antiseptic for the following types of stomatitis:
- Bacterial. It develops as a result of pathogenic microflora (most often staphylococci and streptococci) entering the damaged oral mucosa.
- Candida. It occurs when yeast-like fungi actively multiply, most often of the genus Candida. Infants and adults with reduced immunity are mainly affected.
- Radiation stomatitis occurs in cancer patients after a course of radiation therapy.
- Allergic. It can occur when using any oral care products, even installing a denture.
- Traumatic. It develops as a result of damage to the mucous membrane by the sharp edge of a tooth, an incorrectly installed denture, or other sharp objects.
- Viral. The most common pathogens are herpes simplex and Epstein-Barr viruses.
- Aphthous stomatitis becomes the result of autoimmune diseases and chronic inflammatory processes of the gastrointestinal tract.
It should be noted that treatment of stomatitis caused by the herpes simplex virus with chlorhexidine is inappropriate, since it does not have antiviral activity. It is better to use other antiseptics that are active against viruses.
READ The appearance of signs of stomatitis on the cheeks
Chlorhexidine effectively relieves inflammation during the eruption of a wisdom tooth, when the tooth has not yet penetrated the gum and has only lifted part of the mucous membrane above itself. It is into this space that bacteria and food debris enter. By actively multiplying, microbes provoke the development of the inflammatory process. Thorough rinsing helps remove germs and their waste products, significantly alleviating the patient’s condition.
Contraindications
Chlorhexidine is widely used in the treatment of surgical spaces and surgeons' hands, as well as in cold sterilization of instruments. The drug is used in the following cases:
- treatment of the oral cavity for stomatitis;
- treatment of wounds and burns;
- infectious diseases of the ENT organs (as a rinse);
- cystitis, inflammatory processes of the bladder;
- prevention of sexually transmitted infections;
- colpitis of various etiologies, bacterial vaginosis;
- prevention of infectious and inflammatory complications in obstetric practice and gynecology.
Chlorhexidine has the following contraindications for use:
- the use of antiseptic solutions for sanitation of the oral cavity (Miramistin for stomatitis, hydrogen peroxide);
- individual intolerance to the active substance.
The use of chlorheskidine is primarily associated with the need to disinfect the skin and mucous membranes:
- for periodontal disease, stomatitis and gingivitis.
- when injured;
- fungal infection;
- minor burn;
- after operations;
- after opening tonsillar abscesses (necessary to prevent the formation of a repeated infectious form with the accumulation of purulent formations);
- as a prophylaxis to prevent the formation of sexually transmitted diseases (usually syphilis or chlamydia);
- for disinfection of medical devices.
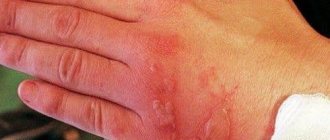
Stomatitis on the inner lip
Doctors prohibit rinsing your mouth with chlorhexidine:
- Newborns;
- In case of an allergic reaction to the main component;
- For burns and dermatitis of high severity;
- During pregnancy and lactation.
In addition, it is strictly forbidden to use the solution in complex therapy with another antiseptic agent (this can have a very detrimental effect on health). A bacteriostatic effect is formed when an aqueous solution is used, which has a minimum concentration of 0.01 percent.
Like many other medications, Chlorhexidine has a number of contraindications. Under no circumstances should it be taken by pregnant or breastfeeding mothers; it is also not recommended to take the medicine for children under five years of age. Particular care should be taken with the drug for people who complain or have complained of allergies.
Side effects of the medicine include:
- variable perception of taste for an indefinite period of time;
- change in color of the mucous membrane and teeth;
- skin irritation;
- swelling of the salivary glands.
In addition to the medicinal properties of Chlorhexidine for stomatitis, it also has others. This drug can also be used for other inflammatory processes:
- Tooth extraction and gum inflammation.
- For throat diseases: sore throat, tonsillitis.
How to use Chlorhexidine after tooth extraction or gum inflammation
The drug is usually prescribed by a dentist after a tooth extraction procedure. This product is aimed at destroying bacteria that lead to pain and inflammatory processes. The medicine must be used at least three times a day. One rinsing process after tooth extraction must last at least a minute. Its intensity should be at a medium level.
It is not recommended to use the medicine in the following situations:
- if you plan to use some other antiseptics (Miramistin and others);
- allergy to the active ingredient;
- Children, nursing mothers and pregnant women are treated with special care;
Possible side effects:
- formation of brown plaque on teeth;
- change in tooth enamel color.
Like any medication, Chlorhexidine has contraindications and some side effects.
Possible side effects of Chlorhexidine in the treatment of stomatitis:
- Staining of tooth enamel;
- Provoking the appearance of tartar;
- Change in sense of taste perception;
- Development of dermatitis;
- Allergic manifestations in the mucous membrane area;
- The bitter taste lingers in the mouth for some time.
Contraindications to the use of Chlorhexidine:
- Intolerance to the active component by the body;
- Presence of dermatitis;
- The use of the drug in children under one year of age is prohibited;
- Chlorhexidine should not be combined with other antiseptic drugs such as hydrogen peroxide or miramistin.
The main prohibition against using Chlorhexidine for stomatitis is an allergy to the medication. Another contraindication to therapy is the combined use of Chlorhexidine with other antiseptics. Otherwise, irritation and damage to the oral mucosa may occur, which aggravate the course of stomatitis.
You cannot prolong drug therapy on your own. The maximum possible time for using the solution is 10 days. After long-term treatment, the risk of disruption of the microflora of the oral cavity increases, which threatens the activation of the growth of fungal flora. For women during pregnancy and lactation, the medicine is allowed after consultation with a dentist.
Chlorhexidine is used for stomatitis to inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria and prevent secondary infection of the mucous membranes of the mouth. The effect of therapy will be more pronounced if you refuse to eat after the procedure for 15-20 minutes.
Chlorhexidine is not used in the following cases:
- Previously, episodes of allergy to the drug were noted;
- if other antiseptics are used, for example, Miramistin. Chlorhexidine can be combined with drugs from other pharmaceutical groups, including those intended for the treatment of stomatitis.
In children, the drug should be used only under the supervision of a doctor.
Possible side effects: formation of tartar and dark plaque on the enamel (easily removed in the dentist's office), temporary changes in taste, dermatitis and other skin reactions.
Use in childhood
When treating stomatitis in children three years of age and younger, the affected areas are treated using a cotton swab soaked in Chlorhexidine. You need to do the procedure up to 4 times a day.
Older children already know how to gargle and spit out the product, so when the diagnosis is confirmed, medicinal rinses can be used. Before this, you need to clear your mouth of any remaining food by rinsing with warm water. Then one dessert spoon of solution will be enough. Rinsing should take no more than half a minute. Amount per day - 2-3 times.
For medicinal purposes, a spray is also convenient, which can be applied to any problem areas affected by aphthae.
The duration of therapy in young patients takes 5-7 days. But quite often, children flatly protest rinsing with this drug, since it has an unpleasant aftertaste.
The choice of treatment for stomatitis is always preceded by the identification of the factors that provoked the disease. If the baby is diagnosed with a viral form of the disease, the doctor may prescribe the use of antiviral drugs. To clean and disinfect the oral cavity, wipe the sores with a cotton swab moistened with a solution of Chlorhexidine.
Is it possible to use chlorophyllipt for stomatitis in children?
Stomatitis is a pathology of the oral mucosa. This is the most common disease of the mucous membrane. The pathology most often occurs in children. A child learns about the world by taking samples through taste buds.
Stomatitis can be recognized by the ulcers characteristic of this disease. They are red, with an accumulation of pus and painful sensations around the formed “pimples”.
Treatment of stomatitis, especially in children, should be discussed with a specialist. The most commonly recommended drugs are chlorhexidine and chlorophyllipt.
Chlorhexidine for stomatitis
Benefits of using chlorhexidine
- It is an antibacterial drug.
- Effective against fungal diseases.
- Works against various viruses.
The drug is produced in various forms, for example in the form of a solution, creams, gels, patches.
Treatment of stomatitis with chlorheskidine occurs with local application of the solution. Chlorhexedine, in addition to being a disinfectant, has a healing effect on ulcers. This drug also has protective properties. It creates a film, preventing the entry of new bacteria.
Also, treating children with chlorhexidine is safe and can be safely used on young children. But it is worth remembering that treatment with this drug should not last more than 12 days, otherwise it may develop into oral dysbiosis.
Rules for rinsing your mouth with chlorhexidine
The medicine works effectively in the form of a solution. The solution cleanses the oral cavity better, but for this you need to carry out the work steps correctly.
- Before starting work, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the oral cavity of food debris and dental plaque. To do this, use toothpaste and floss. Afterwards, rinse with boiled warm water. After this, you can proceed to rinsing with chlorhexidine.
- For rinsing, use a 0.05% solution. You should not swallow the medicine. The duration of the procedure is about one and a half minutes. The action is carried out several times a day.
Rules to follow
If you follow them, your recovery will be much faster.
- After the procedure of rinsing the oral cavity, you must stop eating for a few more hours.
- Do not increase the duration of the rinsing procedure unless your doctor says so.
- Chlorhexidine may be combined with other medications for oral thrush.
Chlorophyllipt for stomatitis in children and adults
Chlorophyllipt solution comes in different dilutions. Oil and alcohol based. Oil-based containing 2% of the active substance, alcohol-based - 0.25 to 1% of the substance. Chlorophyllipt has an antibacterial and healing effect. Also, it strengthens the immune system and enriches it with oxygen.
Treatment of children
For inflammation of the mucous membrane, various forms of the drug are used, for example:
- In spray form. Most convenient for use by small children.
- Tablets for oral administration. The medicine dissolves after eating and is convenient for children who do not know how to rinse their mouths or who do not tolerate treatment with an oil preparation.
- Alcohol solution. Excellent for rinsing for adults; the procedure is performed 2-3 times after eating.
- Oil-based chlorophyllite. Most effective for local treatment of ulcers in children. Before treatment, you need to clean your teeth well and get rid of plaque. Then carefully, using a cotton swab, treat the ulcers locally.
Also, oil-based medicine can be wiped over the oral mucosa, like alcohol-based medicine.
If there are no contraindications for the use of this drug, then it can be combined with other pharmacological agents for stomatitis.
It is wiser to use chlorophyllite after meals. Treatment with this drug should last about four days.
Treatment for adults
The most effective solution for an adult patient is an alcohol-based solution. Initially, the oral cavity is rinsed with a solution, and then applied locally to areas of inflammation.
The solution cannot be used in its pure form, only diluted. To do this, take 0.25% of the drug and dilute it in water in a ratio of one to five. The duration of the procedures varies from three to five days.
During treatment procedures, adults should avoid alcoholic beverages. Also, if you need to use other medications in parallel, you need to consult a specialist for a more accurate answer.
Contraindications for use
Before use, you must make sure that the patient is not allergic to the components of the medicine. To do this, you need to drink a whole spoonful of the eucalyptus-based drug and observe the reaction for 7 hours. If everything went well, then chlorophyll can be safely consumed.
medistoriya.ru
Instructions for use of the preparation for rinsing
For adults
For stomatitis, chlorhexidine is recommended to be taken as a course, its duration does not exceed 10 days. Rinsing should be done in the morning and evening for 2 minutes, it is best to do this after dinner and breakfast.
The drug begins to act after a certain time; you should avoid eating for at least 2 hours.
The scheme is very simple - after breakfast, you need to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with water, this will help get rid of toothpaste residues, since some of its components can reduce the effectiveness of the drug. To treat the oral cavity with an antiseptic, you need to take a small amount of the product into your mouth and rinse for a minute.
Treatment for adults
To treat stomatitis, the most commonly used solution is “Chlorhexidine” 0.05%. They should rinse their mouth 2 times a day. It is advisable not to eat or drink anything 2-3 hours before rinsing. Before carrying out manipulations, you need to clear your mouth of food debris and brush your teeth. It is necessary to rinse the affected mucous membrane for a minute.
We suggest you read: Stomatitis in adults - symptoms, causes, photos and treatment at home
Contraindications
Chlorhexidine should not be used for stomatitis by young children, pregnant or lactating women. The medicine should not be used by those who are intolerant to the substances that make up the antiseptic and by patients prone to allergies to medications. And also the instructions for use of the drug prohibit mixing it with other antiseptics.
The use of ethyl alcohol during treatment can enhance the effect of Chlorhexidine. The solution itself can enhance the effect of drugs from the group of antibiotics. You cannot combine Chlorhexidine with other antiseptic drugs, including iodine-based medications and with iodine itself, as well as with hydrogen peroxide.
Chlorhexidine has powerful antiseptic properties and acts locally on oral tissue. Let's consider several properties of the remedy for stomatitis:
- destruction of pathogenic bacteria;
- fight against fungal flora;
- elimination of inflammation and ulcers.
On the surface of the mucous membranes, the substance forms a protective film that prevents pathogenic flora from entering the resulting ulcers.
The effect of the medication lasts for several hours after its use. Chlorhexidine continues to have a bacteriostatic effect on wounds in the oral cavity.
You can use Chlorhexidine for stomatitis at home. Relief will come after the first procedure. When performing the procedure, a 0.05% solution does not require additional dilution.
Release forms of Chlorhexidine for the treatment of stomatitis:
- water solution;
- alcohol solution;
- ointment;
- mouth spray.
You should not decide on your own to continue the course of treatment, since the drug can accumulate after each treatment session.
When a doctor prescribes this drug, each patient is interested in the question: “How to rinse your mouth with Chlorhexidine for stomatitis?” The question is important, since the result of treatment and the speed of recovery depend on the correctness of the procedures performed.
If it is not possible to purchase a ready-to-use solution with a concentration of 0.05%, then you can use a concentration of 20%. This liquid requires mandatory dilution before use. The solution is diluted with alcohol or distilled water. For stomatitis, 20% liquid is diluted with plain water in proportions equal to 2.5 ml per 1 liter of water.
- The prepared solution is taken into the mouth and the mouth is rinsed for a minute;
- The medicine must be spat out;
- It is forbidden to eat or drink water for 2.5 hours.
It is recommended to carry out 3 similar procedures per day. When rinsing your mouth with medicine for stomatitis, it is important to ensure that the solution does not enter the esophagus. The duration of treatment sessions can be up to 10 days. You should not exceed the recommendations for the duration of the course of treatment, as the risk of disruption of the natural microflora and the development of harmful microorganisms increases.
Most often, doctors prescribe to patients to treat ulcers caused by stomatitis, rinsing the mouth with Chlorhexidine.
Positive effect of the solution for stomatitis:
- The substance penetrates deep into the epidermis;
- Microbes are destroyed;
- The inflammatory process stops;
- Dead cells of microbes and bacteria are removed from the skin surface;
- The wounds are cleared of pus;
- Foci of inflammation are disinfected if the pus comes out.
This preparation is intended for rinsing and treating different types of membranes. When using the drug, you should know that oral use is undesirable, but if suddenly a small part of the drug enters the body, do not be alarmed.
How to properly use the medicine for stomatitis can be found in the instructions for use. On the pharmaceutical market, the drug is produced in different doses according to the percentage: 0.01; 0.05; 0.1.
Rules:
- You need to rinse your mouth and throat twice a day, morning and evening (after meals).
- Before doing this, be sure to brush your teeth (even if you just had breakfast). It is also advisable to rinse your mouth with regular boiled water at the beginning.
- It is important to carry out the procedures for a sufficiently long time, i.e. not 10 seconds, but at least 1 minute. This rule should not be neglected, since as a result, a thin film of the substance is formed on the mucous membranes of the mouth, which lasts for another 2-3 hours.
- Doctors recommend not eating for at least another 2 hours after rinsing.
- The course of treatment is from 7 to 10 days, but no more (prescribed by the dentist).
- The product does not need to be diluted, as it is completely ready for use.
Also now the drug is often prescribed in the form of a gel, for example the drug Hexicon based on chlorhexidine. This product is applied to ulcers, also 2 times a day.
The child has
Chlorhexidine is also prescribed for stomatitis in children. For small children (but not infants), the doctor prescribes the following treatment regimen:
- Sterile gauze is pre-moistened in the solution.
- Next, carefully treat the surfaces of the tongues.
- The procedures need to be carried out twice a day.
Medicines for stomatitis: the best drugs Chlorhexidine, Vinilin
Stomatitis is an inflammatory disease of the epithelial mucous tissues that line the oral cavity. It is the body's immune response to the effects of unfavorable irritating factors. Stomatitis mainly occurs in childhood, but it can also affect adults.
Bubbles are localized on the palate, cheeks, tongue, and less often in the sublingual area. The reasons for their formation are a decrease in the body’s defenses and contact with unfavorable factors. To completely eliminate the problem, you need to choose the right treatment.
Therapy should take into account the form of the disease and include appropriate medications.
Features of treatment depending on the type of disease
A correctly selected therapeutic regimen will eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of the disease and cure stomatitis before it becomes chronic and persistent. The impact should be complex - local treatment, relief of acute symptoms, identification and elimination of the cause of the disease.
If the cause of stomatitis is not eliminated, the rash will bother you again and again.
Viral form
Viral stomatitis in adults is an infectious disease that affects the soft tissues of the oral cavity. The disease is a reaction of a weakened body to a negative external influence - any virus like the flu can cause it. If the immune defense is good, the problem will go away on its own and quickly enough; if not, you are guaranteed frequent relapses.
The main treatment for viral stomatitis consists of local treatment of problem areas:
- Oxolinic ointment - it can also be used by children and pregnant women. The treatment is long-term and effective; the ointment is applied to the blisters several times a day.
- Aerosol Tantum verde – relieves inflammation, relieves pain. Use every 3 hours until symptoms disappear.
- Zovirax is an effective remedy for herpes rashes, suitable for children over 12 years of age and adults. Lubricate the affected areas every 4 hours for a week.
- Acyclovir-acri is an analogue of Zovirax at an affordable price.
- Cholisal for stomatitis is an antimicrobial dental gel that relieves pain. Apply it to your gums three times a day.
- Metrogyl denta is an antiseptic that destroys germs and bacteria. The affected areas are lubricated 3-5 times a day.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe immunomodulators (Viferon, Anaferon), Paracetamol, Nurofen will help relieve the temperature.
Fungal
A fungal infection is activated against a background of decreased immunity, so the main goal of treatment is to stimulate the body’s defenses.
If you are taking immunosuppressants or antibiotics, they may need to be stopped. Other measures: Regularly remove plaque from the mucous membrane, treat the tissue with a solution of borax, potassium permanganate or baking soda.
Adults can use Lugol. Read on for more information about fungal stomatitis.
Application of antifungal ointments - Nystatin, Levorin, Decamine, Clotrimazole.
If local remedies do not help, you need to take antifungal drugs orally. The main ones are Clotrimazole, Nystatin, Fluconazole, Levorin. The dosage and duration of treatment are determined by the doctor (sometimes a single dose is sufficient). If fungal stomatitis occurs in a small child, after feeding you need to treat the nipples, bottles, and mother's breasts with a soda solution.
For chronic forms of fungal stomatitis, antihistamines and multivitamins are prescribed. As a maintenance therapy, you can rinse your mouth with decoctions of calendula, juniper, chamomile, and yarrow. To speed up recovery, exclude fermented milk products and carbohydrates from your diet.
Bacterial
Treatment of bacterial stomatitis is possible only in a hospital setting. Self-medication at best simply will not help, at worst it will worsen the situation. Main methods of therapy:
- Antibiotics - their use is indicated when bacterial stomatitis becomes severe or if the disease is caused by systemic pathologies of internal organs. Treatment with antibiotic ointments (Kanacimin, Gentamicin, Lincomycin) gives good results.
- Antiseptics - rinsing with chlorhexidine, treating mucous membranes with anti-inflammatory gel (possibly with an analgesic effect). When the main wounds have healed, begin using epithelializing agents to speed up healing. In case of necrosis, dead tissue is removed surgically, then the oral cavity is sanitized.
- Immunostimulants of general and local action. They strengthen the immune system and reduce inflammation.
A diet is mandatory, as is the case with other forms of stomatitis - irritating foods cause pain and delay the recovery process.
Traumatic
The choice of treatment tactics in this case is made taking into account the factor that caused the disease.
New dentures and braces are made, broken teeth are treated and restored, and tartar is removed through professional scaling. After eliminating the traumatic factors, the doctor proceeds to the treatment of stomatitis.
The wounds are washed with antiseptics and treated with anti-inflammatory drugs. Sutures are applied for extensive damage.
At home, you will need to rinse your mouth, make applications and other procedures to speed up recovery. For rinsing, Chlorhexidine and herbal decoctions are usually used, and the same ointments are applied topically as for the fungal form.
Allergic
The first thing you need to do is identify the allergen and eliminate contact with it. Medicines - antihistamines (Loratadine, Citrine, Aleron), folic acid, vitamins B, PP, C. Local treatment of the mucous membranes with painkillers, antiseptics, enzymes, corticosteroids, healing ointments or sea buckthorn oil is necessary.
If an allergic reaction occurs due to unsuccessful dental treatment, consultation with a specialized specialist - an orthopedic dentist, therapist or orthodontist is required. Fillings, crowns, denture bases are replaced if necessary. Read on for more information about the treatment of allergic stomatitis.
Review of the best drugs
Let's look at the most popular drugs used to treat stomatitis.
Chlorhexidine
An antiseptic solution, used for rinsing, removes bacteria and accelerates the processes of restoration of damaged epithelium. It has the appearance of a transparent liquid. The concentration of the active substance in an aqueous solution can be different - from 0.05 to 20%.
Chlorhexidine is a basic remedy for the treatment of not only stomatitis, but also periodontal disease and gingivitis.
Chlorhexidine for stomatitis cannot be used if you are allergic to the active ingredient, dermatitis or severe burns.
The product is also not suitable for infants; during pregnancy and lactation it is used with extreme caution. Chlorhexidine should not be used together with other antiseptics. If you rinse too often, the enamel surface may become covered with a brownish-yellow coating that is difficult to remove.
Miramistin
An antimicrobial bactericidal solution that affects gram-positive and gram-negative microflora, inhibits the development and proliferation of fungi, and stops the progression of the disease.
The medicine also allows you to form the correct immune response, strengthens local immunity, stops the spread of infection, accelerates tissue restoration, draws out pus, and removes waste products of microbes.
You can buy Miramistin in the form of an ointment, solution, or spray. For details on the use of Miramistin for stomatitis, see this material.
Use the drug strictly topically, up to 3-4 times a day. Compatibility with antibiotics is good; due to the pleasant taste, small children tolerate treatment with Miramistin normally. Do not use the drug for more than 10 days.
Chlorophyllipt
Chlorophyllipt is a natural remedy with myrtle and eucalyptus. Release forms: spray, oil, alcohol solutions. The hue is green, rich, pine aroma.
Chlorophyllipt is effective in the treatment of ENT and dental pathologies; it can be used to treat non-healing wounds, since the active substance has a pronounced antiseptic effect. The product is used in the treatment of stomatitis due to its pronounced bactericidal effect, heals tissue well, and strengthens the immune system.
Use it for compresses or orally. Give to children with caution, beware of allergic reactions. Read more information about the use of Chlorophyllipt for stomatitis here.
Vinylin
An antimicrobial drug that accelerates the regeneration processes of tissues affected by pathogenic organisms. It can be used for traumatic, bacterial and other forms of stomatitis. Vinilin for stomatitis cleanses wounds well, regenerates the epithelium, and kills microbes. There may be cases of individual intolerance to the active components.
The drug is non-toxic and safe for children and adults. It is applied to the affected areas up to 3 times a day; it is most convenient to do this with a cotton swab.
After the procedure, do not drink or eat for half an hour. If stomatitis is infectious in nature, treatment with vinylin is recommended for all members of the patient’s family.
In severe forms of the disease, local treatments are combined with complex antibiotic therapy.
Blue
Thiazine dye methylene blue (or as it is also called blue for stomatitis) is a good antibacterial agent. Its molecules bind microbial proteins and neutralize them.
The drug is effective for fungal, bacterial, herpes forms of stomatitis, purulent and inflammatory skin lesions. Release forms: alcohol, aqueous solution, powder.
If there is damage to the mucous membranes or skin, it is better to use an aqueous solution (it will not cause burns to the mucous membranes). Before applying bluing, the ulcers must be cleaned of plaque using flax or sea buckthorn oil. Children tolerate treatment with the drug well.
Blue is effective for acute and chronic forms of stomatitis; treatment should not last more than 10 days in the acute form and 21 in the chronic form. For children, wounds are treated up to 2-4 times a day, for adults up to 10.
Metronidazole
Metronidazole is an antiprotozoal agent with a strong antibacterial effect. For stomatitis it is used topically. This is the best option for the treatment of Vincent's ulcerative-necrotic ulcerations.
Metronidazole is most often used in combination with antibiotics. Release forms - tablets and gel, the simplest pathogenic organisms are eliminated effectively and in the shortest possible time.
The tablet form of the drug is taken 500 mg twice a day for no more than 5 days. It is advisable to supplement the treatment by rinsing with a solution or applying a gel to problem areas.
The drug is rarely prescribed for children, but should not be used independently without a doctor’s advice.
Viferon
A homogeneous substance of a yellow hue with the smell of lanolin. The main active component of the ointment is human recombinant interferon, auxiliary components are tocopherol acetate, lanolin, petroleum jelly, peach oil, ascorbic acid.
The product has a pronounced antiviral, immunomodulatory effect, regenerates tissues, and stimulates the processes of rapid restoration of cell membranes. The inflammatory process is stopped, local immunity is increased. Viferon is used to treat children and adults.
Use of painkillers
Stomatitis gives a person a lot of unpleasant sensations, since aphthae and ulcers cause pain and can burst, making it difficult to drink, eat, and speak. General discomfort has a negative impact on the patient’s quality of life, so it is recommended to take painkillers to make you feel better.
It is not only possible, but also necessary, to give painkillers for stomatitis to children - they tolerate the disease more difficult than adults.
Painkillers can be produced in the form of gels, ointments, and sprays. Local anesthesia will be most effective when using the gel form.
This product is quickly absorbed by the mucous membrane, penetrates into the deep layers of tissue and has a targeted effect on the nerve endings. Special lollipops, lozenges, and aerosols help a lot.
The main active ingredients of these products are lidocaine, trimecaine, benzocaine.
Hexoral tablets can be used by adults and children over 4 years of age (maximum dosages are 4 tablets per day for children and 6 for adults), Hexoral spray effectively relieves pain in bacterial stomatitis.
A powerful antibacterial drug – Stopangin. Adults and children over 6 years of age need to dissolve a tablet every 3 hours; treatment should not be continued for more than 5 days.
Kamistad gel is applied three times a day to the affected areas for one week.
For more information regarding the use of medications for stomatitis, watch the video
In the footsteps of the experienced
Reviews from patients who used Chlorhexidine rinses in the treatment of stomatitis.
Previously, I often suffered from stomatitis - about once a month. On one site I found positive reviews about a 0.05% solution of Chlorhexidine bigluconate. It is sold in absolutely every pharmacy, and is very cheap.
I rinsed 5 times a day, at approximately equal intervals. The taste is neutral, there is a little bitterness in the aftertaste. After 4 days, the ulcers disappeared without a trace, and stomatitis has not bothered me for three months now.
Ekaterina, 26 years old
Elena, 45 years old
Analogs
Analogues of the drug include the following:
- Malavit is a naturopathic drug, characterized by a disorienting, decongestant, and analgesic effect. The drug is prescribed for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract, as well as burns, frostbite, and dermatological lesions of the skin. There are no age restrictions, the medicine can also be taken during pregnancy, the only contraindication is considered to be individual intolerance to the components;
- Miramistin is an antimicrobial antibacterial agent for external use, prescribed for inflammatory diseases of the throat, dental diseases, chickenpox, thrush, sinusitis, rhinitis, inflamed adenoids, for the prevention of diseases of the oral cavity and throat. It is used in the treatment of children aged three years and older; in extreme cases, it is prescribed to infants; it is allowed for pregnant women; it is contraindicated in case of sensitivity to the components;
- Lizak is a combined drug that has antibactericidal, fungicidal and antiseptic effects. It is prescribed for dental diseases of the mouth, throat, tonsils, and is used in the prevention of infectious lesions of the mouth and throat during surgery. The drug is contraindicated in case of individual intolerance, lactose deficiency, galactosemia. Lizak is prescribed to children over four years of age; during pregnancy, use is allowed if the potential harm does not outweigh the benefit;
- Protargol belongs to the group of disinfectants and antiseptics, prescribed for nasopharyngitis, inflammation of the middle ear, pharyngitis, sinusitis, inflammatory eye lesions, as well as for the treatment of gynecological diseases. The medication should be taken from the age of five; hypersensitivity to the components, pregnancy and lactation are considered contraindications;
- Furacilin is an antiprotozoal antimicrobial drug, has a wide spectrum of action, is used topically and externally. It is prescribed for wounds of any depth, burns, trophic ulcers, diseases of the oral cavity, furunculosis, osteomyelitis. Its use should be avoided in case of bleeding, allergic dermatoses, or hypersensitivity to components. The drug can be prescribed during pregnancy and is prescribed from infancy.
Summing up
The following advantages of the drug can be highlighted:
- antimicrobial activity is much higher than that of similar drugs;
- accessibility for any person - available in any pharmacy, low price;
- long-lasting antiseptic effect due to the formation of a protective membrane.
- slightly unpleasant taste;
- viruses are resistant to the drug, so the viral form of stomatitis is poorly treatable with Chlorhexidine;
- with prolonged use, the medication can temporarily stain the surface of the teeth and tongue a darkish color.
We suggest you read: How to rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine
Advantages and disadvantages of the drug
Due to its high antimicrobial activity, chlorhexidine is often used in dentistry. It is cheap and effective - these are its main advantages. But the coin also has a downside. In addition to the fact that rinsing is unlikely to give the patient a pleasant sensation (the solution has a pronounced bitter taste), they can also stain the teeth and tongue brown.
The fact is that blackening is a reaction of microbes to the active substance. Where the accumulation of microorganisms is most abundant, dark spots appear. However, you can easily get rid of them by making an appointment with your dentist for tartar cleaning. But even if this is not done, after a few days after completing the course of rinsing, the darkening will go away on its own.
It must be said that not all dentists prescribe chlorhexidine for stomatitis. Some doctors generally believe that the effectiveness of this drug in the treatment of ulcerative inflammation of the mucous membrane is zero. They argue their position by the fact that 9 out of 10 stomatitis are caused not by bacteria, but by viruses, in particular herpes viruses. And if chlorhexidine fights microbes with a bang, then it is practically powerless against viruses.
Of course, there is also an aphthous form of the disease, but it is usually the result of a local allergic reaction, vitamin deficiency or injury (burn, scratch, cut), and therefore it is not treated with antiseptics. They can be used for only one purpose - to prevent bacterial infection from joining the foci of erosions and ulcers. If we are talking about the herpetic form of stomatitis, then it is appropriate to use another antiseptic - Miramistin, which can affect not only bacteria, but also viruses.
So you shouldn’t place too much hope on recovery by doing just rinsing. Chlorhexidine is effective only as part of complex therapy and only after deposits of stones and plaque have been removed from the oral cavity. Treatment of stomatitis is often impossible without taking antihistamines and antifungals, and in some cases without antibiotics.
Dentists warn
By trying to suppress inflammation with an antiseptic, patients are doing themselves a disservice. Until the cause of the inflammation is determined and eliminated, it will develop one way or another, only with less pronounced symptoms. The result of such amateur efforts can be sad: when the patient does get to the doctor (and this is inevitable), the only way out of this situation may be the removal of loose teeth.
Note! Like any medical product, chlorhexidine has an expiration date. You cannot rinse your mouth with a solution that has been stored in your medicine cabinet for more than 2 years. Moreover, even if you are sure of the date, make sure that all this time the packaging was stored correctly (at a temperature not exceeding 25 degrees) and was not exposed to direct sunlight.
What is Chlorhexidine?
As you know, an integral element of the treatment of stomatitis is rinsing the mouth with all kinds of antiseptic agents. This helps to cleanse the mucous membrane of plaque and microorganisms accumulated on it, as well as prevent the worsening of the inflammatory process. After removing harmful bacteria, the restoration of damaged tissues is accelerated, which contributes to a speedy recovery.
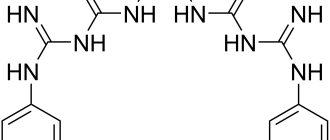
Chlorhexidine is produced in the form of a clear liquid, which is sold in plastic containers with a volume of one hundred or five hundred milliliters. The active substance is chlorhexidine bigluconate. It also contains purified water. On pharmacy shelves you can find a solution with different concentrations of the active ingredient (0.05%, 0.1%, 1%, 5% and 20%).
In clinical settings, the solution is used to treat all kinds of instruments and disinfect surfaces. This medication is also used to disinfect the surface of the skin for wounds, fungal diseases, minor burns and after operations. Chlorhexidine is also prescribed after opening tonsillar abscesses to prevent re-accumulation of pus.
It is strictly forbidden to use Chlorhexidine if you are allergic to its active ingredient, dermatitis or severe burns. It is extremely undesirable to give this drug to infants, as well as resort to purchasing it during pregnancy and lactation. Moreover, the solution should not be combined with other antiseptic drugs.
During the period of use of the medicine, a number of side effects may occur. With regular rinsing, the enamel surface may become covered with a yellow-brown coating, which is difficult to remove. Painful sensations also often occur when the solution gets on ulcers and inflamed mucous membranes. Moreover, the perception of taste is distorted.
How to use the remedy for a sore throat
Instructions for use for stomatitis:
- brush your teeth;
- rinse your mouth with warm boiled water;
- Take about 15 ml of solution into your mouth, hold for about 1-2 minutes, making rinsing movements, spit it out.
For moderate and severe stomatitis, repeat every 2-3 hours until the unpleasant symptoms completely disappear (usually this takes about 5-7 days).
If the disease does not cause severe discomfort and pain, you can limit yourself to two or three rinses per day. Chlorhexidine creates a protective film on the mucous membrane that lasts for several hours, so relief is noted immediately.
The above instructions apply to the finished solution when used in adults. Ingestion of even a small amount of the drug can cause unpleasant health consequences, so parents should approach the treatment of stomatitis in children with Chlorhexidine as responsibly as possible.
Features of the use of the drug depend on age. Those who already know how to rinse their mouth can use Chlorhexidine in the same way as described above. Young children are recommended to purchase a special spray for irrigation - it costs several times more, but it minimizes the risk of accidentally swallowing the medicine. In addition, this form is more convenient to use.
For children, instead of a spray, you can use a cotton swab soaked in a solution (0.05%) - you will have to treat the oral cavity at least 3-4 times a day.
After the oral cavity treatment procedure, you must refrain from eating and drinking for at least one hour (preferably several).
You should not use the drug for more than 10 days in a row - this can lead to serious disruption of the microflora.
First of all, it should be emphasized that the use of antiseptic alone will not help get rid of the disease. Therefore, it is necessary to take care of purchasing anti-inflammatory medications. It is recommended to rinse your mouth with Chlorhexidine for no more than ten days in a row. Failure to comply with this recommendation is fraught with the development of candidiasis on the surface of the mucosa. It is also important to mention that the remedy will in no way help with herpetic stomatitis.
Adults are recommended to purchase twenty percent Chlorhexidine and dilute two milliliters of the solution with a liter of warm boiled water. If severe pain occurs after rinsing, it is better to reduce the dosage by half. Before the procedure, be sure to thoroughly brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with plain water.
Children under three years of age need to treat the oral cavity with a cotton pad or bandage soaked in Chlorhexidine twice a day. You should purchase a solution with a minimum concentration of the active substance. But an older child will be able to rinse the mouth independently, so you will need to mix the drug with warm water in a one-to-one ratio.
The most common throat diseases are sore throat and tonsillitis. Such ailments are bacterial infections of the throat mucosa. Using Chlorhexidine for the above diseases, you can significantly improve your health and significantly stop inflammatory processes in the throat area.
It is very important to remember that if any symptoms of stomatitis or inflammatory processes appear, you must immediately contact a specialist, who, in turn, will prescribe the appropriate treatment. You should not try to overcome the disease on your own, because this can lead to negative consequences and cause even more harm to your health.
Each medicine has its own prescription for use, and Chlorhexidine is no exception.
How to effectively treat stomatitis in a child?
For older children, rinsing is more suitable.
Children are more likely to suffer from stomatitis. Often these are children who have not yet reached three years of age. Their immunity is just developing and is not always able to cope with bacteria, viruses and fungi. It is these little ones who most often learn about the world through their mouths. They lick and chew everything that comes their way. At the same time, many microorganisms enter the mucous membrane.
Treatment of the mucous membrane in children under three years of age and infants is carried out using a sterile cotton swab. It is moistened in the preparation and all ulcers and areas of inflammation are carefully lubricated with the solution. The procedure is performed after meals 3-4 times a day.
For older children, rinsing is more suitable. As we already mentioned, before them you need to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with water. The baby should take about a dessert spoon of the solution into his mouth. The procedure lasts about half a minute.
Important : Before rinsing, be sure to explain to your child that swallowing the solution is strictly forbidden! He must understand that this is medicine.
Treatment lasts on average about five days. The child may refuse such rinsing. The problem is that the drug has an unpleasant taste.
The product should be used with caution when treating pregnant women and children.
If a child swallows the solution, it is necessary to rinse it. Then you need to drink activated carbon (one tablet per 10 kg).
How to rinse Chlorhexidine for stomatitis?
Chlorhexidine is an antiseptic with a pronounced bactericidal effect and intended for local external use.
Active regarding:
- streptococci;
- staphylococci;
- coli;
- Proteus;
- Klebsiella
And a number of other pathogenic microorganisms.
Since Chlorhexidine is able to quickly and effectively destroy harmful flora, the use of an antiseptic is completely justified.
Chlorhexidine is one of the most prescribed mouthwashes for stomatitis. The beneficial effect is noticeable after the first procedure. The general course of treatment is from 3 to 5 days.
One of the main advantages of the drug is that the active substances are not absorbed into the bloodstream.
Chlorhexidine is a well-known antiseptic used regularly in medical practice. Chlorhexidine is often used for stomatitis caused by microflora of harmful bacteria. Before using the product, it is necessary to study the medical instructions so that the product is used correctly and has the expected therapeutic result.
Mechanism of action
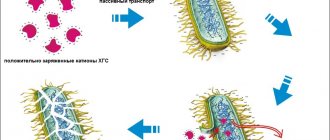
The full name of Chlorhexidine is chlorhexidine bigluconate.
The mechanism of its action depends on the percentage of the active substance in the solution. At a concentration of more than 0.01%, chlorhexidine molecules actively attach to the bacterial cell membrane, violating its integrity, as a result of which the cell dies (bactericidal effect).
Photo of the drug
At lower concentrations, the transport of nutrients through the bacterial cell wall is blocked, which leads to a gradual decrease in the number of microorganisms (bacteriostatic effect).
Biological fluids (blood and pus) somewhat reduce the activity of the drug, but the drug still remains effective.
Chlorhexidine is not absorbed into the bloodstream and therefore has no general effect on the body. When it enters the digestive tract, it does not interact with the body and is excreted unchanged.
When applied topically, it forms a film on the treated surface that retains bactericidal properties several hours after application.
Advantages
Many patients leave positive reviews about the use of the product. They talk about the following advantages:
- Low cost;
- Strong antiseptic effect;
- Quick effect.
Sometimes people leave negative reviews, which are most often associated with unpleasant side reactions after use. For example, when chlorhexidine was used for too long (more than 10 days).
Chlorhexidine has many advantages over other disinfectants for the treatment of stomatitis and other purulent and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
- Possibility to buy without a prescription;
- The drug is available in every pharmacy;
- Low cost;
- Wide range of applications;
- Good antibacterial effect;
- The appearance of a protective film on the mucous membrane after the procedure. The film protects the affected area for several hours, between rinsing procedures;
- The ability to use the solution in the treatment of stomatitis in pregnant women, since the active substance does not have a negative effect on the fetus.
Benefits and side effects of the drug
Chlorhexidine has a number of advantages over other disinfectants intended for the treatment of purulent-inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity. The positive features of the drug are:
- Availability in pharmacies - the medicine is sold without a prescription.
- Relatively cheap.
- High antibacterial activity and wide spectrum of action.
- Prolonged effect of using the solution. The protective film that forms on the oral mucosa after rinsing helps protect the affected tissues from infection for 4-6 hours.
- The ability to treat stomatitis using the drug during pregnancy. The components present in the composition of the drug do not affect the development of the child in the prenatal period.